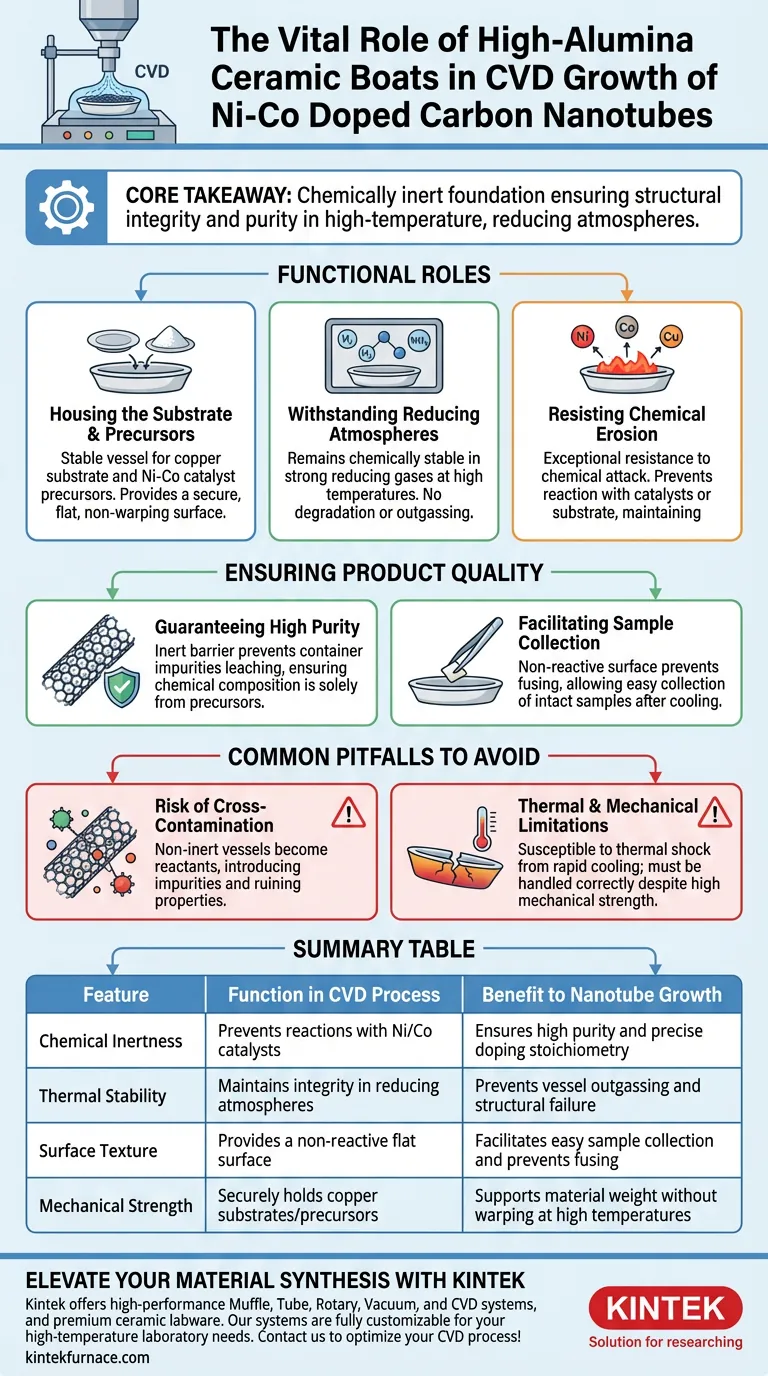
The high-alumina ceramic boat acts as the chemically inert foundation for the synthesis of Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes. It serves as the primary vessel to hold the copper substrate and catalyst precursors, maintaining structural integrity while shielding the reaction from contamination.
Core Takeaway The boat’s critical function is to remain physically and chemically stable in high-temperature, reducing atmospheres. By preventing reactions between the vessel and the sample, it ensures the synthesized nanotubes remain pure and easily collectible.
The Functional Roles of the Alumina Boat
The high-alumina ceramic boat is not merely a container; it is an active component in maintaining the integrity of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) environment. Its specific roles are defined by the harsh conditions required to grow Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes.
Housing the Substrate and Precursors
The primary mechanical role of the boat is to serve as a stable vessel. It physically holds the copper substrate and the catalyst precursors required for the reaction.
