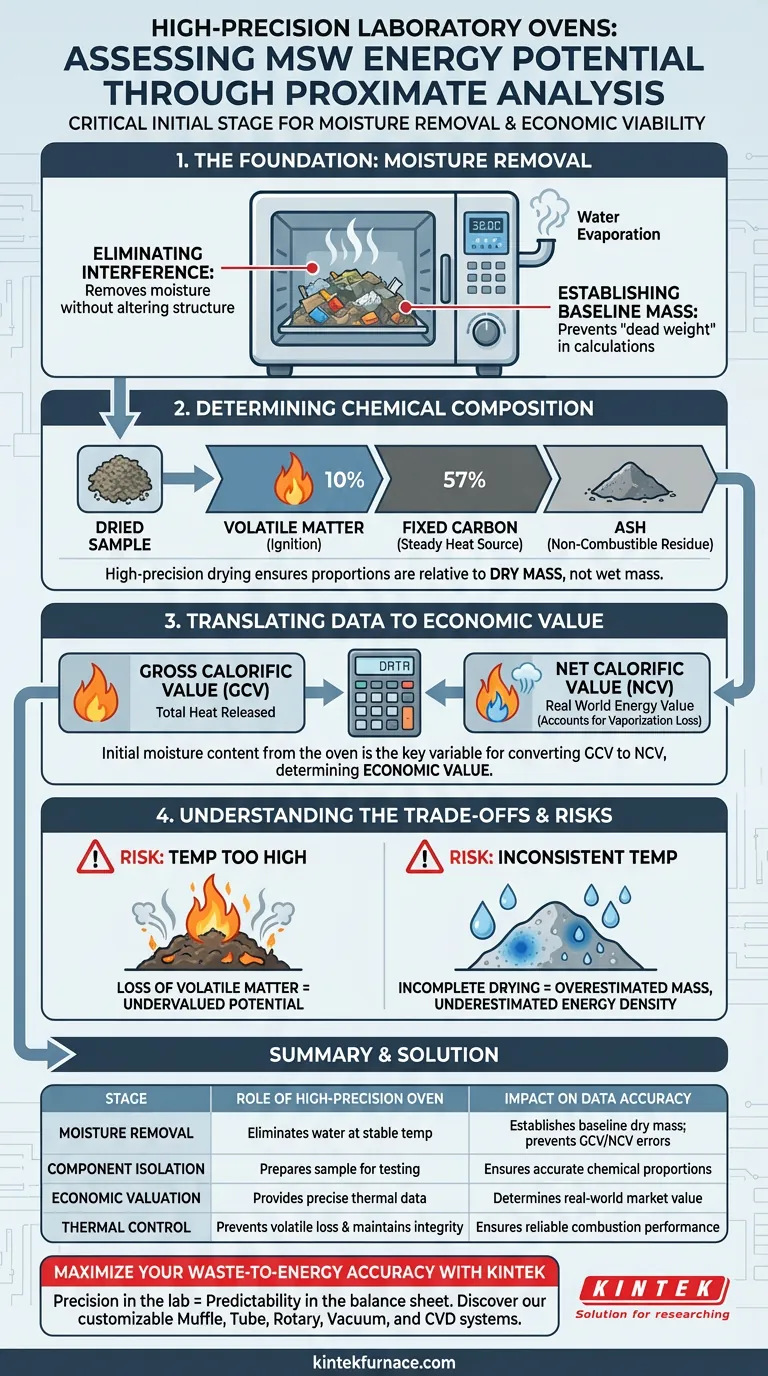
High-precision laboratory ovens serve as the critical initial stage in the proximate analysis of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) by strictly controlling the drying process. Their primary function is to isolate and remove moisture content at specific temperatures, ensuring that water weight does not skew the measurement of other chemical components. This precision is a prerequisite for accurately determining the waste's energy potential and economic viability as a biomass fuel.
The reliability of energy potential calculations rests entirely on the accuracy of moisture removal. By eliminating moisture interference, high-precision ovens provide the baseline data necessary to calculate Gross Calorific Value (GCV) and Net Calorific Value (NCV), determining the true value of waste-to-energy projects.

The Role of Moisture Removal in Analysis
Eliminating Analytical Interference
Moisture is the single largest variable in fresh MSW samples. Before any chemical analysis can occur, this water must be removed without altering the sample's chemical structure. High-precision ovens accomplish this by maintaining specific, stable temperatures designed solely to evaporate water.
