In short, heat treatment processes directly dictate the ideal configuration of a vertical tube furnace by defining the required heating uniformity, cooling rate, and atmospheric conditions. Processes like quenching demand features that facilitate rapid cooling, such as an open-bottom design, while processes like annealing prioritize features that ensure maximum temperature uniformity, such as multi-zone heating elements.
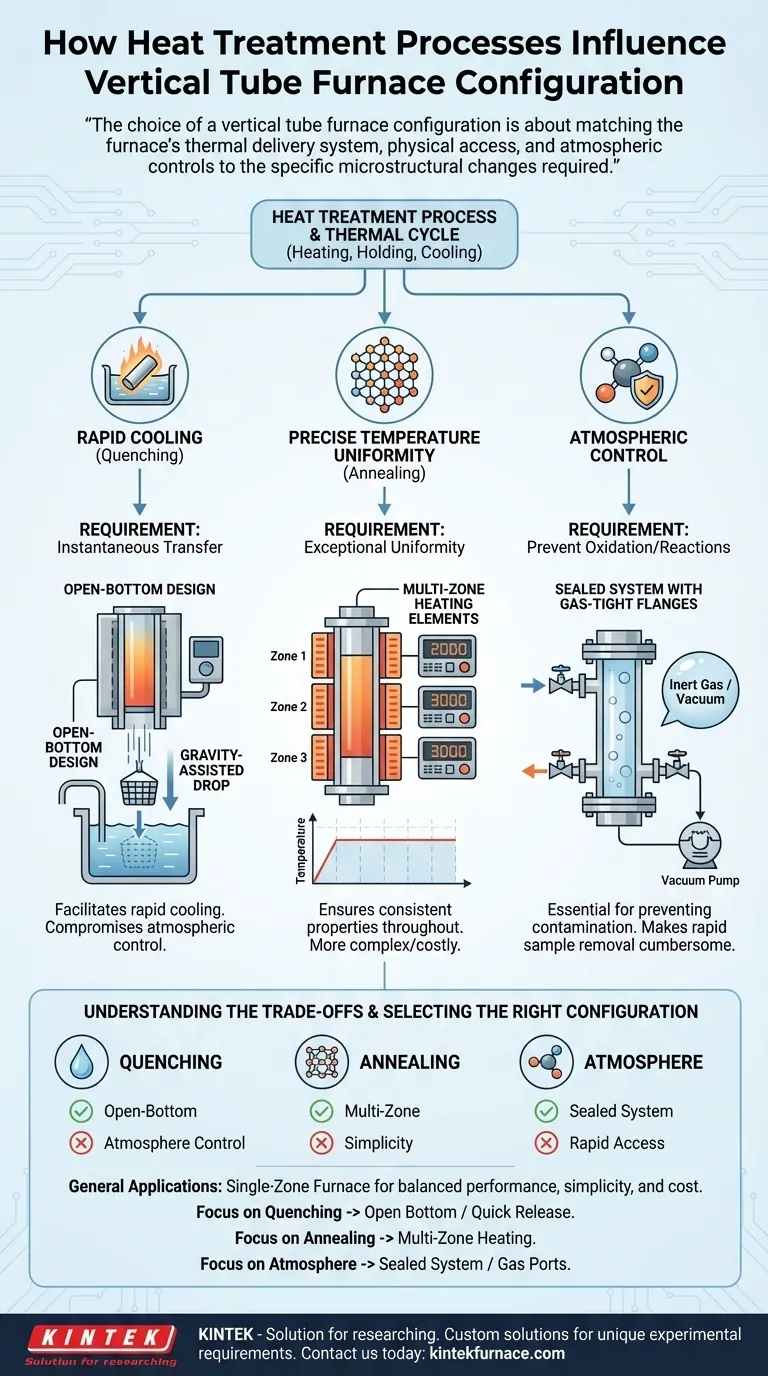
The choice of a vertical tube furnace configuration is not merely about reaching a target temperature. It is about matching the furnace’s thermal delivery system, physical access, and atmospheric controls to the specific microstructural changes required by your heat treatment process.

The Core Principle: From Process to Physical Design
The goal of any heat treatment is to alter a material's internal microstructure to achieve desired properties like hardness or ductility. This is accomplished through a precise thermal cycle: heating, holding at temperature, and cooling.
