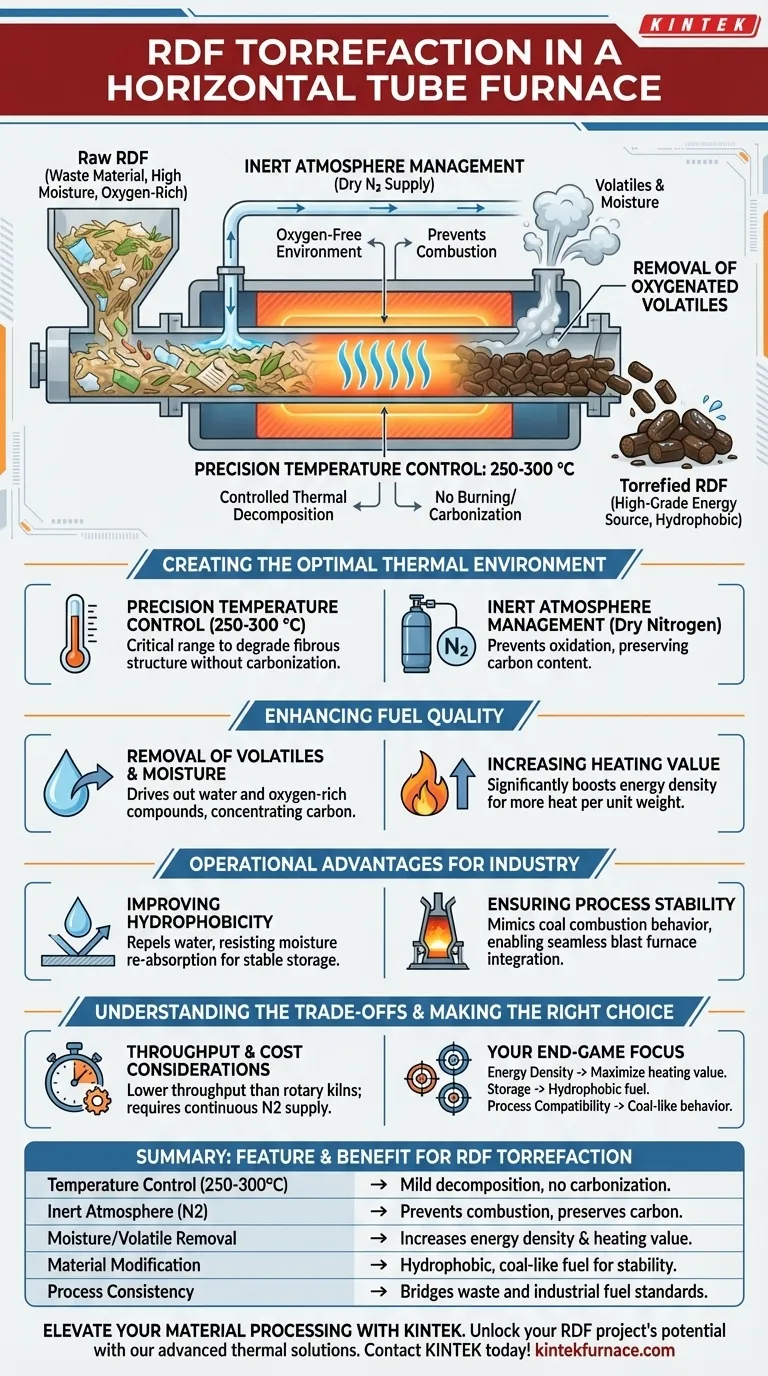
A Horizontal Tube Furnace is the ideal instrument for torrefaction because it establishes a precise, oxygen-free environment necessary to upgrade Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) into a high-grade energy source. By treating the material at temperatures between 250°C and 300°C under a dry nitrogen atmosphere, the furnace facilitates a controlled thermal decomposition that fundamentally alters the fuel's properties without burning it.
The core purpose of using a Horizontal Tube Furnace is to standardize unpredictable waste material into a stable industrial fuel. By driving off moisture and volatile oxygen, it increases energy density and hydrophobicity, allowing the RDF to mimic the combustion behavior of coal in critical applications like blast furnaces.

Creating the Optimal Thermal Environment
Precision Temperature Control
The Horizontal Tube Furnace is specifically designed to maintain a strict temperature window of 250-300 °C.
