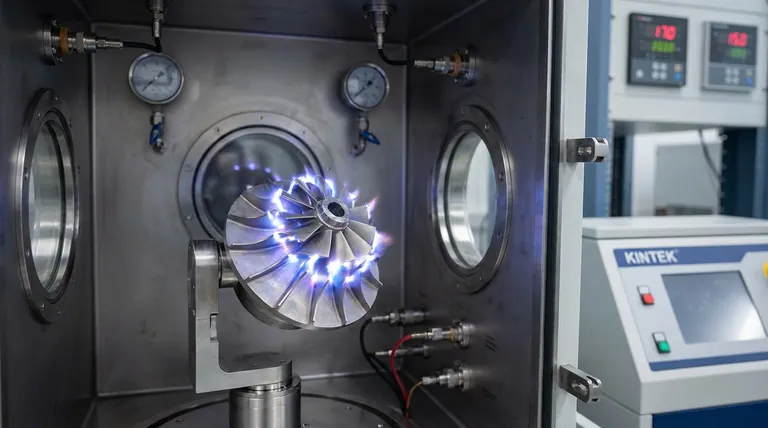
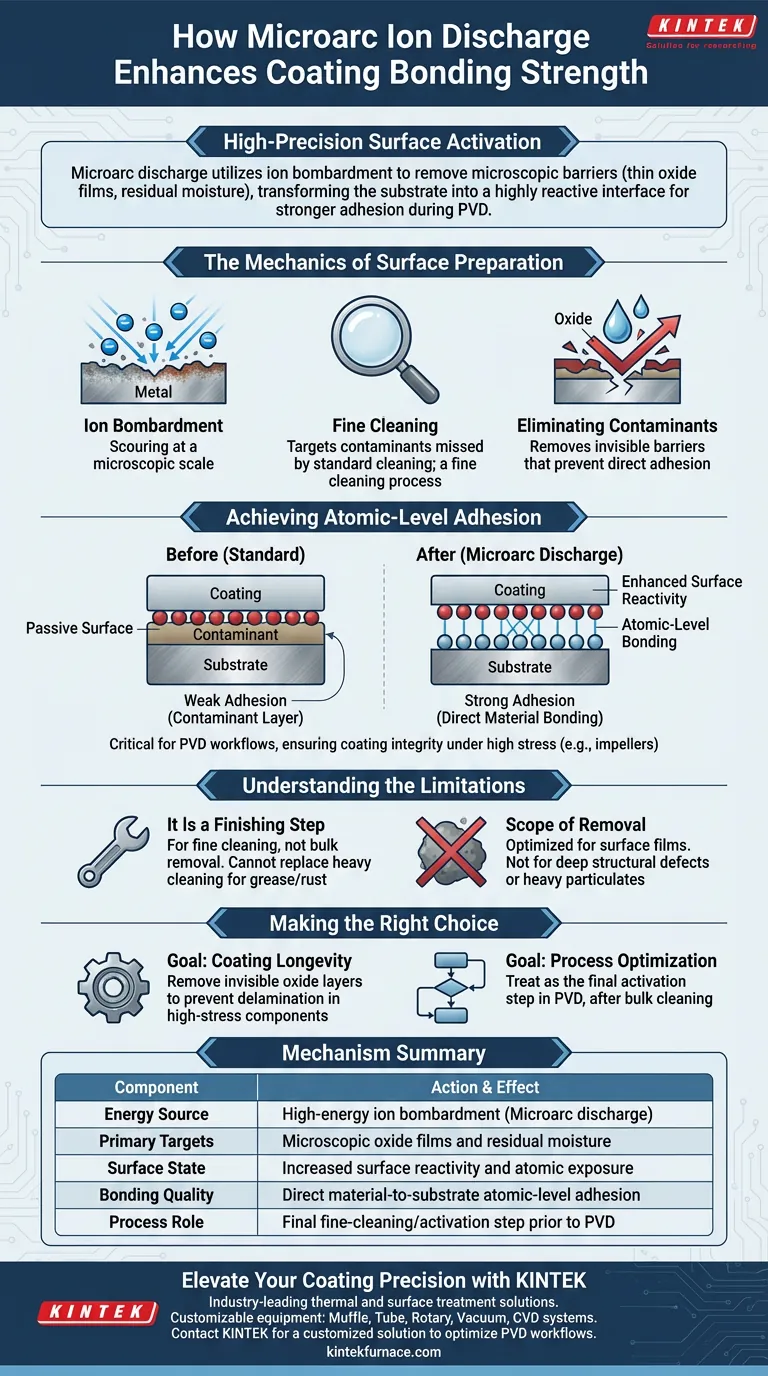
Microarc discharge functions as a high-precision surface activation technique that utilizes ion bombardment to prepare components for coating. This process works by aggressively removing microscopic barriers—specifically thin oxide films and residual moisture—to expose the raw, reactive material underneath.
