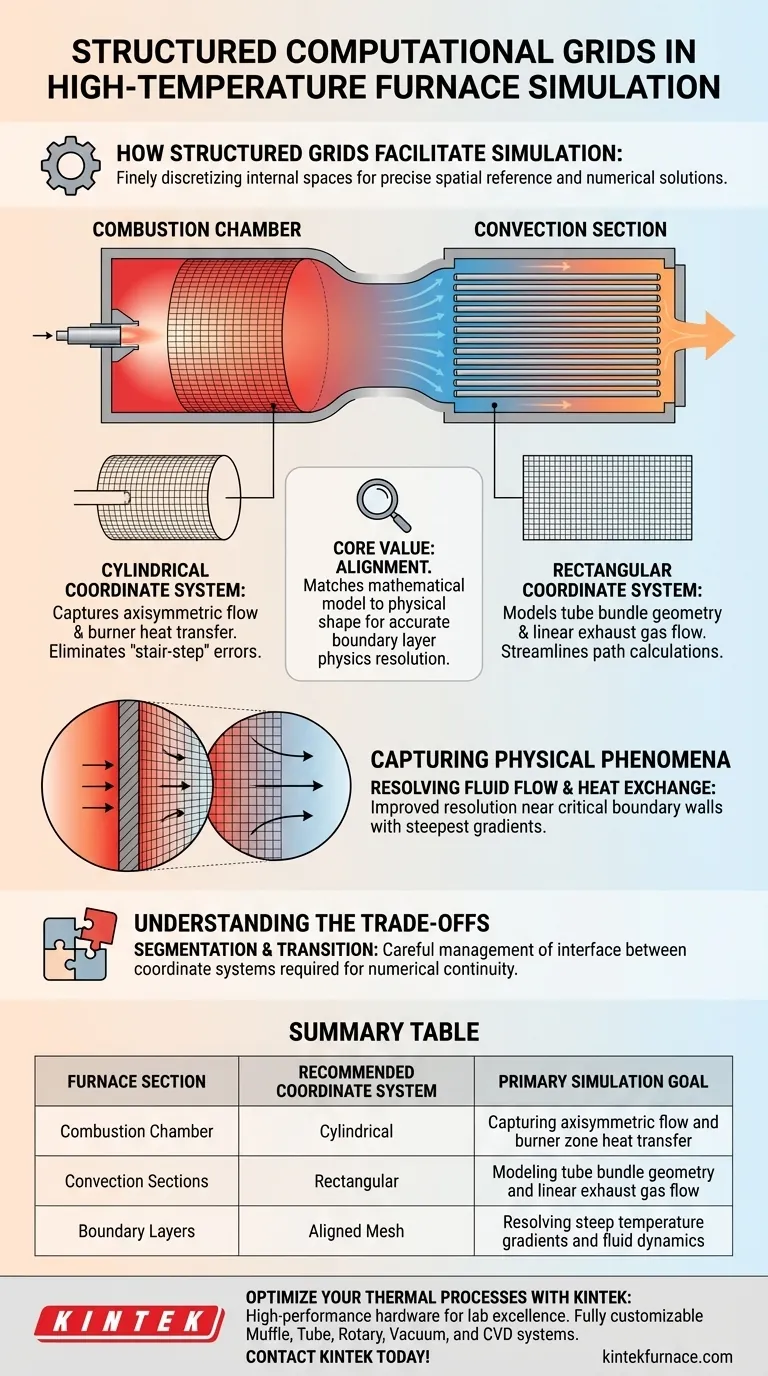
Structured computational grids facilitate simulation by finely discretizing the internal spaces of high-temperature furnaces to create a precise spatial reference for numerical solutions. By applying specific coordinate systems—cylindrical for axisymmetric sections and rectangular for convection tube bundles—these grids align the computational mesh with the physical geometry. This alignment enables the accurate capture of complex fluid flow details and heat exchange conditions, particularly near the interior walls.
The core value of structured grids is their ability to match the mathematical model to the physical shape of the furnace, ensuring that critical boundary layer physics are resolved accurately rather than approximated.

