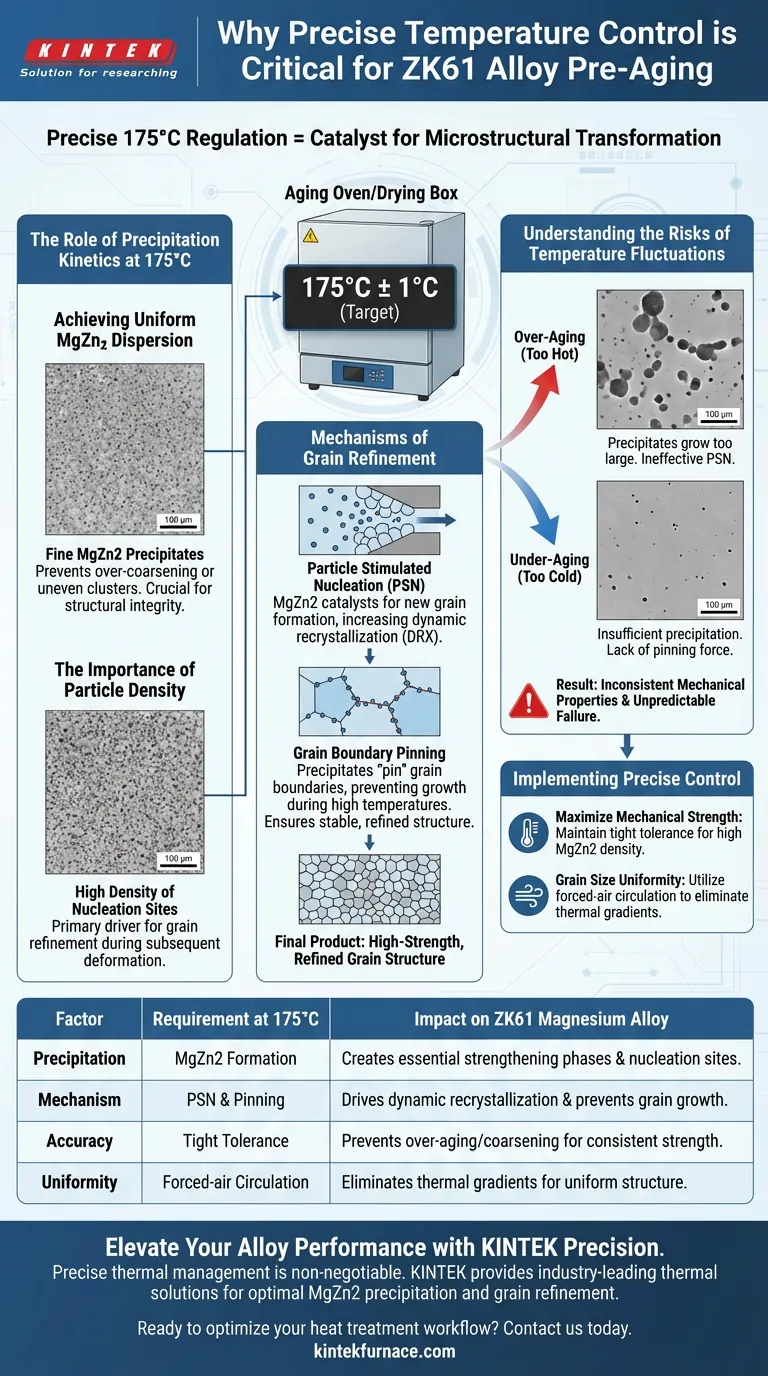
Precise temperature regulation at 175°C is the catalyst for microstructural transformation in ZK61 alloys.
Maintaining exact temperatures during pre-aging ensures the formation of fine, uniformly dispersed MgZn2 strengthening phases. These particles are essential for triggering Particle Stimulated Nucleation (PSN) during subsequent processing, which ultimately dictates the final grain size and mechanical strength of the alloy.
Precise temperature control ensures the optimal precipitation of MgZn2 phases, which serve as the foundation for grain refinement through Particle Stimulated Nucleation and boundary pinning during extrusion.