Because the synthesis involves solid precursors and metal substrates, the boat must provide a secure, flat surface that does not warp or degrade during the process.
Withstanding Reducing Atmospheres
CVD processes for nanotube growth often utilize strong reducing atmospheres (typically involving hydrogen or ammonia).
The high-alumina ceramic composition is selected specifically for its ability to remain stable in these environments. Unlike lesser materials that might degrade or outgas when exposed to reducing gases at high heat, the alumina boat maintains its chemical structure.
Resisting Chemical Erosion
High temperatures increase the reactivity of all materials involved in the process.
The high-alumina boat provides exceptional resistance to chemical erosion. This prevents the vessel itself from reacting with the metal catalysts (Nickel and Cobalt) or the copper substrate, which would otherwise alter the stoichiometry of the reaction.
Ensuring Product Quality
The choice of boat material directly correlates to the quality of the final nanomaterial.
Guaranteeing High Purity
The ultimate goal of the CVD process is to create high-purity Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes.
By acting as an inert barrier, the boat prevents the container material from leaching impurities into the growing nanotubes. This ensures that the chemical composition of the final product is defined solely by the precursors, not by the labware.
Facilitating Sample Collection
In addition to purity, the boat facilitates the practical aspect of harvesting the material.
Because the alumina surface resists reacting with the sample, it prevents the synthesized nanotubes or the substrate from fusing to the boat. This ensures the samples are easy to collect intact after the system cools down.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While the high-alumina boat is robust, understanding the limitations of CVD vessel selection is vital for reproducibility.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
If a boat is not sufficiently inert (or if a lower-grade ceramic is used), the vessel becomes a reactant. This introduces foreign elements into the crystal lattice of the nanotubes, ruining their electronic or mechanical properties.
Thermal and Mechanical Limitations
While high-alumina boats offer high mechanical strength, they must be handled correctly. Like all ceramics, they are susceptible to thermal shock if cooled too rapidly. However, their primary advantage over other materials in this specific context is their superior ability to withstand the combination of high mechanical stress and chemical attack without structural failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct vessel is as important as selecting the right catalyst. Here is how to prioritize your equipment choices based on your objectives:
- If your primary focus is high purity: Prioritize a high-alumina boat to eliminate chemical leaching and ensure no foreign atoms interfere with the Ni-Co doping.
- If your primary focus is sample recovery: Rely on the high-alumina boat’s inert surface to prevent the substrate from adhering to the vessel, ensuring maximum yield during collection.
Success in growing Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes relies on an inert vessel that isolates the reaction from the environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in CVD Process | Benefit to Nanotube Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reactions with Ni/Co catalysts | Ensures high purity and precise doping stoichiometry |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains integrity in reducing atmospheres | Prevents vessel outgassing and structural failure |
| Surface Texture | Provides a non-reactive flat surface | Facilitates easy sample collection and prevents fusing |
| Mechanical Strength | Securely holds copper substrates/precursors | Supports material weight without warping at high temperatures |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in nanomaterial growth starts with the right environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with premium ceramic labware designed for rigorous research. Whether you are growing doped carbon nanotubes or specialized thin films, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique high-temperature laboratory needs.
Ready to optimize your CVD process? Contact KINTEK today to consult with our experts!
Visual Guide
References
- A. Shameem, P. Sivaprakash. A High-Performance Supercapacitor Based on Hierarchical Template-Free Ni/SnO2 Nanostructures via Hydrothermal Method. DOI: 10.3390/ma17081894
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
People Also Ask
- What is lab vacuum used for? Mastering Environmental Control for Purity and Precision
- Why is a stainless steel crucible selected for melting AM60 magnesium alloy? Ensure Alloy Purity and Safety
- What are tube furnace tubes made of? Select the Right Material for Your Process
- What are the core functions of high-purity graphite molds and graphite paper in SPS? Optimize Sintering Quality
- How does the geometric design of a sample basket affect measurement accuracy in thermogravimetric analysis?
- What maintenance is required for a water circulating vacuum pump? Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity
- Why are alumina ceramic tubes preferred for high-temperature furnaces? Ensure Stability and Control Up to 1800°C
- How is the vacuuming operation performed with a water circulating vacuum pump? Master the Liquid Ring Technique



