This range is critical for torrefaction. It is hot enough to degrade the fibrous structure of the waste but cool enough to prevent carbonization or complete combustion.
Inert Atmosphere Management
The equipment operates under a dry nitrogen atmosphere.
This prevents the RDF from reacting with oxygen. Instead of burning, the material undergoes mild thermal decomposition, ensuring the preservation of carbon while removing less desirable elements.
Enhancing Fuel Quality
Removal of Volatiles and Moisture
The process targets the removal of excess moisture and the decomposition of oxygenated volatiles.
Raw RDF often contains significant water and oxygen-rich compounds that dilute its energy potential. The furnace drives these out, leaving behind a more carbon-rich product.
Increasing Heating Value
By concentrating the carbon content, the furnace significantly boosts the energy density of the fuel.
The resulting material possesses a much higher heating value than raw RDF. This makes it a more potent fuel source, capable of generating more heat per unit of weight.
Operational Advantages for Industry
Improving Hydrophobicity
The thermal treatment renders the RDF hydrophobic, meaning it repels water.
Unlike raw waste, which acts like a sponge, torrefied RDF resists re-absorbing moisture from the air. This makes storage and transport significantly more stable and efficient.
Ensuring Process Stability
The treated fuel exhibits pyrolysis characteristics that are remarkably similar to traditional coal.
For industries using blast furnaces, this is the most critical benefit. It allows operators to switch from coal to RDF with minimal impact on process stability, as the fuels behave similarly during combustion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Throughput Limitations
Horizontal tube furnaces offer exceptional control, but they generally have lower throughput compared to large-scale rotary kilns.
They are often better suited for pilot-scale operations or precise batch processing rather than massive, continuous municipal waste processing.
Inert Gas Requirements
The reliance on a continuous dry nitrogen supply adds an operational cost and logistical layer.
Maintaining this atmosphere is non-negotiable; if oxygen leaks into the tube, the torrefaction process fails, potentially leading to combustion or inconsistent fuel quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating the use of a Horizontal Tube Furnace for RDF, consider your specific end-game requirements:
- If your primary focus is Energy Density: The furnace is essential for removing oxygenated volatiles to maximize the heating value per kilogram.
- If your primary focus is Storage Logistics: The treatment is necessary to create hydrophobic fuel that will not degrade or rot during long-term storage.
- If your primary focus is Process Compatibility: The controlled torrefaction is the only way to ensure the RDF behaves like coal, protecting your blast furnace operations from instability.
The Horizontal Tube Furnace effectively bridges the gap between variable waste streams and the rigorous consistency required by heavy industry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for RDF Torrefaction |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control (250-300°C) | Ensures mild thermal decomposition without carbonization. |
| Inert Atmosphere (N2) | Prevents combustion and preserves carbon content. |
| Moisture/Volatile Removal | Increases energy density and heating value. |
| Material Modification | Produces hydrophobic, coal-like fuel for stable storage. |
| Process Consistency | Bridges the gap between variable waste and industrial fuel standards. |
Elevate Your Material Processing with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) projects with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Horizontal Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your specific torrefaction needs. Whether you require precise pilot-scale control or customizable lab high-temp furnaces, our equipment ensures maximum energy density and fuel stability for your waste-to-energy applications.
Ready to optimize your fuel quality? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique requirements with our technical experts!
Visual Guide
References
- Eurig W. Jones, Peter J. Holliman. Pyrolysis-GCMS of Plastic and Paper Waste as Alternative Blast Furnace Reductants. DOI: 10.3390/chemengineering9010015
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory high-temperature tube furnace play in the phase formation of Ni-rich oxide cathode materials?
- In which fields are fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces commonly applied? Explore Key Uses in Materials Science and Energy
- How does a drop tube work? A Key Tool for Microgravity Materials Research
- What functions does a tube atmosphere furnace perform for high-entropy alloy catalysts? Essential Reduction & Control
- How is a High Temperature Tube Furnace used in material science? Unlock Precise Material Synthesis & Control
- How do heat treatment processes influence the configuration of a vertical tube furnace? Optimize for Quenching, Annealing, and More
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a three-zone furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency for Your Thermal Processes
- How does a three-zone tube furnace facilitate the synthesis of germanium nanowires? Achieve High-Quality SVG Results



















