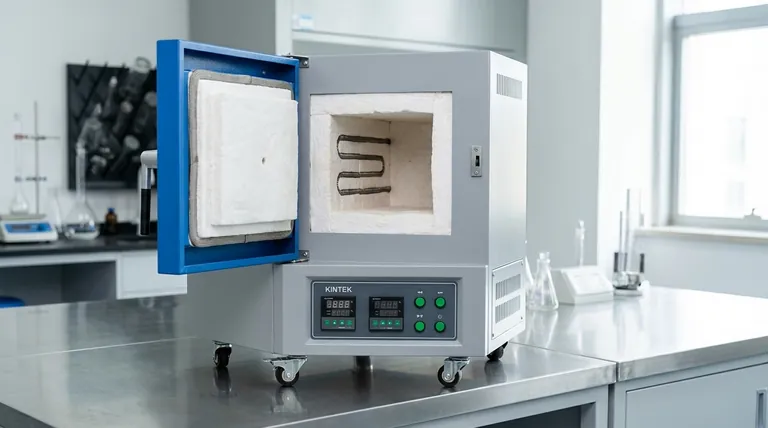
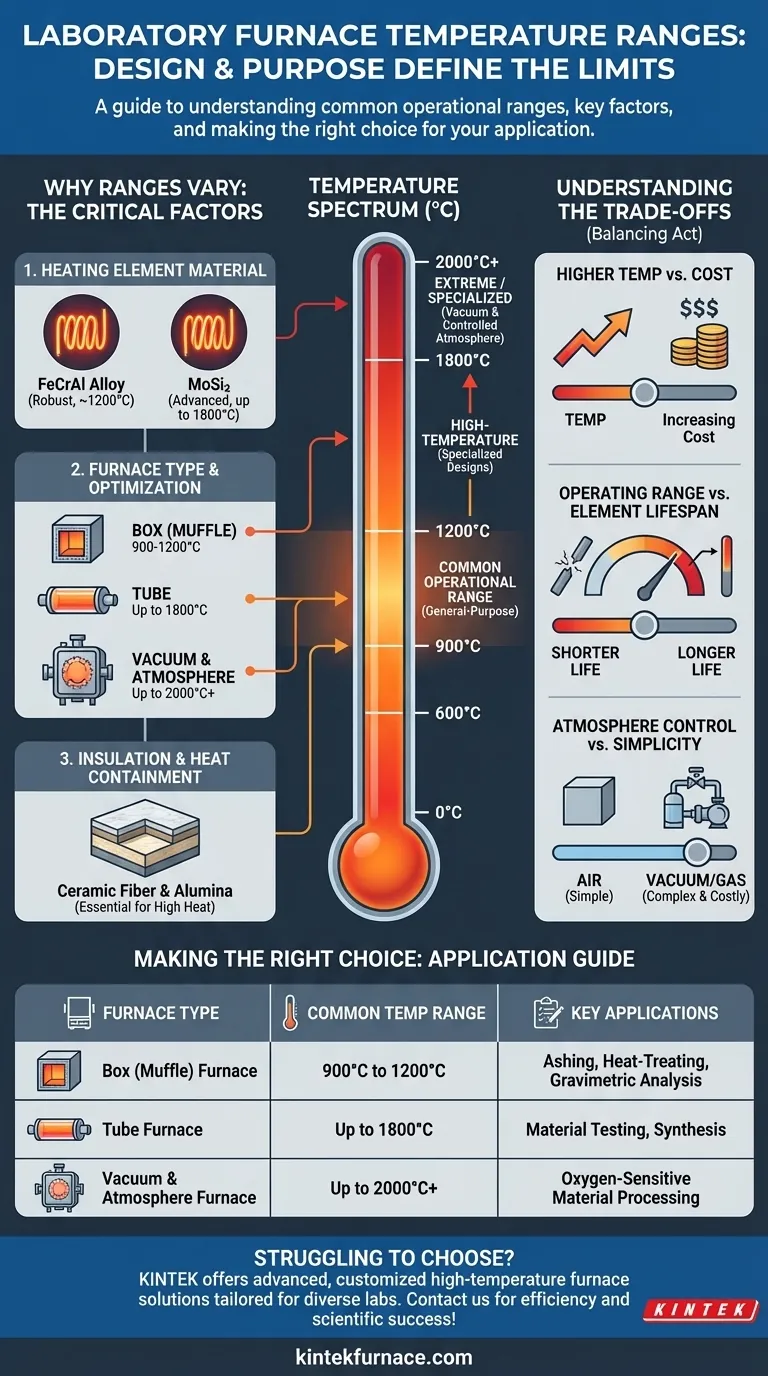
In short, the answer depends entirely on the furnace's design and intended purpose. While laboratory furnaces can be designed for maximum temperatures from 600°C up to 1800°C, the most common operational range for general-purpose units falls between 900°C and 1200°C. Specialized designs, such as high-temperature tube or vacuum furnaces, are required to reach the upper end of this spectrum.
