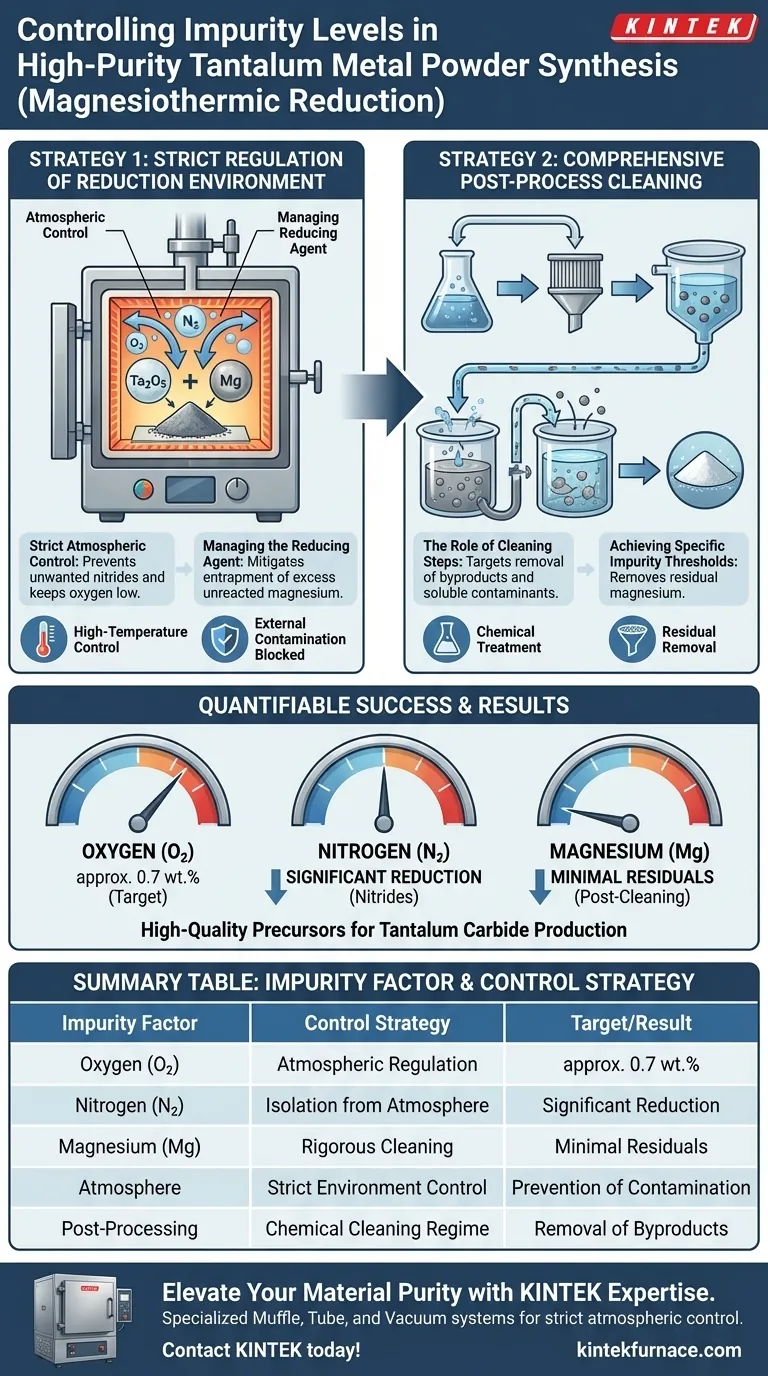
Strict control of impurity levels in the synthesis of high-purity tantalum metal powder is achieved through a dual-strategy approach: rigorous regulation of the reduction environment and comprehensive post-process cleaning. By isolating the reaction from atmospheric contamination and chemically treating the resulting powder, manufacturers effectively minimize critical impurities such as oxygen, nitrogen, and residual magnesium.
Core Takeaway: The quality of magnesiothermic-reduced tantalum relies on managing the reaction atmosphere and executing precise cleaning steps. This process caps oxygen content at approximately 0.7 wt.% and significantly lowers nitrogen and magnesium residuals, yielding high-quality precursors essential for applications like tantalum carbide production.

Regulating the Reduction Environment
Strict Atmospheric Control
The primary defense against impurities begins during the reduction of tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5). The reduction environment must be strictly regulated to prevent the ingress of external contaminants.