Each phase of this cycle places specific demands on the furnace, directly influencing its necessary configuration.
Process Requirement: Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
Quenching is a process that involves cooling a material with extreme rapidity to lock in a specific, non-equilibrium crystal structure, which typically increases hardness. Solution treatment follows a similar path, requiring a fast quench after holding the material at temperature.
The vertical tube furnace is uniquely suited for this. Its vertical orientation allows gravity to be used for an almost instantaneous transfer of the sample from the hot zone into a quenching medium (like water, oil, or forced air) placed directly below.
This requirement directly influences the furnace's physical access configuration. The ideal setup is an open-bottom design or one with a quick-release bottom flange, allowing the sample to drop without delay. Any hesitation in this transfer risks unintended cooling, compromising the entire process.
Process Requirement: Precise Temperature Uniformity (Annealing)
Annealing aims to soften a material, increase its ductility, and relieve internal stresses. This is achieved by heating it to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it very slowly.
The critical factor for annealing is not cooling speed but exceptional temperature uniformity. The entire sample must experience the exact same temperature for the entire holding period to ensure consistent properties throughout.
This requirement influences the heating element configuration. While a single-zone furnace (one heating element and controller) is simpler, it naturally has cooler spots at the ends of the tube. For high-precision annealing, a multi-zone furnace is superior. These use two, three, or more independent heating zones, each with its own thermocouple and controller, to create a highly uniform temperature profile along the length of the processing area.
Process Requirement: Atmospheric Control
Many heat treatments, especially at high temperatures, must be performed in a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions on the material's surface.
This need dictates the furnace's sealing and gas handling configuration. A furnace intended for these processes must be configured with gas-tight flanges, ports for introducing inert gases like argon or nitrogen, and a connection for a vacuum pump to first evacuate ambient air. The choice of furnace tube material—such as quartz versus high-purity alumina—also becomes a critical configuration detail, dictated by the maximum temperature and reactivity of the process gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a configuration is a matter of balancing performance against complexity and cost. There is no single "best" furnace; there is only the best furnace for a specific application.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone
A single-zone furnace is less expensive and simpler to operate. It is perfectly adequate for many applications, especially when the sample is small relative to the length of the furnace's "hot zone."
A multi-zone furnace, while more expensive and complex, offers unparalleled temperature uniformity. This is a non-negotiable feature for processes where even minor temperature variations across the sample are unacceptable.
Open-Bottom vs. Sealed Tube
An open-bottom design is optimized for rapid quenching but makes achieving a high-purity vacuum or controlled atmosphere more challenging.
A fully sealed system with high-quality flanges provides excellent atmospheric control but can make the rapid removal of a sample for quenching more cumbersome. Some designs attempt to bridge this gap, but a trade-off almost always exists.
Heating Method
Most common vertical tube furnaces use resistive heating elements wrapped around the ceramic tube. This method provides excellent stability and control.
Other methods, like induction heating, use electromagnetic fields to heat a conductive crucible inside the tube. This can achieve very high temperatures and rapid heating rates but is a more specialized and often more expensive configuration.
Selecting the Right Configuration for Your Process
Your decision should be driven entirely by the metallurgical outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is hardening via quenching: Prioritize a furnace configuration with an open bottom or a quick-release mechanism for gravity-assisted sample dropping.
- If your primary focus is high-precision annealing or sintering: Prioritize a multi-zone heating configuration to guarantee the best possible temperature uniformity over the entire sample length.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface oxidation: Prioritize a furnace with vacuum-tight seals, appropriate gas handling ports, and a tube material compatible with your atmosphere and temperature.
By aligning the furnace's configuration with the specific thermal demands of your process, you move from simply heating a material to precisely engineering its final properties.
Summary Table:
| Heat Treatment Process | Key Requirements | Ideal Furnace Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Quenching / Solution Treatment | Rapid cooling | Open-bottom design for gravity-assisted sample drop |
| Annealing | High temperature uniformity | Multi-zone heating elements |
| Processes with Atmospheric Control | Controlled gas environment | Sealed system with gas-tight flanges and vacuum pump |
| General Applications | Balanced performance | Single-zone furnace for simplicity and cost-effectiveness |
Ready to configure the perfect vertical tube furnace for your heat treatment needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace precisely meets unique experimental requirements for quenching, annealing, or atmospheric control. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















