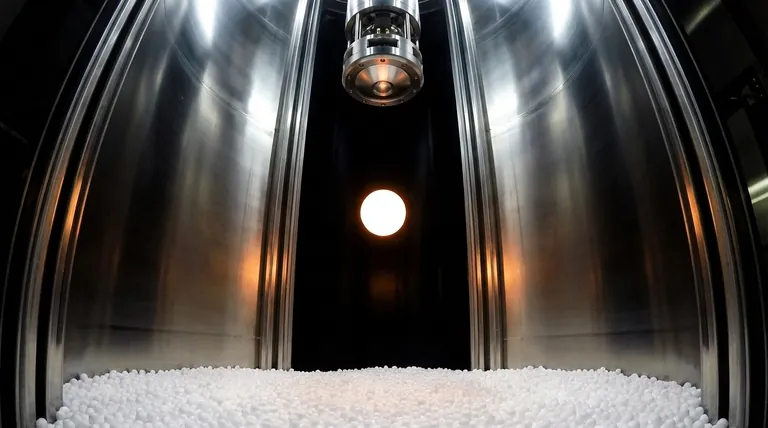
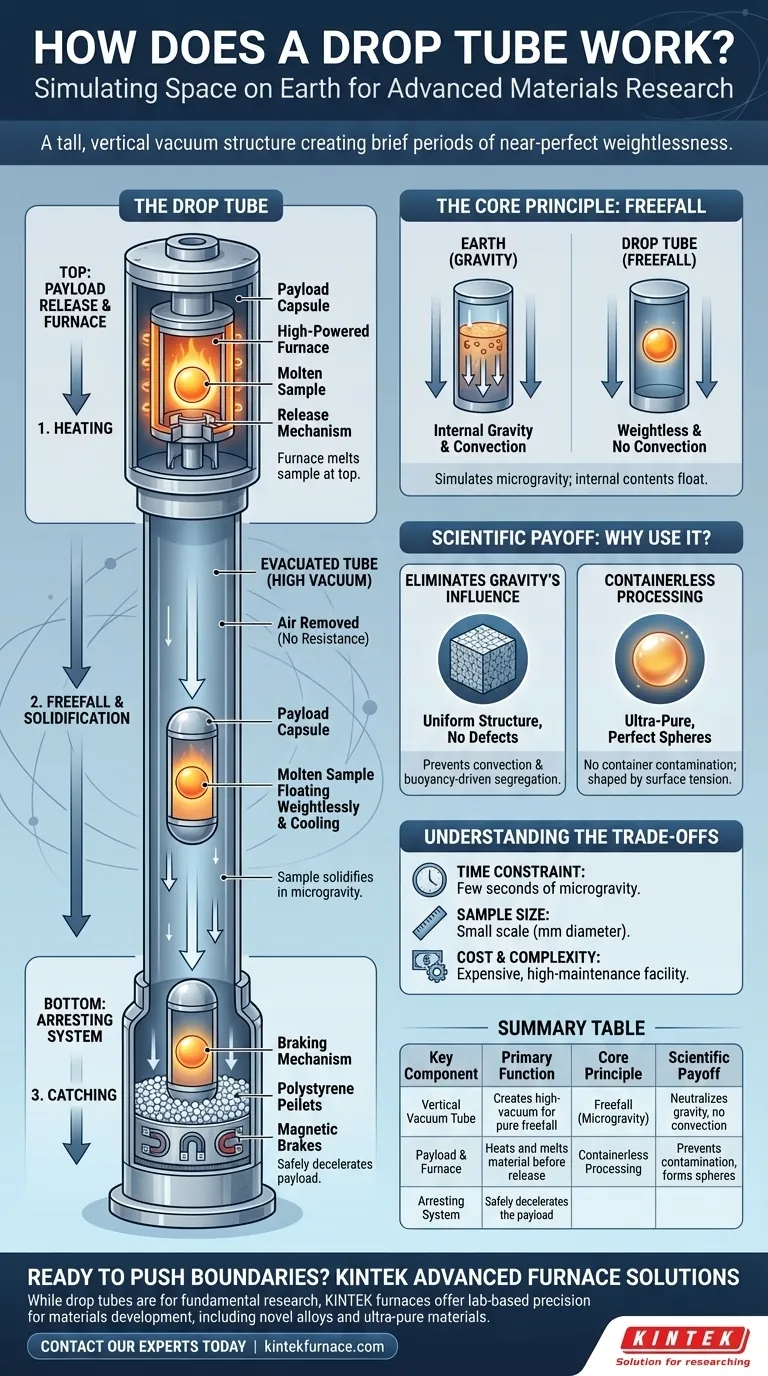
At its core, a drop tube is a tall, vertical structure designed to create a brief period of near-perfect weightlessness. By dropping an experimental package down a long, evacuated tube, scientists can simulate the microgravity environment of space for a few seconds. This allows them to study how materials behave and solidify when freed from the distorting effects of gravity.
The true purpose of a drop tube is not just to drop things, but to use the state of freefall to conduct "containerless processing." By melting a material and letting it solidify while falling, scientists can create ultra-pure, perfectly spherical samples and novel alloys that are impossible to produce on Earth's surface.