A laboratory furnace's temperature range is not a universal specification but is determined by its core components. The critical question isn't "what's the general range," but "which heating element and furnace type can achieve the specific temperature my process requires?"

Why Temperature Ranges Vary So Widely
Understanding a furnace's temperature rating requires looking at its fundamental design. The maximum achievable temperature is not an arbitrary number; it is a direct consequence of the materials used in its construction.
The Critical Role of the Heating Element
The heart of any furnace is its heating element. The material used for this element is the single greatest factor determining the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Different materials have different physical limits before they degrade or fail. A furnace designed for 1200°C might use a robust iron-chrome-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy, while a furnace needing to reach 1800°C will require a fundamentally different, more advanced element, such as molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂).
Furnace Type Dictates Capability
The overall design of the furnace is optimized for specific applications, which in turn influences its temperature range.
- Box (Muffle) Furnaces: These are the most common type, handling a wide variety of tasks like ashing, heat-treating, and gravimetric analysis. They typically operate in the 900°C to 1200°C range.
- Tube Furnaces: Designed to heat a small sample within a cylindrical tube, these can achieve excellent temperature uniformity. High-temperature models are common and can reach up to 1800°C.
- Vacuum & Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces: These furnaces are for processing materials that cannot be exposed to oxygen or other reactive gases. Their temperature range is broad, from a few hundred to over 2000°C, depending entirely on the specific heating elements and chamber design.
Insulation and Heat Containment
A furnace's ability to safely contain extreme heat is just as important as its ability to generate it. Furnaces operating at higher temperatures require more advanced, multi-layer insulation, often using high-purity alumina and ceramic fiber boards to prevent heat loss and ensure the outer casing remains safe to touch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace is an exercise in balancing performance with practical constraints. Simply choosing the highest possible temperature is often an expensive mistake.
Higher Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its price. The specialized heating elements (like MoSi₂) and advanced insulation required for temperatures above 1400°C are significantly more expensive than the materials used in standard models.
Operating Range vs. Element Lifespan
Heating elements have a finite lifespan that is shortened by operating near their maximum temperature limit. Consistently running a 1200°C furnace at 1190°C will degrade the elements far more quickly than running it at 1000°C.
Atmosphere Control vs. Simplicity
While a simple air-atmosphere box furnace is straightforward to operate, a vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace adds significant complexity. These systems require vacuum pumps, gas flow controllers, and more intricate sealing, increasing both initial cost and maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace based on the specific requirements of your application, not on a theoretical maximum temperature.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or ashing (up to 1200°C): A standard box or muffle furnace with FeCrAl elements is your most cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is material testing or synthesis at high temperatures (1200°C to 1800°C): You will need a specialized high-temperature furnace, likely a tube or chamber model with silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide elements.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials at any temperature: Your choice is dictated by the need for a controlled atmosphere, requiring a dedicated vacuum or inert gas furnace regardless of the target temperature.
Understanding these core factors allows you to select a furnace not just based on its maximum temperature, but on its true suitability for your scientific objective.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Common Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Box (Muffle) Furnace | 900°C to 1200°C | Ashing, heat-treating, gravimetric analysis |
| Tube Furnace | Up to 1800°C | Material testing, synthesis |
| Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnace | Up to 2000°C+ | Oxygen-sensitive material processing |
Struggling to choose the right lab furnace for your specific temperature needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Don't compromise on performance—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve your scientific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Mastering Thermal Polycondensation for Semiconductors
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength



















