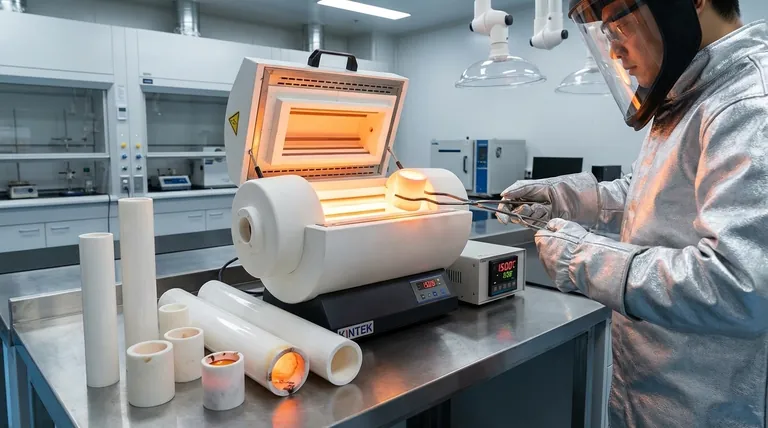
High-purity alumina (Al2O3) is the preferred choice for high-temperature smelting primarily because of its exceptional chemical stability and refractoriness. These components can withstand aggressive environments up to 1500°C without degrading or reacting with the vessel's contents. By resisting corrosion from molten slag and liquid alloys, alumina ensures that the container material does not leach into the sample, thereby guaranteeing the accuracy of subsequent elemental analysis.
The core value of high-purity alumina is its ability to provide a chemically neutral, high-heat environment. It acts as an inert barrier that isolates the molten sample from external contamination, which is the single most critical factor for accurate metallurgical testing and analysis.

The Mechanics of Thermal Stability
Refractoriness at 1500°C
Smelting processes subject materials to extreme thermal stress. High-purity alumina is defined by its high refractoriness, allowing it to maintain structural integrity in temperatures as high as 1500°C. This capability prevents physical failure of the crucible during the transition from solid to molten states.
Controlled Heat Conduction
Beyond simply surviving the heat, the material plays an active role in process control. Alumina provides a stable heat conduction environment. This stability is essential for processes requiring uniform temperature distribution, such as the controlled sintering of powders or the melting of alloys.
Chemical Inertness and Sample Integrity
Resisting Corrosive Attack
Molten materials, particularly slag and liquid alloys, are chemically aggressive and can eat away at lesser container materials. Alumina components possess a specific resistance to this type of corrosion. This durability prevents the vessel from eroding during the smelt, ensuring safety and containment.
Preventing Elemental Leaching
The most significant technical advantage of alumina is its impact on analytical precision. Because it resists corrosion, it prevents the container material from leaching into the molten sample.
Ensuring Analytical Accuracy
When the goal is recovering products for elemental analysis, purity is paramount. By eliminating cross-contamination between the crucible and the alloy, high-purity alumina ensures that the final analysis reflects only the sample's true composition, not the degradation of the tools used to melt it.
Operational Considerations and Limits
The Necessity of High Purity
It is critical to note that the benefits described rely on the material being high-purity. Lower-grade ceramics may contain impurities that could leach into the sample or lower the material's maximum operating temperature, negating the specific advantages required for precise analysis.
Adhering to Thermal Boundaries
While alumina is robust, its effectiveness is bound by specific thermal limits, such as the 1500°C ceiling for smelting or specific softening points for sintering. Exceeding these validated temperature ranges risks compromising the material's refractoriness and chemical stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your high-temperature process, align your material choice with your specific technical objective:
- If your primary focus is Elemental Analysis: Prioritize high-purity alumina to prevent container leaching and ensure that your slag and alloy composition data remains uncompromised.
- If your primary focus is Sintering or Processing: Leverage the material's stable heat conduction to ensure controlled formation of internal structures, such as air-filled cavities or crystals.
High-purity alumina is the industry standard not just because it survives the heat, but because it protects the integrity of your science.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for Smelting | Maximum Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High Refractoriness | Withstands temperatures up to 1500°C | Prevents structural failure/melting |
| Chemical Stability | Resists corrosion from molten slag/alloys | Eliminates container leaching |
| Heat Conduction | Uniform thermal distribution | Ensures consistent sintering & melting |
| High Purity (Al2O3) | Provides a neutral, inert environment | Guarantees accurate elemental analysis |
Elevate Your Lab's Precision with KINTEK
Maximize the integrity of your metallurgical research with high-performance alumina components. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-purity Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the most rigorous thermal demands. Whether you need standard crucibles or fully customizable lab high-temp furnaces for unique smelting needs, our solutions prevent contamination and ensure repeatable results.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes?
Contact KINTEK today for expert consultation and customized solutions.
Visual Guide
References
- Chen Wang, Hongbin Ling. Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination. DOI: 10.3390/met15070732
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for Laboratory Type Furnaces? Find Your Ideal Heat Solution
- What are the primary functions of a self-preheating heat exchanger? Maximize Thermal Efficiency in Double-P Tubes
- What chemical resistance properties should be verified for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure High-Temperature Durability
- Why is Internal Radiation Baffle (IRB) technology used in mold designs? Enhance Directional Solidification Quality
- What advanced material processing applications use graphite crucible furnaces? Unlock Precision in Nanomaterial Synthesis and More
- How does a vacuum pump facilitate the synthesis process of rare earth-based halide electrolytes? Boost Chemical Purity
- What are the main components of a Laboratory Furnace? Essential Parts for Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the purpose of using an insulating layer in CCCM thermal conductivity tests? Ensuring 1D Heat Flow Accuracy



















