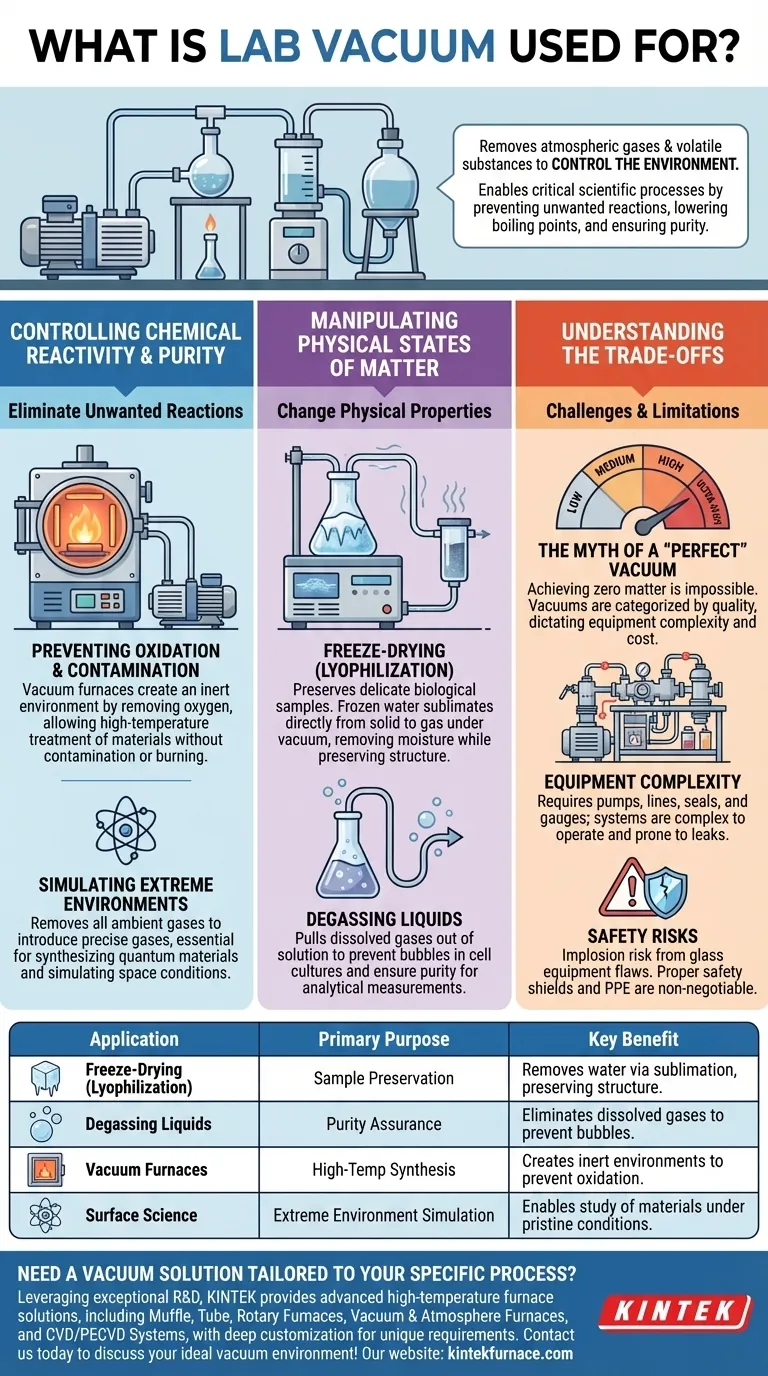
In a laboratory setting, a vacuum is used to remove atmospheric gases and other volatile substances from a sealed space. This enables a range of critical scientific processes, from freeze-drying biological samples and degassing liquids to conducting high-temperature material synthesis in a controlled, non-reactive environment.
The core purpose of a lab vacuum is not simply to create emptiness, but to precisely control an environment. By removing interfering gases, scientists can prevent unwanted reactions, lower boiling points, and create the pure conditions necessary for sensitive experiments.

Controlling Chemical Reactivity and Purity
One of the primary reasons to use a vacuum is to eliminate unwanted chemical reactions. Atmospheric air, rich in oxygen and water vapor, can interfere with or ruin many sensitive processes.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, many materials will readily oxidize or burn in the presence of air. Vacuum furnaces create an inert environment by removing the oxygen.
This allows for the high-temperature treatment of new materials to study how they change and optimize their performance without the risk of contamination or unwanted side reactions.
Simulating Extreme Environments
In fields like physics and materials science, a vacuum is the starting point for creating highly specific conditions. Scientists can remove all ambient gases and then introduce a precise amount of a specific gas.
This technique is essential for synthesizing novel materials, such as quantum materials, and for simulating the reactive conditions found in space or other extreme environments.
Manipulating Physical States of Matter
Applying a vacuum fundamentally changes the physical properties of substances, most notably their boiling point. This principle is the basis for several common lab techniques.
Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization)
For preserving delicate biological samples, freeze-drying is a critical process. The sample is first frozen, and then a vacuum is applied.
Under vacuum, the frozen water turns directly from a solid (ice) into a gas (water vapor) without passing through a liquid phase. This process, called sublimation, removes water while preserving the sample's structure for long-term storage.
Degassing Liquids
Dissolved gases in liquids can cause problems in many experiments, such as creating bubbles in cell cultures or interfering with analytical measurements.
Placing a liquid under a vacuum effectively pulls the dissolved gases out of the solution. This ensures the liquid is pure and will not produce unexpected bubbles or reactions during an experiment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, working with a vacuum involves specific challenges and limitations that must be managed.
The Myth of a "Perfect" Vacuum
Achieving a "perfect" vacuum—a space with zero matter—is impossible. Lab vacuums are categorized by their quality, from low and medium vacuums used for simple filtration to high and ultra-high vacuums for surface science.
The required level of vacuum dictates the complexity and cost of the equipment. Using a system more powerful than necessary is inefficient, while using one that is too weak will compromise the experiment.
Equipment Complexity
Creating and maintaining a high-quality vacuum requires specialized pumps, lines, seals, and gauges. These systems can be complex to operate and are prone to leaks, which can be difficult to find and fix.
Safety Risks
A vessel under vacuum is under immense external pressure from the atmosphere. If glass equipment has a flaw, it can implode violently, scattering shards. Proper safety shields and personal protective equipment are non-negotiable when working with vacuum glassware.
Applying This to Your Work
The type of vacuum system you need is dictated entirely by your experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is sample preservation or concentration: Techniques like freeze-drying or rotary evaporation require a moderate vacuum to gently remove solvents without excessive heat.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or surface science: You will need a high or ultra-high vacuum system to create a pristine, non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is routine filtration or degassing: A simple, robust vacuum pump and flask setup is typically sufficient to remove air and pull liquids through a filter.
Ultimately, a vacuum is one of the most versatile tools in science, enabling control over the fundamental physical and chemical properties of matter.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization) | Sample Preservation | Removes water via sublimation, preserving structure. |
| Degassing Liquids | Purity Assurance | Eliminates dissolved gases to prevent bubbles and interference. |
| Vacuum Furnaces | High-Temperature Synthesis | Creates inert environments to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Surface Science | Extreme Environment Simulation | Enables the study of materials under pristine, controlled conditions. |
Need a Vacuum Solution Tailored to Your Specific Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements for purity, precision, and control.
Contact us today to discuss how we can design the ideal vacuum environment for your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















