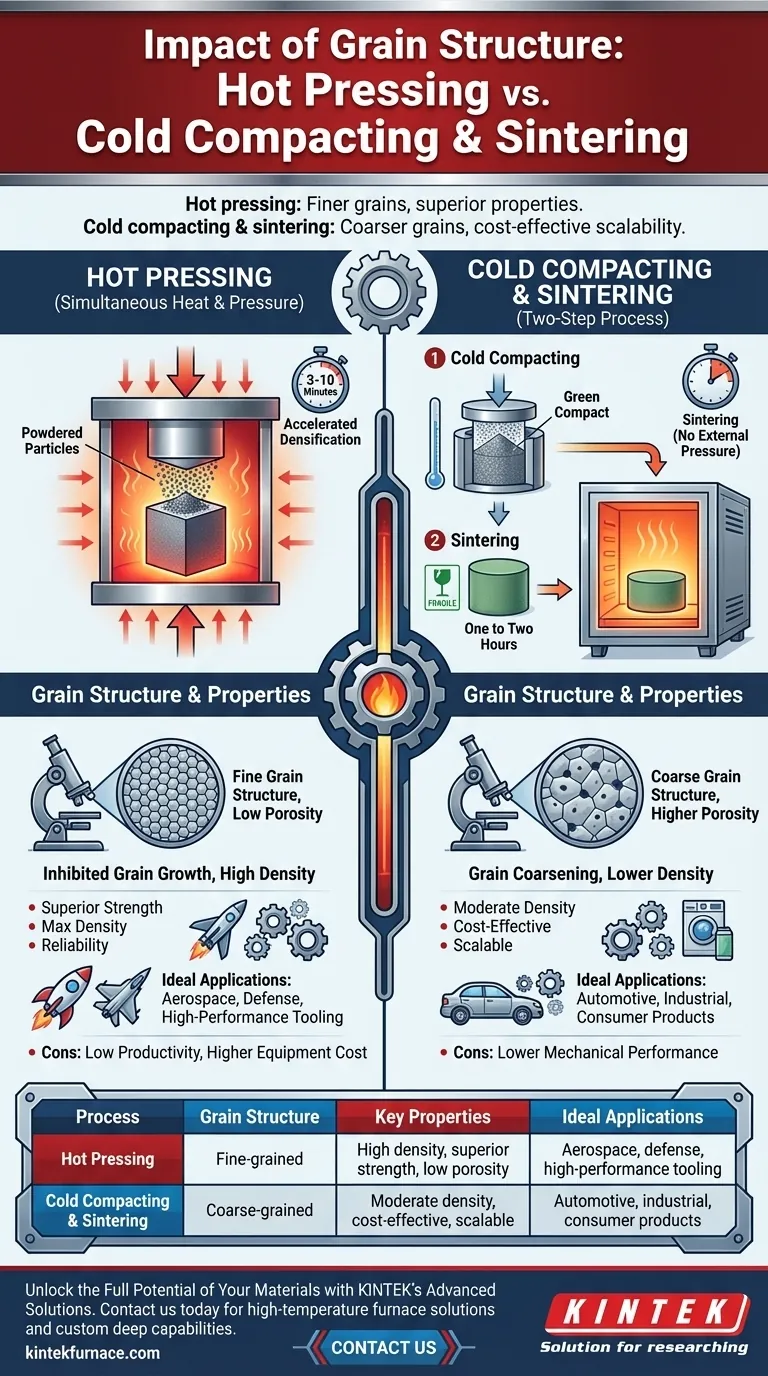
In short, hot pressing generally produces materials with a finer grain structure and superior mechanical properties, while cold compacting followed by sintering often results in a coarser grain structure and potentially lower performance. The core difference lies in how each process applies heat and pressure, which directly dictates the final density and microstructure of the component.
The choice between these two powder metallurgy techniques is fundamentally a trade-off. Hot pressing optimizes for material performance, achieving high density and strength, whereas cold compacting and sintering prioritize manufacturing scalability and cost-effectiveness.

