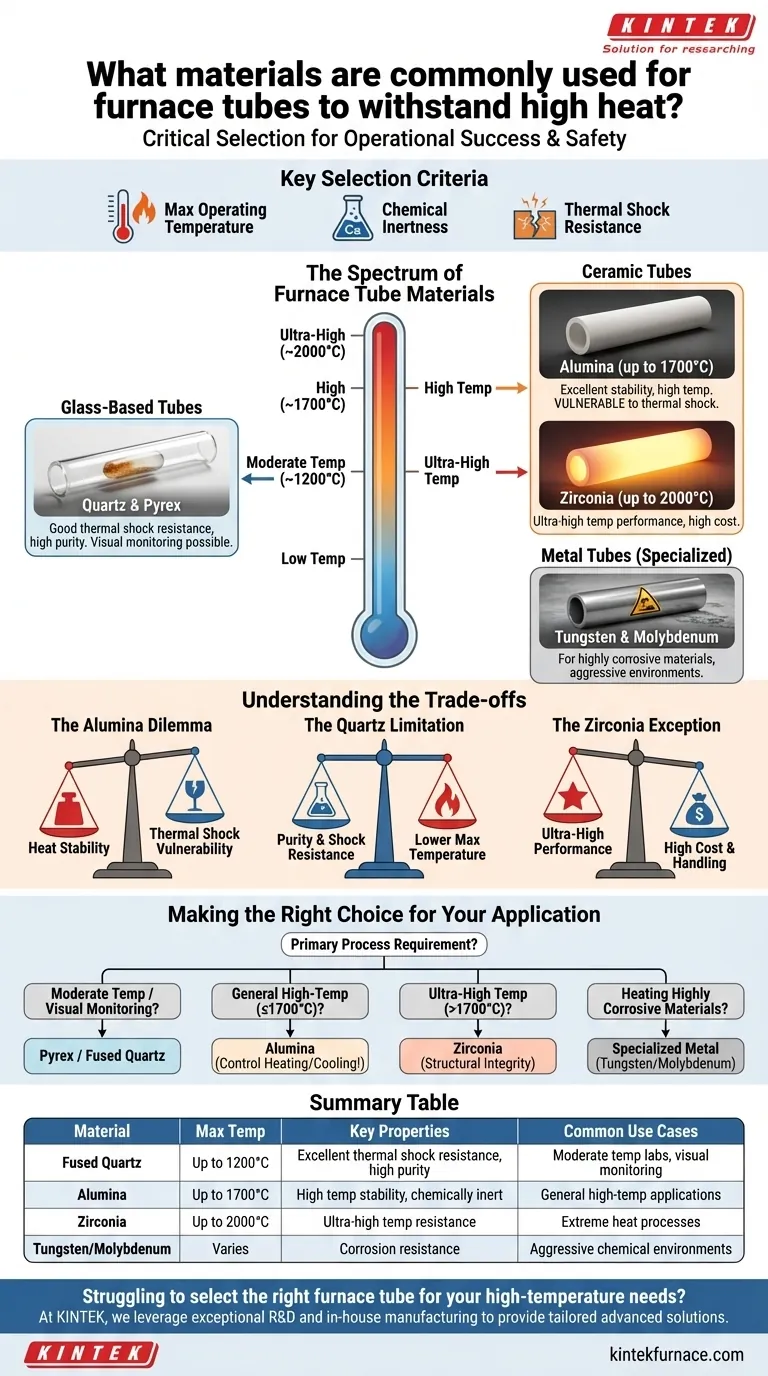
In high-temperature furnaces, the selection of tube material is critical for operational success and safety. The most common materials used are fused quartz, alumina, and in some cases, specialized ceramics like zirconia or metals like tungsten. These materials are chosen for their ability to maintain structural integrity and chemical inertness at extreme temperatures.
The ideal furnace tube material is always a trade-off. You must balance the need for maximum temperature resistance against factors like thermal shock vulnerability, chemical compatibility, and cost. There is no single "best" material, only the right material for a specific application.
