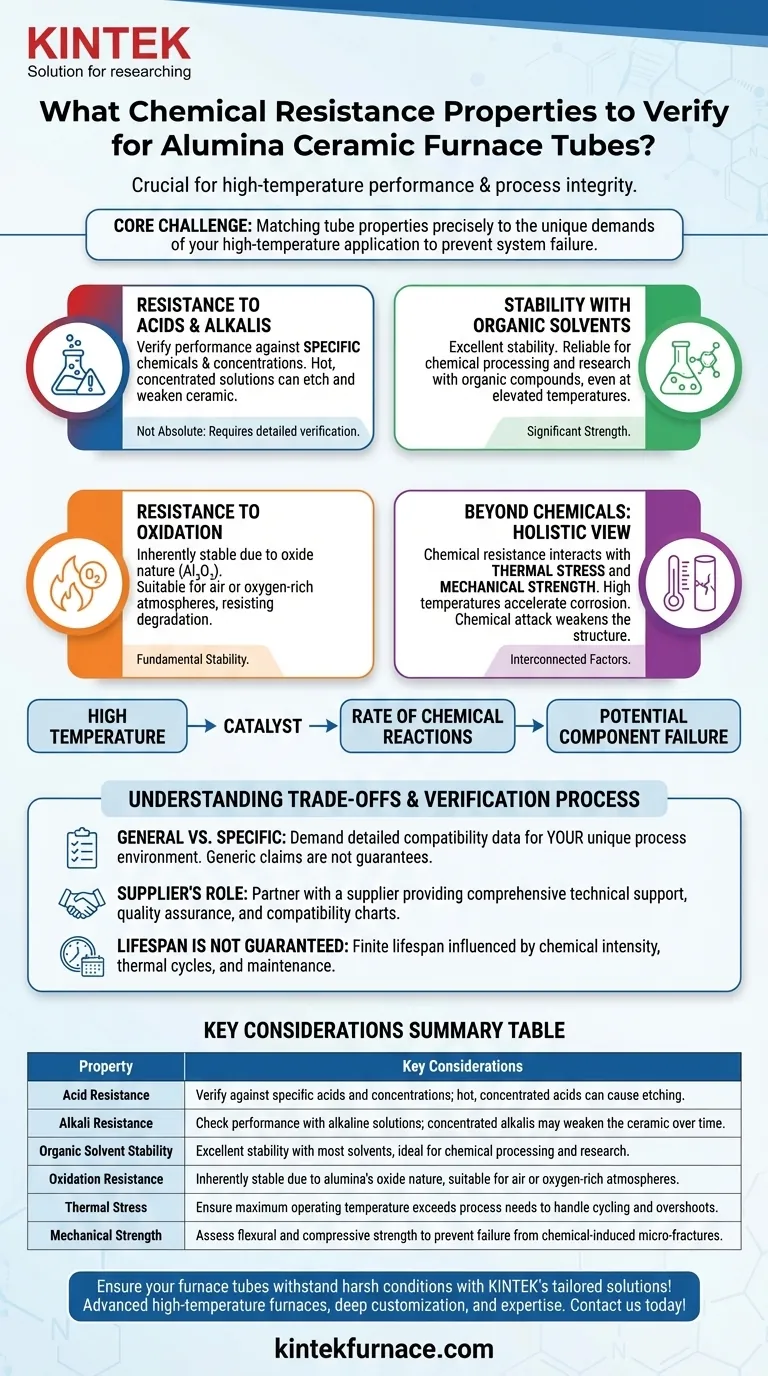
In short, you must verify an alumina ceramic furnace tube's resistance to acids, alkalis, organic solvents, and oxidation. These properties are critical because, at high temperatures, even minor chemical interactions can be severely accelerated, leading to component failure and compromised process integrity.
The core challenge isn't just finding a tube with good chemical resistance, but ensuring that its specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties are precisely matched to the unique demands of your high-temperature application. A mismatch in any one area can undermine the entire system.