By controlling the atmosphere within the reaction vessel, the process minimizes the absorption of atmospheric gases. This is critical for preventing the formation of unwanted nitrides and keeping oxygen levels within manageable limits before the powder even leaves the furnace.
Managing the Reducing Agent
The process utilizes magnesium to reduce the oxide. While magnesium is the active agent, it can become an impurity if not properly managed.
Regulating the reduction environment ensures that the interaction between the magnesium and the tantalum pentoxide proceeds efficiently. This control helps mitigate the entrapment of excess unreacted magnesium within the tantalum matrix.
Post-Processing and Purification
The Role of Cleaning Steps
Synthesis is followed by subsequent cleaning steps which are as critical as the reduction itself. These steps are designed to remove byproducts generated during the reaction.
This phase specifically targets the removal of residual magnesium and other soluble contaminants that adhere to the tantalum particles. Without this cleaning regime, the metallic powder would retain high levels of magnesium, compromising its purity.
Achieving Specific Impurity Thresholds
The success of this two-stage control system is quantifiable. Through these measures, the process successfully limits oxygen content to approximately 0.7 wt.%.
Additionally, these protocols significantly reduce the levels of nitrogen and residual magnesium. This results in a high-purity powder that serves as an excellent precursor for producing high-performance materials, such as tantalum carbide.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Residual Oxygen Levels
It is important to note that while this process controls oxygen, it does not eliminate it entirely. The process targets an oxygen content of approximately 0.7 wt.%.
For applications requiring ultra-low oxygen levels (below this threshold), additional deoxidation steps or alternative synthesis methods might be required. This level is, however, sufficiently low for high-quality carbide precursors.
Process Complexity
Relies on a multi-step workflow. The necessity of strict environmental regulation combined with aggressive cleaning steps increases the operational complexity.
Failure in either the atmospheric control or the cleaning phase will result in powder that exceeds the nitrogen or magnesium limits, rendering it unsuitable for high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the production of high-quality tantalum powder, consider the following based on your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance Tantalum Carbide: Prioritize the strict regulation of the reduction environment to ensure the precursor material meets the necessary purity baseline.
- If your primary focus is minimizing metallic residuals: optimize the subsequent cleaning steps to maximally reduce the residual magnesium content left over from the reduction process.
By synchronizing atmospheric control with rigorous cleaning, you can consistently achieve the purity required for advanced material synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Impurity Factor | Control Strategy | Target/Result |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen (O₂) | Atmospheric regulation in vessel | Approximately 0.7 wt.% |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Isolation from atmospheric gases | Significant reduction in nitrides |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Rigorous post-process cleaning | Minimal residual magnesium levels |
| Atmosphere | Strict reaction environment control | Prevention of external contamination |
| Post-Processing | Chemical cleaning regime | Removal of byproducts and residuals |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK Expertise
Precision in high-purity tantalum synthesis requires more than just a process; it requires the right high-temperature environment. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems designed to maintain the strict atmospheric control necessary for magnesiothermic reduction.
Whether you are producing high-performance tantalum carbide or advanced lab precursors, our customizable lab furnaces ensure your research and production meet the most rigorous purity standards. Contact KINTEK today to find the ideal thermal solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Seon-Min Hwang, Dong‐Won Lee. Carburization of Tantalum Metal Powder Using Activated Carbon. DOI: 10.3390/ma18122710
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why Use a Laboratory Drying Oven for Re2O7/Al2O3 Catalysts? Ensure High Dispersion & Performance
- How does a batch furnace differ from a continuous furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Production Needs
- What are the advantages of using a high-pressure oxygen annealing furnace for La1-xSrxMnO3 thin films?
- Why is high-precision constant temperature heating equipment required when preparing 17-4 PH stainless steel composite?
- Why is a high flow rate of synthetic air maintained during magnetite oxidation? Ensure Accurate Kinetic Modeling
- How does an aluminum foil mask regulate temperature in the Floating-Zone process? Optimize Crystal Growth Precision
- What is the effect of sintering BZCYYb electrolyte pellets at 1000°C? Boost Your PCFC Performance Today
- Why is vacuum distillation preferred for biodiesel ethanol removal? Protect Fuel Quality with Low-Temp Processing


