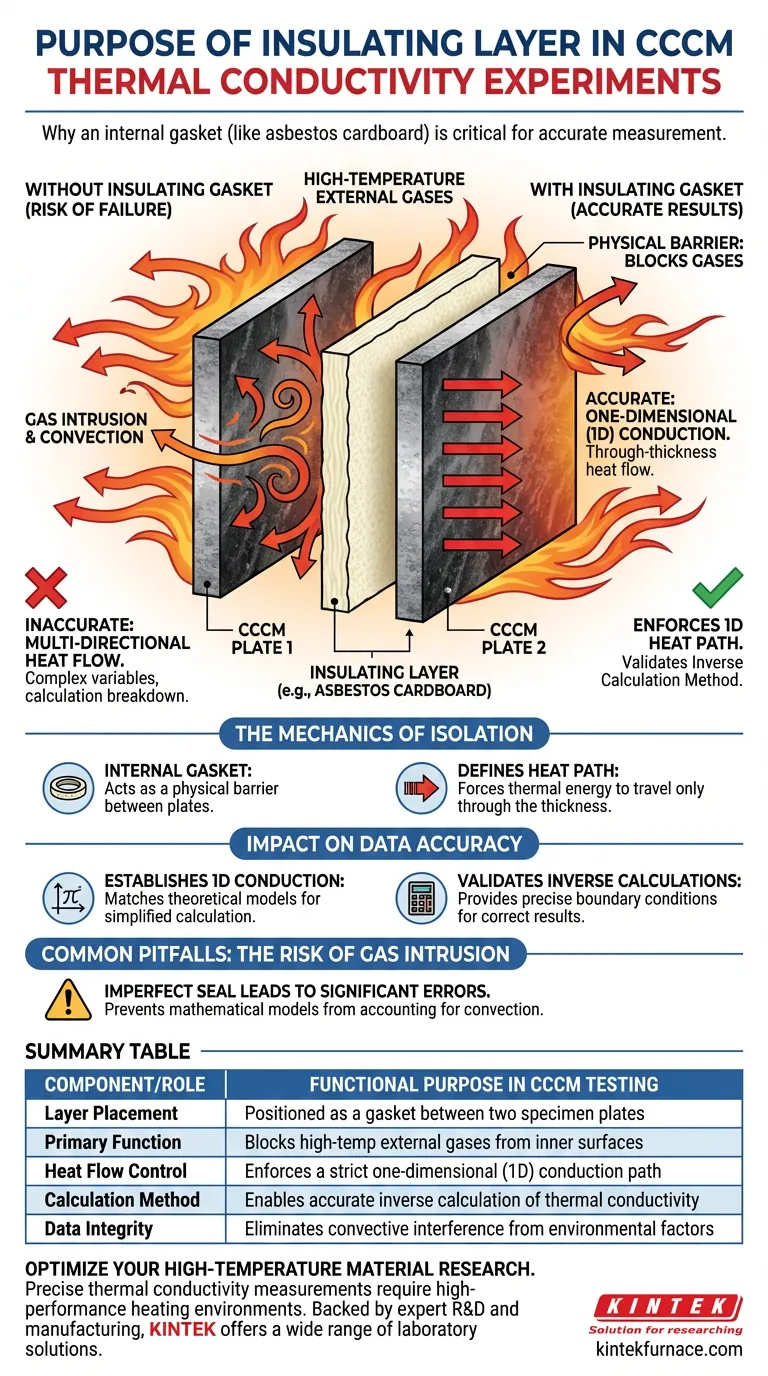
The primary purpose of using an insulating layer, such as asbestos cardboard, in Carbon-Carbon Composite Material (CCCM) experiments is to function as a protective internal gasket between two specimen plates. This layer physically blocks high-temperature external gases from penetrating the space between the inner surfaces of the plates. By preventing this gas intrusion, the setup ensures that heat transfer occurs exclusively through the thickness of the material, rather than being skewed by external environmental factors.
By effectively sealing the inner surfaces, the insulating layer enforces a one-dimensional heat conduction path. This controlled environment is the fundamental requirement for using inverse calculation methods to accurately determine thermal conductivity.
The Mechanics of Isolation
Acting as an Internal Gasket
In this experimental configuration, the setup typically involves a "package" consisting of two CCCM plates.