Why Chemical Resistance is Critical in Furnace Environments
At room temperature, many materials are inert. However, the extreme heat inside a furnace acts as a powerful catalyst, dramatically increasing the rate of chemical reactions. A tube that seems robust can degrade rapidly in a hot, corrosive atmosphere.
Resistance to Acids and Alkalis
Alumina is well-regarded for its general resistance to most acids and alkalis. However, this resistance is not absolute.
You must verify its performance against the specific chemicals and concentrations used in your process. Hot, concentrated alkaline solutions or certain strong acids can slowly etch and weaken the ceramic over time.
Stability with Organic Solvents
This is a significant strength of alumina ceramics. They exhibit excellent stability when exposed to most organic solvents, even at elevated temperatures.
This makes them a reliable choice for applications in chemical processing and research that involve organic compounds.
Resistance to Oxidation
This property is fundamental for any process running in an air or oxygen-rich atmosphere. Because alumina (Al₂O₃) is already a stable oxide, it is inherently resistant to further oxidation.
This intrinsic stability is a primary reason it is chosen for high-temperature applications where other materials would burn away or degrade.
Beyond Chemicals: A Holistic View of Tube Integrity
Chemical resistance is only one piece of the puzzle. For a furnace tube to survive, its thermal and mechanical properties must work in concert with its chemical stability.
The Interplay with Thermal Stress
A tube must first withstand the heat before its chemical resistance becomes relevant. Its maximum operating temperature is a non-negotiable limit.
Always select a tube with a temperature rating significantly higher than your process requires. This safety margin accounts for thermal cycling and potential temperature overshoots.
The Role of Mechanical Strength
Chemical corrosion is a silent threat to mechanical integrity. As chemicals attack the tube's surface, they can create micro-fractures that weaken the material.
This makes properties like flexural strength (resistance to bending) and compressive strength (resistance to crushing) critical. A chemically weakened tube is far more likely to fail under mechanical load or thermal shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Verification Process
Relying on generic data sheets is a common and costly mistake. The success of your application hinges on a detailed verification process.
General vs. Specific Resistance
A manufacturer's claim of "excellent acid resistance" is a starting point, not a guarantee. The critical question is how the tube performs against your specific chemical, at your operating temperature and concentration.
Always demand detailed compatibility data for your unique process environment.
The Supplier's Role in Verification
A reputable supplier acts as a technical partner. They should provide comprehensive technical support, quality assurance documentation, and detailed chemical compatibility charts.
Their experience and willingness to help you validate the material for your application is a key indicator of product reliability.
Lifespan is Not Guaranteed
Even the highest-quality alumina tube has a finite lifespan. Factors like the intensity of the chemical environment, the frequency of thermal cycles, and maintenance practices all play a role.
Proper handling and adherence to operating limits are essential for maximizing the tube's service life, which can often extend for several years under the right conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be guided by the most demanding aspect of your process.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness: Prioritize the highest-purity alumina available and demand specific compatibility data for any aggressive chemicals in your process.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability in air: Confirm the maximum operating temperature, thermal expansion, and creep resistance are well above your process needs.
- If your primary focus is overall durability: Balance the chemical, thermal, and mechanical specifications against your process and partner with a supplier who can help validate your choice.
Ultimately, successful selection comes from a precise alignment of the material's complete performance profile with the specific environment in which it must operate.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Acid Resistance | Verify against specific acids and concentrations; hot, concentrated acids can cause etching. |
| Alkali Resistance | Check performance with alkaline solutions; concentrated alkalis may weaken the ceramic over time. |
| Organic Solvent Stability | Excellent stability with most solvents, ideal for chemical processing and research. |
| Oxidation Resistance | Inherently stable due to alumina's oxide nature, suitable for air or oxygen-rich atmospheres. |
| Thermal Stress | Ensure maximum operating temperature exceeds process needs to handle cycling and overshoots. |
| Mechanical Strength | Assess flexural and compressive strength to prevent failure from chemical-induced micro-fractures. |
Ensure your furnace tubes withstand harsh conditions with KINTEK's tailored solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability and process integrity. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your high-temperature applications and extend equipment lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