The Role of Precipitation Kinetics at 175°C
Achieving Uniform MgZn2 Dispersion
The pre-aging process specifically targets the 175°C threshold to facilitate the precipitation of the MgZn2 strengthening phase.
Precise control prevents these particles from over-coarsening or forming uneven clusters, which would compromise the alloy's structural integrity.
The Importance of Particle Density
A fine and dispersed distribution of precipitates creates a higher density of nucleation sites.
This density is the primary driver for the subsequent refinement of the alloy's grain structure during mechanical deformation.
Mechanisms of Grain Refinement
Particle Stimulated Nucleation (PSN)
During extrusion, the MgZn2 precipitates act as catalysts for Particle Stimulated Nucleation.
PSN encourages the formation of new grains around the precipitates, significantly increasing the rate of dynamic recrystallization (DRX).
Grain Boundary Pinning
These precipitates also serve to "pin" grain boundaries, preventing them from migrating and growing larger during high-temperature processing.
This pinning effect ensures that the refined grain structure remains stable, resulting in a high-strength final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Risks of Temperature Fluctuations
Even minor deviations from the 175°C target can lead to "over-aging," where precipitates grow too large to effectively trigger PSN.
Conversely, under-aging results in insufficient precipitation, failing to provide the necessary pinning force to maintain a fine grain structure.
Impact on Mechanical Consistency
Temperature gradients within an oven can lead to localized variations in mechanical properties across the alloy.
This inconsistency makes the final component unpredictable under stress, potentially leading to premature structural failure.
Implementing Precise Control for ZK61 Processing
To achieve the best results with ZK61 magnesium alloys, your thermal management strategy must be rigorous.
- If your primary focus is maximizing mechanical strength: Ensure the aging oven maintains a tight tolerance to maximize the density of fine MgZn2 precipitates.
- If your primary focus is grain size uniformity: Utilize forced-air circulation within the drying box to eliminate thermal gradients that cause uneven grain growth.
Mastering the thermal environment during pre-aging is the most effective way to guarantee the superior mechanical performance of ZK61 magnesium alloys.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Requirement at 175°C | Impact on ZK61 Magnesium Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | MgZn2 Formation | Creates essential strengthening phases and nucleation sites. |
| Mechanism | PSN & Pinning | Drives dynamic recrystallization and prevents grain growth. |
| Accuracy | Tight Tolerance | Prevents over-aging/coarsening for consistent mechanical strength. |
| Uniformity | Forced-air Circulation | Eliminates thermal gradients to ensure uniform grain structure. |
Elevate Your Alloy Performance with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal management is non-negotiable for achieving the mechanical integrity required in ZK61 magnesium alloy processing. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—along with customizable lab high-temperature furnaces—delivers the exact temperature uniformity and stability needed to ensure optimal MgZn2 precipitation and grain refinement.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment workflow? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and discover how our advanced furnace technology can provide the consistency your lab requires.
Visual Guide
References
- INFLUENCE OF EXTRUSION TEMPERATURE AND COOLING RATE ON THE MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF PRE-AGED EXTRUDED ZK61 Mg ALLOY. DOI: 10.17222/mit.2023.1025
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do high-temperature industrial furnaces play in the pretreatment of spodumene for lithium extraction?
- What are the requirements for synthesizing Magnesium alloys via ampoule method? Expert Synthesis Protocols
- What is the importance of providing technical documentation for high-temperature furnaces in multiple languages?
- Why is stepped temperature control in a laboratory precision oven necessary? Mastering Porous TiCO Ceramic Curing
- What is the significance of using a vacuum drying oven? Optimize Supercapacitor Electrode Performance
- How are impurity levels controlled during tantalum powder synthesis? Master High-Purity Magnesiothermic Reduction
- What is the purpose of adding wax organic binders to glass powder? Enhance Structural Integrity in Glass Sealing
- What is the primary role of a ball mill in raw material preparation for vacuum carbothermic reduction of magnesium? Ensure a Complete and Rapid Reaction



