The asbestos cardboard is placed between these plates to serve as a physical barrier.
Its immediate mechanical role is to prevent the high-temperature gases surrounding the experiment from flowing into the gap between the plates.
Defining the Heat Path
Without this gasket, external heat sources would interact with the inner faces of the composite material.
The insulating layer ensures that the inner surfaces remain isolated from the convective heat of the surrounding gases.
This forces the thermal energy to travel in a specific direction: through the thickness of the specimen.
The Impact on Data Accuracy
Establishing One-Dimensional Conduction
Scientific calculations for thermal conductivity are often based on simplified mathematical models.
The most common model assumes one-dimensional (1D) heat conduction.
The insulating layer creates the physical reality that matches this theoretical model by eliminating multi-directional heat flow caused by gas leaks.
Validating Inverse Calculations
The determination of thermal conductivity in this context relies on an "inverse calculation" method.
This mathematical approach requires precise boundary conditions to yield correct results.
If the gasket fails and allows heat transfer on the inner surfaces, the mathematical model breaks down, leading to significant errors in the calculated thermal conductivity.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
The Risk of Gas Intrusion
The most critical failure point in this setup is an imperfect seal.
If the insulating layer does not perfectly block external gases, the heat transfer becomes two- or three-dimensional.
This introduces complex variables—such as convection between the plates—that the inverse calculation algorithms cannot account for.
Material Selection Dependencies
While the reference specifies asbestos cardboard, the success of the experiment relies on the material's insulating properties.
Using a gasket with high thermal conductivity would defeat the purpose, as it would act as a thermal bridge rather than a barrier.
The material must remain stable at high temperatures to maintain the integrity of the seal throughout the test.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
To ensure your thermal conductivity data is reliable, you must prioritize the integrity of the specimen assembly.
- If your primary focus is Model Validity: Ensure the insulating gasket covers the entire interface between plates to strictly enforce one-dimensional heat flow.
- If your primary focus is Calculation Accuracy: Verify that the chosen gasket material is robust enough to prevent any high-temperature gas leakage that would corrupt the inverse calculation inputs.
Ultimately, the precision of your thermal conductivity measurement is directly proportional to the effectiveness of the isolation provided by this insulating layer.
Summary Table:
| Component/Role | Functional Purpose in CCCM Testing |
|---|---|
| Layer Placement | Positioned as a gasket between two specimen plates |
| Primary Function | Blocks high-temp external gases from inner surfaces |
| Heat Flow Control | Enforces a strict one-dimensional (1D) conduction path |
| Calculation Method | Enables accurate inverse calculation of thermal conductivity |
| Data Integrity | Eliminates convective interference from environmental factors |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Material Research
Precise thermal conductivity measurements require high-performance heating environments and expert equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of laboratory solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet the unique needs of your Carbon-Carbon Composite (CCCM) testing and advanced material research.
Ensure experimental accuracy and reliability—Contact KINTEK today for expert solutions!
Visual Guide
References
- Dmytro Borovyk, D.I. Skliarenko. DETERMINATION OF THERMOPHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CARBON-CARBON MATERIALS BY A COMPUTATIONAL-EXPERIMENTAL METHOD. DOI: 10.31472/ttpe.4.2024.4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Ultra High Vacuum CF Flange Stainless Steel Sapphire Glass Observation Sight Window
- Ultra High Vacuum CF Observation Window Flange with High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the roles of laboratory vacuum drying ovens and precision analytical balances in moisture monitoring?
- What additional convenience feature is included with the water circulating vacuum pump? Discover Easy Mobility and More
- Why are fume hoods and sealed quartz tubes mandatory for BiF3 and SbF3? Safety in High-Temp Fluoride Reactions
- What are the main applications of laboratory furnaces? Unlock Precision Heat Processing for Your Lab
- What materials are commonly used for furnace tubes to withstand high heat? Choose the Best for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory vacuum pump play in a static batch desulfurization evaluation system? Ensure Data Integrity
- Is a work tube included with the furnace? Customize Your Setup for Optimal Performance
- What is the technical necessity of using a glass boat in a pyrolysis furnace? Precision in Thermal Decomposition



















