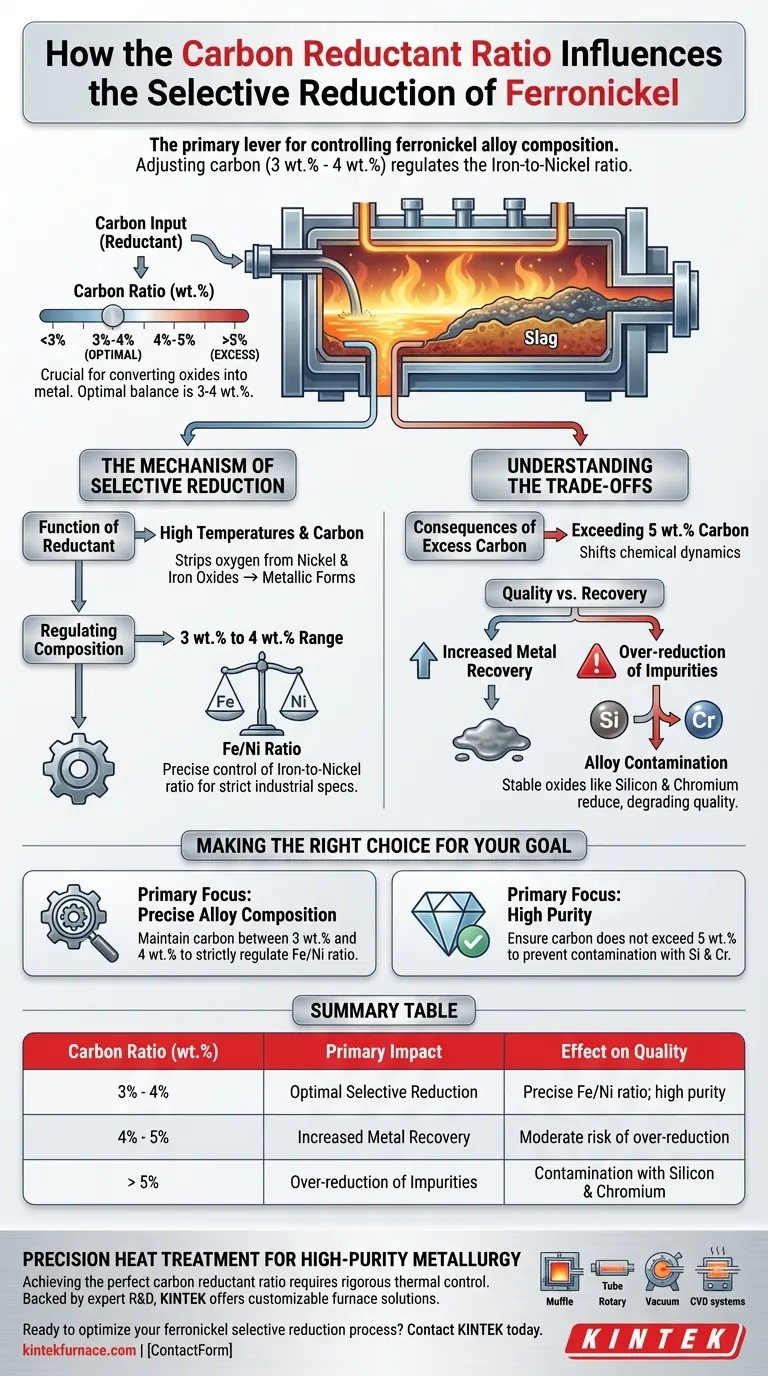
The carbon reductant ratio is the primary lever for controlling the composition of ferronickel alloys. By adjusting the specific weight percentage of carbon—typically between 3 wt.% and 4 wt.%—metallurgists can precisely regulate the ratio of iron to nickel in the final product.
While increasing carbon acts as a medium to convert oxides into metal, there is a critical threshold for efficiency. The optimal balance for selective reduction generally lies between 3 wt.% and 4 wt.%; exceeding this limit risks compromising the alloy's purity.

The Mechanism of Selective Reduction
The Function of the Reductant
At high temperatures, carbon serves as the essential medium for chemical conversion. Its primary role is to strip oxygen from nickel and iron oxides, transforming them into their metallic forms.
Regulating Alloy Composition
The specific proportion of carbon added allows for fine-tuning of the final alloy. By staying within the 3 wt.% to 4 wt.% range, you can control the iron-to-nickel (Fe/Ni) ratio with high precision.
This control is vital for producing ferronickel grades that meet strict industrial specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Consequences of Excess Carbon
It may be tempting to increase carbon levels to maximize yield, but this comes with significant downsides. Exceeding a threshold of 5 wt.% carbon shifts the chemical dynamics of the reduction process.
Quality vs. Recovery
While higher carbon input may increase overall metal recovery, it leads to the over-reduction of impurities.
Specifically, excess carbon causes stable oxides like silicon and chromium to reduce into the metal phase. This results in an alloy with unwanted contaminants, degrading the quality of the final ferronickel product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your reduction process, you must weigh the need for volume against the requirement for chemical purity.
- If your primary focus is Precise Alloy Composition: Maintain carbon addition between 3 wt.% and 4 wt.% to strictly regulate the Fe/Ni ratio.
- If your primary focus is High Purity: Ensure carbon addition does not exceed 5 wt.% to prevent the contamination of the alloy with silicon and chromium.
Mastering the carbon reductant ratio is the key to balancing high metal recovery with superior alloy quality.
Summary Table:
| Carbon Ratio (wt.%) | Primary Impact | Effect on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| 3% - 4% | Optimal Selective Reduction | Precise Fe/Ni ratio; high purity |
| 4% - 5% | Increased Metal Recovery | Moderate risk of over-reduction |
| > 5% | Over-reduction of Impurities | Contamination with Silicon & Chromium |
Precision Heat Treatment for High-Purity Metallurgy
Achieving the perfect carbon reductant ratio requires rigorous thermal control and specialized equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical research and production needs.
Ready to optimize your ferronickel selective reduction process? Contact KINTEK today to discover how our advanced furnace solutions can help you balance high metal recovery with superior alloy quality.
Visual Guide
References
- Erdenebold Urtnasan, Jei‐Pil Wang. Relationship Between Thermodynamic Modeling and Experimental Process for Optimization Ferro-Nickel Smelting. DOI: 10.3390/min15020101
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How do structured computational grids facilitate the simulation of complex geometric boundaries? Master Furnace Design
- How does a high-precision PID temperature controller ensure the quality of biochar? Master Teff Husk Pyrolysis
- What is the importance of dynamic sealing in an InP crystal growth furnace? Ensure Pressure Integrity & Motion Control
- Why are temperature control and pressure critical for V-NbOPO4@rGO electrode sheets? Optimize Your Battery Performance
- Why Use a Vacuum Oven for Cu-Cu2O/g-C3N4 Catalysts? Preserve Purity and Structural Integrity
- How does the ramp rate affect LDO properties? Master Rapid Thermal Control for 69% More Efficiency
- What is the primary function of multi-stage oxidation ovens? Secure High-Strength Carbon Fiber Stabilization
- What is the physicochemical mechanism of phosphoric acid in ceramic sintering? Master Berlinite Densification



