The Role of Discretization in Furnace Simulation
Establishing a Spatial Reference
To simulate a high-temperature furnace, the continuous volume of the internal space must be broken down into small, distinct units. This process, known as fine discretization, creates a structured map of the furnace interior.
Defining Boundaries for Numerical Solutions
Structured grids provide the foundational framework for numerical calculations. They define exactly where the boundaries of the furnace lie, allowing the software to solve physics equations at specific points relative to the walls.
Tailoring Coordinate Systems to Geometry
Handling Axisymmetric Sections
High-temperature furnaces often contain combustion chambers that are cylindrical or rotationally symmetric. Structured grids facilitate the application of a cylindrical coordinate system to these specific sections. This ensures the grid lines follow the natural curvature of the chamber, preventing the "stair-step" approximation errors common in non-aligned grids.
Addressing Convection Tube Bundles
In contrast to the combustion chamber, the convection sections typically contain tube bundles arranged in blocks. Here, the structured grid strategy shifts to a rectangular coordinate system. This alignment matches the linear arrangement of the tubes, streamlining the calculation of flow paths between them.
Capturing Physical Phenomena
Resolving Fluid Flow Details
The primary advantage of aligning the grid with the geometry is the improved resolution of fluid dynamics. By following the contours of the furnace, the grid allows for a more realistic simulation of how gases move through combustion and convection zones.
Optimizing Heat Exchange Accuracy
Accurate thermal simulation relies heavily on resolving what happens at the boundary walls. Structured grids enable precise modeling of heat exchange conditions near the interior walls, where temperature gradients are often steepest and most critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Segmentation
The approach described relies on a segmented strategy rather than a "one-size-fits-all" mesh. You cannot apply a single coordinate system to the entire furnace.
Grid Transition Challenges
Because you are applying cylindrical coordinates to one section and rectangular coordinates to another, the simulation requires careful management of the interface between these zones. The transition between the combustion chamber grid and the convection section grid must be handled precisely to maintain numerical continuity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Simulation
To maximize the accuracy of your high-temperature furnace model, you must match your grid strategy to the specific component you are analyzing.
- If your primary focus is the combustion chamber: Prioritize a cylindrical coordinate system to accurately capture the axisymmetric flow and heat transfer inherent to the burner zone.
- If your primary focus is the convection section: Utilize a rectangular coordinate system to best represent the geometry of tube bundles and the linear flow of exhaust gases.
By adapting the coordinate system to the specific furnace section, you ensure that your simulation data reflects the physical reality of the boundary conditions.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Section | Recommended Coordinate System | Primary Simulation Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion Chamber | Cylindrical | Capturing axisymmetric flow and burner zone heat transfer |
| Convection Sections | Rectangular | Modeling tube bundle geometry and linear exhaust gas flow |
| Boundary Layers | Aligned Mesh | Resolving steep temperature gradients and fluid dynamics |
Optimize Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Precise simulation is only the first step toward laboratory excellence. KINTEK provides the high-performance hardware needed to bring your digital models to life. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other specialized lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research and industrial requirements.
Whether you are refining fluid dynamics in a combustion chamber or optimizing heat exchange in convection tubes, our engineering team is ready to provide the precision equipment you deserve. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- O. I. Varfolomeeva, D. A. Khvorenkov. Development of a universal model for numerical analysis of firebox processes in heat-generating plants. DOI: 10.30724/1998-9903-2025-27-6-171-186
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do lab furnaces simulate fire environments for UHPFRC testing? Achieving ISO834 Standard Compliance
- How does a resistance heating furnace contribute to Al/Cu bimetallic interface preparation? Expert Thermal Solutions
- What heat treatment conditions are required for SDSS2507 solution treatment? Achieve Precise 1100°C Thermal Profiles
- What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)? Master Thin Film Coating for Enhanced Materials
- What are the advantages of a high-pressure nitrogen environment? Speed and Efficiency in Wood Thermal Modification
- Why are specific heating pulses applied when monitoring molten metal surface oscillations? Unlock Material Insights
- What are the advantages of supersonic inert gas cooling in DGCC? Transform Heat Treatment and Microstructure Control
- What are the advantages of the re-coating process? Boost Adsorbent Capacity Beyond Original Performance



