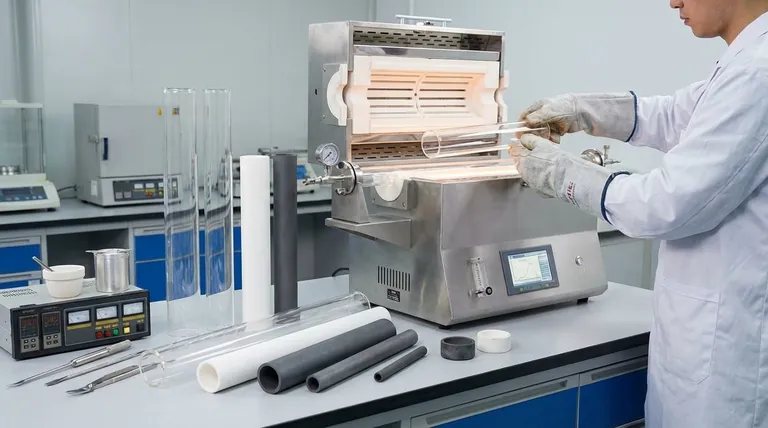

The Spectrum of Furnace Tube Materials
Furnace tubes are not one-size-fits-all. They fall into distinct categories, each suited for different thermal and chemical environments. Understanding these categories is the first step in making an informed choice.
Glass-Based Tubes: Quartz & Pyrex
Pyrex is a cost-effective option for lower-temperature applications where visual monitoring of the process is beneficial.
Fused quartz is a step up, offering excellent thermal shock resistance and high purity. It is chemically inert in most situations, making it a versatile choice for many laboratory processes that do not exceed its temperature limits.
Ceramic Tubes: Alumina & Zirconia
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) is the workhorse for high-temperature applications, often stable up to 1700°C (3092°F). It offers excellent high-temperature stability and structural integrity.
Zirconia is a specialized ceramic used for ultra-high temperature work. When your process requires temperatures approaching 2000°C (3600°F), zirconia is often the only viable ceramic option.
Metal Tubes: Tungsten & Molybdenum
In rare cases where you are heating highly corrosive materials, standard ceramic or quartz tubes may not be suitable. Specialized metal tubes, such as tungsten or molybdenum, are used for these aggressive chemical environments, though they come with their own operational complexities.
Key Selection Criteria
Choosing the right tube requires evaluating your process against three fundamental criteria. Missing any one of these can lead to failed experiments, equipment damage, or safety hazards.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the most important factor. Each material has a clear upper limit that should not be exceeded. Exceeding this limit will cause the tube to soften, deform, or break.
Chemical Inertness
Your tube material must not react with the sample or atmosphere inside the furnace. Quartz and alumina are inert for most applications, which is why they are so common. However, specific chemicals may require specialized materials.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress induced in a material when it is heated or cooled too quickly, causing it to crack. Materials like quartz handle rapid temperature changes well, while high-temperature ceramics like alumina are much more vulnerable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every material choice involves a compromise. The strongest material at high temperatures may be the most fragile during heating and cooling.
The Alumina Dilemma: Heat vs. Shock
Alumina is exceptional for its high-temperature stability, but it is highly susceptible to thermal shock. It must be heated and cooled slowly and controllably to prevent cracking. As a rule, smaller-diameter alumina tubes have better resistance to thermal shock than larger ones.
The Quartz Limitation: Purity vs. Temperature
Fused quartz offers outstanding chemical purity and good thermal shock resistance. Its primary limitation is a lower maximum operating temperature compared to alumina. You trade top-end heat resistance for ease of use and purity.
The Zirconia Exception: Performance at a Cost
Zirconia pushes the temperature boundary significantly higher than alumina. This extreme performance, however, comes with increased material cost and its own handling considerations, making it a material reserved for only the most demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary process requirement as the starting point to select the correct material.
- If your primary focus is moderate temperatures with visual process monitoring: A Pyrex or fused quartz tube is your most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, high-temperature work (up to 1700°C): Alumina is the standard material, provided you can control heating and cooling rates to prevent thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperatures (above 1700°C): A zirconia tube is required to maintain structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is heating highly corrosive materials: You must investigate specialized metal tubes like tungsten or molybdenum.
By matching the material's properties to your specific operational needs, you ensure a safe, effective, and reliable process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Properties | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance, high purity | Moderate temp labs, visual monitoring |
| Alumina | Up to 1700°C | High temp stability, chemically inert | General high-temp applications |
| Zirconia | Up to 2000°C | Ultra-high temp resistance | Extreme heat processes |
| Tungsten/Molybdenum | Varies | Corrosion resistance | Aggressive chemical environments |
Struggling to select the right furnace tube for your high-temperature needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental requirements precisely. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and safety with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















