Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite (CFRC) plates function as a strategic thermal barrier. They are inserted between the water-cooled electrodes and the graphite spacers in Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) devices to effectively block heat from escaping. By leveraging their anisotropic thermal properties, these plates minimize heat loss to the cooling system, ensuring a stable and uniform temperature profile within the sample.
Core Takeaway In SPS configurations, the cooling effect of the electrodes can create severe temperature disparities within the sample. CFRC plates mitigate this by utilizing anisotropic thermal conductivity to insulate the processing zone, significantly reducing axial temperature gradients and ensuring high-quality sintering for large-scale components.
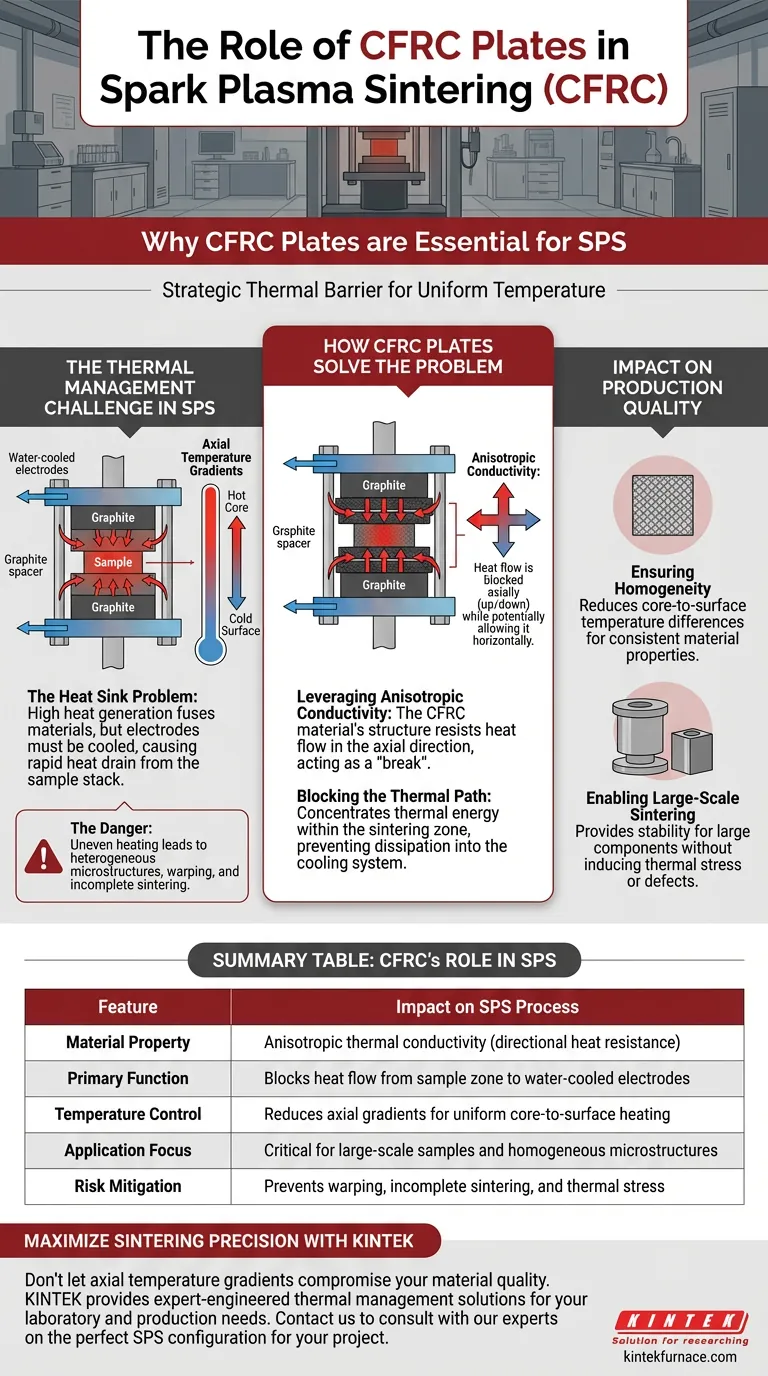
The Thermal Management Challenge in SPS
The Heat Sink Problem
Spark Plasma Sintering generates high heat to fuse materials, but the system's electrodes are water-cooled to prevent damage to the equipment.