The Fundamental Difference: Process Mechanics
To understand the impact on grain structure, you must first understand how each process works. The timing and application of heat and pressure are the critical variables.
Hot Pressing: Simultaneous Heat and Pressure
In hot pressing, powdered material is heated and pressed at the same time within a single die. This is considered an activated sintering process.
The external pressure significantly accelerates densification—the process of reducing porosity and bonding particles together. This allows the process to be completed at lower temperatures or for much shorter times (3-10 minutes) compared to conventional sintering.
Cold Compacting & Sintering: A Two-Step Journey
This is a sequential process. First, powder is compressed into a desired shape at room temperature, creating a fragile "green" compact.
Second, this green compact is heated in a furnace in a separate step called sintering. During sintering, which can take one to two hours, the particles bond and the part densifies without external pressure.
How Process Dictates Microstructure and Properties
The differences in process mechanics have a direct and predictable impact on the final grain size and density of the material, which in turn control its mechanical performance.
Hot Pressing: Inhibited Grain Growth and High Density
The simultaneous application of pressure in hot pressing provides a strong driving force for densification. This efficiency means the material spends less time at high temperatures.
This kinetic limitation inhibits grain growth, resulting in a finer grain structure. Combined with the elimination of voids, hot pressing produces materials with very low porosity and near-theoretical density, leading to excellent mechanical strength and durability.
Cold Sintering: The Risk of Grain Coarsening
Without external pressure, sintering relies solely on high temperatures and longer times to densify the material. This extended exposure to heat provides ample energy and opportunity for grains to grow larger.
This process, known as grain coarsening, leads to a coarser grain structure. While still effective, this method often results in higher residual porosity compared to hot pressing, which can negatively affect mechanical properties like strength and fracture toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Performance vs. Cost
Neither method is universally superior; they serve different strategic goals. The decision hinges on balancing the required material properties against production realities.
The Case for Hot Pressing: Maximum Performance
Hot pressing is the ideal choice when the absolute highest material performance is non-negotiable. It consistently delivers components with a fine-grained microstructure and maximum density.
This makes it perfect for demanding applications in aerospace, defense, and high-performance tooling where strength, hardness, and reliability are paramount.
The Case for Cold Compacting: Scalability and Economy
Cold compacting and sintering is the workhorse of high-volume powder metallurgy. The process is simpler, more automated, and significantly more cost-effective for large-scale production.
While it may not achieve the peak density or fine grain structure of hot pressing, it offers excellent properties for a vast range of automotive, industrial, and consumer product applications where cost is a major driver.
Key Disadvantages to Consider
Hot pressing suffers from low productivity due to its batch-style nature and the need for simultaneous heating and pressing. The equipment is also more complex and expensive, leading to higher overall costs.
The primary disadvantage of cold sintering is the potential for lower mechanical performance due to coarser grains and higher porosity, making it unsuitable for the most mission-critical components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific technical and commercial requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Choose hot pressing to achieve the finest grain structure and lowest porosity possible.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Choose cold compacting and sintering for its scalability and economic advantages.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex geometries: Cold compacting often provides more flexibility and is more cost-effective for intricate shapes that are difficult to produce in a hot press die.
Understanding the relationship between processing, microstructure, and properties empowers you to select the manufacturing path that aligns perfectly with your engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Process | Grain Structure | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Pressing | Fine-grained | High density, superior strength, low porosity | Aerospace, defense, high-performance tooling |
| Cold Compacting & Sintering | Coarse-grained | Moderate density, cost-effective, scalable | Automotive, industrial, consumer products |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Materials with KINTEK's Advanced Solutions
Struggling to choose between hot pressing and cold compacting for your powder metallurgy needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need fine-grained microstructures for maximum performance or cost-effective scalability, we have the expertise and equipment to help you achieve superior results.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your material properties and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing



