By eliminating physical and chemical contaminants at the atomic level, microarc discharge transforms the substrate from a passive surface into a highly reactive interface, enabling stronger adhesion during Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The Mechanics of Surface Preparation
Ion Bombardment
The core mechanism of this process is ion discharge. High-energy ions bombard the surface of the component, effectively scouring the material at a microscopic scale.
Fine Cleaning
This is not a bulk cleaning method; it is a fine cleaning process. It targets contaminants that standard washing or chemical cleaning might miss, ensuring the surface is pristine immediately prior to coating.
Eliminating Contaminants
The primary targets of this bombardment are extremely thin oxide films and residual moisture. These elements act as invisible barriers that prevent coatings from adhering directly to the metal substrate.
Achieving Atomic-Level Adhesion
Enhanced Surface Reactivity
Once the oxides and moisture are stripped away, the substrate's surface reactivity is significantly enhanced. The exposed metal atoms are energetically primed to interact with incoming coating materials.
Direct Material Bonding
This heightened reactivity facilitates atomic-level bonding. Instead of sitting on top of a contaminant layer, the ceramic or alloy phase coating bonds directly with the metal substrate.
Application in PVD
This step is particularly critical in Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) workflows. For components like impellers, which face high stress, this pretreatment ensures the coating remains intact under operational loads.
Understanding the Limitations
It Is a Finishing Step
Microarc discharge is designed for fine cleaning, not gross material removal. It cannot replace the initial heavy cleaning steps required to remove bulk grease, oil, or thick rust.
Scope of Removal
The process is optimized for surface films, such as oxidation layers. Relying on it to remove deep-seated structural defects or heavy particulate matter will likely lead to suboptimal results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of microarc discharge in your coating workflow, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is coating longevity: Ensure this step is utilized to remove invisible oxide layers, which are the leading cause of delamination in high-stress components like impellers.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Treat microarc discharge as the final activation step in your PVD sequence, strictly performed after all bulk cleaning is complete.
True adhesion strength is not just about the coating you apply, but the purity of the surface you apply it to.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism Component | Action & Effect |
|---|---|
| Energy Source | High-energy ion bombardment (Microarc discharge) |
| Primary Targets | Microscopic oxide films and residual moisture |
| Surface State | Increased surface reactivity and atomic exposure |
| Bonding Quality | Direct material-to-substrate atomic-level adhesion |
| Process Role | Final fine-cleaning/activation step prior to PVD |
Elevate Your Coating Precision with KINTEK
Don't let invisible contaminants compromise your material performance. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal and surface treatment solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Whether you require Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our equipment is fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory or production line.
Ensure maximum bonding strength and prevent delamination in your high-stress components today. Contact KINTEK for a customized solution and see how our advanced high-temp furnaces can optimize your PVD and surface activation workflows.
Visual Guide
References
- А.M. Yalova, Nazarii Bondar. The problem of increasing the working resource of energy equipment details. DOI: 10.31498/2225-6733.49.2.2024.321349
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the main advantages of PECVD technology? Unlock Low-Temp, High-Quality Film Deposition
- How does PECVD allow for versatility and control over film properties? Master Thin-Film Engineering with Precision
- What factors contribute to the efficiency of PECVD? Boost Thin-Film Deposition with Low-Temp Plasma
- How does the method of operation in PECVD work? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the geometric coating capabilities of PECVD? Unlock Uniform Coatings on Complex Shapes
- How does temperature affect PECVD film quality? Optimize for Denser, Purer Films
- What substrate sizes are supported by PECVD system platforms? Optimize Your Lab's Efficiency with Standard Sizes



