Establishing the Baseline Mass
Proximate analysis relies on measuring weight loss under controlled conditions. If moisture is not completely removed, it acts as "dead weight" in the calculations. This distorts the percentages of the remaining components, leading to flawed data regarding the fuel's actual composition.
Determining Chemical Composition
Isolating Key Fuel Components
Once the oven has effectively removed moisture, researchers can proceed to isolate the remaining components. The dried sample allows for the accurate assessment of volatile matter, fixed carbon, and ash.
The Hierarchy of Components
These three components—volatiles, carbon, and ash—define how the fuel will burn. Volatile matter indicates how easily the fuel ignites, fixed carbon represents the steady heat source, and ash represents the non-combustible residue. High-precision drying ensures these proportions are calculated relative to the dry mass, not the wet mass.
Translating Data to Economic Value
Calculating Gross Calorific Value (GCV)
The data derived from the oven-dried samples are fundamental inputs for calculating the GCV. This metric represents the total heat released during combustion. Without precise moisture content figures, the GCV calculation would be speculative rather than empirical.
Determining Net Calorific Value (NCV)
The NCV is often considered the "real world" energy value, as it accounts for the energy lost to vaporize water during combustion. The initial moisture content determined by the laboratory oven is the key variable in converting GCV to NCV. This final figure directly reflects the economic value of the MSW as a biomass energy source.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Thermal Precision
Using an oven without high-precision controls introduces significant risk. If the temperature drifts too high, you risk burning off volatile matter along with the water, effectively destroying part of the fuel potential before it can be measured.
The Risk of Incomplete Drying
Conversely, if the oven cannot maintain a consistent temperature throughout the chamber, "cold spots" may leave residual moisture in the sample. This results in an underestimation of the fuel's energy density and an overestimation of its mass, ultimately devaluing the resource.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
High-precision drying is not just a preparatory step; it is the calibration point for your entire economic assessment.
- If your primary focus is Economic Valuation: Prioritize ovens with superior temperature uniformity to ensure GCV and NCV calculations reflect the true market value of the biomass.
- If your primary focus is Combustion Efficiency: Focus on the accurate isolation of volatile matter and fixed carbon, as these metrics dictate how the fuel performs in a reactor.
Precision in the lab translates directly to predictability in the balance sheet.
Summary Table:
| Stage of Analysis | Role of High-Precision Oven | Impact on Data Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Removal | Eliminates water interference at stable temperatures | Establishes baseline dry mass; prevents GCV/NCV errors |
| Component Isolation | Prepares sample for volatile and fixed carbon testing | Ensures chemical proportions are calculated against dry weight |
| Economic Valuation | Provides precise data for thermal calculations | Determines real-world market value of waste-to-energy projects |
| Thermal Control | Prevents accidental loss of volatile matter | Maintains sample integrity for reliable combustion performance |
Maximize Your Waste-to-Energy Accuracy with KINTEK
Precision in the laboratory is the foundation of predictability on the balance sheet. At KINTEK, we understand that reliable energy potential calculations start with superior thermal control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your specific proximate analysis requirements.
Whether you are assessing MSW, biomass, or specialized fuels, our equipment ensures the temperature uniformity and stability needed to isolate key fuel components without compromising sample integrity.
Ready to elevate your lab's analytical precision? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and discover how KINTEK's advanced heating solutions can optimize your research and manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Paul Adah Ondachi, M.T Zarmai. Harnessing Abuja's Municipal Solid Waste as a Renewable Energy Source: Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis. DOI: 10.53982/ajerd.2024.0701.07-j
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a PID intelligent segmented temperature control system impact diamond tools? Precision Sintering Explained
- What is the primary function of a laboratory electric drying oven in sample prep? Ensure Pure, Grinder-Ready Powders
- Why is a laboratory constant temperature drying oven necessary for biomass adsorbents? Ensure Precision & Integrity
- How does the carbon reductant ratio influence the selective reduction of ferronickel? Mastering Alloy Purity
- What is the significance of using PVD for phosphosulfide thin films? Scale Your Optoelectronic Research to Industry
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for activated carbon? Ensure Accurate BET and Pore Size Analysis
- What are the two methods of temperature control of resistance furnace? Optimize for Precision or Cost
- What are the structural advantages of specialized crystal growth furnaces for CZT? Achieve High-Purity Single Crystals



