This creates a conflict: the sample needs to stay hot, but the electrodes must stay cool. Without intervention, heat rapidly drains from the sample stack into the cooled electrodes.
The Danger of Axial Gradients
When heat flows vertically out of the sample toward the electrodes, it creates axial temperature gradients.
This means the center of your sample may be significantly hotter than the top and bottom surfaces. In material science, such uneven heating leads to heterogeneous microstructures, warping, or incomplete sintering.
How CFRC Plates Solve the Problem
Leveraging Anisotropic Conductivity
The primary reference highlights that CFRC plates utilize anisotropic thermal conductivity.
"Anisotropic" means the material conducts heat differently depending on the direction. In this application, the plates are oriented to resist heat flow in the axial direction (up and down) while potentially allowing it elsewhere.
Blocking the Thermal Path
By inserting these plates between the graphite spacers and the electrodes, you effectively sever the direct thermal path to the cooling system.
The CFRC acts as a "break," keeping the thermal energy concentrated within the sintering zone where it is needed, rather than allowing it to dissipate into the machine's cooling infrastructure.
Impact on Production Quality
Ensuring Homogeneity
The primary function of the CFRC layer is to reduce the temperature difference between the core of the sample and its surfaces.
By insulating the stack, the temperature distribution becomes more uniform. This leads to consistent material properties throughout the final product, which is critical for high-performance applications.
Enabling Large-Scale Sintering
The reference specifically notes the importance of these plates for large-sized samples.
As sample size increases, maintaining temperature uniformity becomes exponentially more difficult. CFRC plates provide the necessary stability to sinter large components without inducing thermal stress or defects caused by uneven cooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Orientation is Critical
Because the material is anisotropic, its performance depends entirely on correct orientation.
If the plates are installed incorrectly regarding their fiber alignment, they may fail to block heat flow or, conversely, impede the necessary electrical current required for the SPS process.
Complexity vs. Quality
Adding CFRC plates increases the complexity of the stacking assembly.
However, this added step is a necessary trade-off to avoid the much costlier issue of scrapped parts due to thermal gradients, particularly when working with expensive raw materials or large geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
To maximize the effectiveness of your SPS setup, consider your specific processing goals:
- If your primary focus is Sample Homogeneity: You must use CFRC plates to minimize axial temperature gradients, ensuring the microstructure at the surface matches the core.
- If your primary focus is Large-Scale Production: These plates are mandatory to maintain thermal stability across the increased volume of material, preventing warping and defects.
By controlling the thermal path with CFRC insulation, you transform the electrodes from a source of thermal instability into a manageable variable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on SPS Process |
|---|---|
| Material Property | Anisotropic thermal conductivity (directional heat resistance) |
| Primary Function | Blocks heat flow from sample zone to water-cooled electrodes |
| Temperature Control | Reduces axial gradients for uniform core-to-surface heating |
| Application Focus | Critical for large-scale samples and homogeneous microstructures |
| Risk Mitigation | Prevents warping, incomplete sintering, and thermal stress |
Maximize Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Don't let axial temperature gradients compromise your material quality. KINTEK provides expert-engineered thermal management solutions for your laboratory and production needs.
Backed by industry-leading R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized high-temperature lab furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique sintering requirements.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency? Contact us today to consult with our experts on the perfect SPS configuration for your project.
Visual Guide
References
- Alexander M. Laptev, Olivier Guillon. Tooling in Spark Plasma Sintering Technology: Design, Optimization, and Application. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202301391
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Ultra High Vacuum CF Flange Stainless Steel Sapphire Glass Observation Sight Window
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the impact of grain structure on material properties in hot pressing vs. cold compacting and sintering? Optimize Your Powder Metallurgy Process
- What role does a high-strength graphite mold play in the hot pressing and sintering of Ag-Ti2SnC? Boost Densification
- How does the vacuum system in these furnaces work? Achieve Purity and Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- What is the maximum working temperature of a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temp Processing
- What role do graphite molds play in ZnS vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Densification and Optical Purity
- What distinguishes a vacuum hot press furnace from simpler vacuum press systems? Unlock Advanced Material Densification
- What are the core functions of graphite molds in the hot press sintering process of Nb-22.5Cr-5Si alloys? Find Out Now
- What core role does a vacuum hot press furnace play in Fe-Cu-Ni-Sn-VN? Mastering Nanostructured Composite Production



