The Core Principle: Simulating Space on Earth
A drop tube's function is rooted in a fundamental principle of physics. It doesn't eliminate gravity, but rather creates a condition where its effects are temporarily neutralized for the object under study.
What is Freefall?
When an object is dropped, it accelerates due to gravity. Everything inside that object—including a molten droplet of metal—accelerates at the same rate.
From the perspective of the falling package, the internal contents are floating weightlessly. This is the same principle that allows astronauts to float inside the International Space Station as it "falls" in orbit around the Earth.
The Role of the Tube
Simply dropping an object in the open air is not enough, as air resistance would quickly interfere with the experiment.
The drop tube is a long, sealed shaft that is pumped down to a high vacuum. By removing the air, the experimental payload can fall with virtually no resistance, achieving a state of pure freefall and a high-quality microgravity environment.
Anatomy of a Drop Tube Experiment
A typical experiment involves more than just dropping a sample. It's a carefully orchestrated process designed to capture a specific physical change during the brief freefall window.
The Payload and Furnace
The object being dropped is a sophisticated capsule, often called a payload. Inside this payload is a small, high-powered furnace containing a tiny sample of material, such as a metal alloy.
The Process in Motion
First, the payload is held at the top of the tube. The furnace rapidly heats the sample until it is completely molten.
At the precise moment of full melting, a release mechanism lets the entire payload go. As it falls through the vacuum, the molten material cools and solidifies while floating weightlessly inside the capsule.
The Arresting System
At the bottom of the tube, a braking mechanism is needed to safely stop the payload, which can be traveling at hundreds of miles per hour. This "catcher" can be a deep bed of polystyrene pellets, a series of air bags, or sophisticated magnetic brakes that decelerate the capsule without damaging the experiment inside.
Why Use a Drop Tube? The Scientific Payoff
The complexity of a drop tube is justified by its ability to create materials with unique properties by removing two key constraints of ground-based processing.
Eliminating Gravity's Influence
On Earth, gravity causes convection currents and buoyancy within a molten liquid. Heavier elements sink and lighter ones rise, leading to segregation and defects when the material solidifies. In freefall, these forces vanish, allowing for a much more uniform material structure.
Enabling Containerless Processing
At high temperatures, most molten materials are extremely reactive. They can easily pick up impurities from the crucible or container holding them.
In a drop tube, the molten droplet floats freely due to weightlessness. With no container walls to touch, contamination is completely avoided. The liquid's own surface tension is the only force shaping it, naturally pulling it into a perfect sphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the drop tube method has clear limitations that define its use cases. It is a specialized tool for a specific type of research.
The Time Constraint
The most significant limitation is time. Even a very tall drop tower, hundreds of meters high, only provides a few seconds of microgravity. This is only suitable for studying rapid phenomena, like the solidification of metals, and not for longer processes like crystal growth.
Sample Size and Throughput
Drop tube experiments are, by necessity, small-scale. The samples are typically only a few millimeters in diameter. This makes the technique ideal for fundamental research but not for mass production.
Cost and Complexity
Drop tubes are major scientific facilities that are expensive to build and operate. Maintaining the high vacuum, operating the release and catch systems, and instrumenting the payload require significant resources and expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the purpose of a drop tube allows you to see its value as a precise tool for specific scientific and engineering challenges.
- If your primary focus is fundamental physics: Use the drop tube to study the properties of liquids—like viscosity and surface tension—without the complicating effects of gravity-driven convection.
- If your primary focus is materials science innovation: Employ the drop tube to create unique amorphous metals (metallic glasses) or metastable alloys that cannot be formed through conventional casting.
- If your primary focus is advanced manufacturing: Leverage this technique to produce perfectly spherical, ultra-pure powders for applications like high-performance 3D printing or precision bearings.
Ultimately, the drop tube serves as a unique bridge between Earth-based labs and the perfect microgravity of space, enabling discoveries that would otherwise be out of reach.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Vertical Vacuum Tube | Creates a high-vacuum environment to eliminate air resistance for pure freefall. |
| Payload & Furnace | Heats and melts a small material sample before release. |
| Arresting System | Safely decelerates the payload at the bottom of the tube (e.g., polystyrene pellets, magnetic brakes). |
| Core Principle | Scientific Payoff |
| Freefall (Microgravity) | Neutralizes gravity's effects, eliminating convection currents and buoyancy in molten materials. |
| Containerless Processing | Prevents contamination by allowing the molten sample to solidify without touching a container, forming perfect spheres. |
Ready to Push the Boundaries of Materials Research?
While drop tubes are powerful for fundamental research, KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions bring unparalleled precision and purity to your lab-based materials development.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you are developing novel alloys, studying solidification phenomena, or producing ultra-pure materials, our furnaces offer the precise control and contamination-free environment critical for success.
Let's discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific research goals. Contact our experts today to explore the possibilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is sulfurization treatment in a quartz tube furnace required after CZTS thin film deposition? Expert Guide
- What are the functional advantages of utilizing a high-temperature vertical tube quartz reactor for MoS2/rGO pyrolysis?
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is the significance of defining the quartz tube as a heat transfer boundary? Optimize Your Furnace Modeling
- What are the common applications of quartz tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing



















