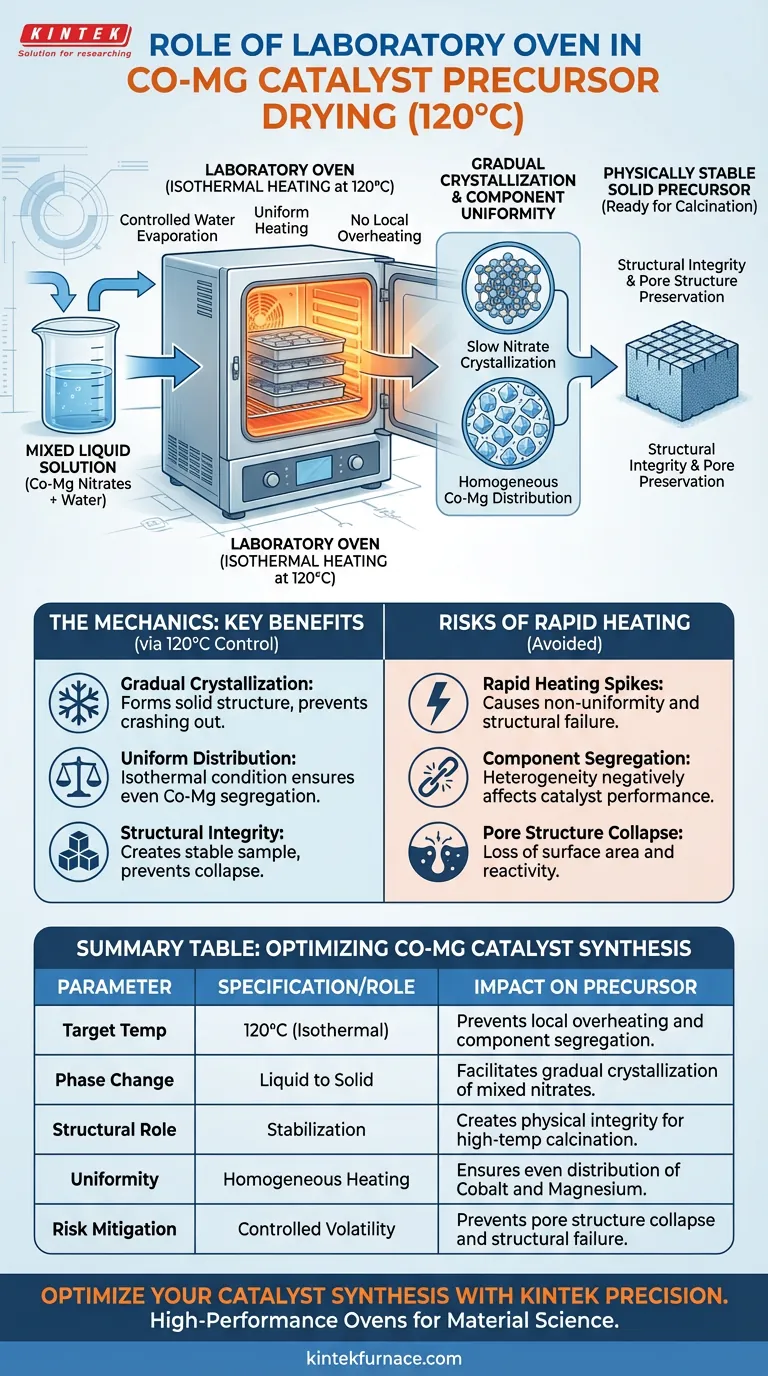
In the synthesis of Cobalt-Magnesium (Co–Mg) catalyst precursors, a laboratory oven serves as a critical instrument for controlled isothermal heating at exactly 120°C. Its primary function is to systematically remove free water from the mixed solution, which forces the mixed nitrates to concentrate and crystallize gradually rather than precipitously.
Core Takeaway The laboratory oven acts as a stabilization chamber that converts a liquid mixture into a solid precursor. By strictly maintaining 120°C, it prevents local overheating and ensures a uniform distribution of components, creating the necessary physical stability for the subsequent high-temperature calcination phase.
The Mechanics of Controlled Drying
Facilitating Gradual Crystallization
The drying phase is not simply about dehydration; it is a phase-change process. The laboratory oven provides a steady 120°C environment to evaporate free water from the mixed solution.
This controlled evaporation allows the mixed nitrates within the solution to concentrate slowly. As the water leaves, the nitrates crystallize gradually, forming a solid structure rather than crashing out of solution randomly.
Ensuring Uniform Component Distribution
A critical challenge in catalyst preparation is maintaining the mixture's homogeneity. The oven's ability to provide isothermal heating is the solution to this problem.
By keeping the temperature constant throughout the chamber, the oven prevents "local overheating." If hot spots were to occur, certain parts of the mixture would dry faster than others, leading to uneven segregation of the Cobalt and Magnesium components.
Establishing Structural Integrity
Creating a Physically Stable Sample
The ultimate output of the oven drying phase is a solid sample. This solid must be physically stable to withstand the rigors of the next step in the process: high-temperature calcination.
If the precursor remains too wet or is dried unevenly, it may lack the structural fortitude required for calcination. The oven ensures the material is fully prepped, acting as the bridge between the liquid solution and the final active catalyst.
Preventing Structural Collapse
While the primary focus for Co-Mg precursors is nitrate crystallization, the principles of controlled drying also protect the material's pore structure. Rapid temperature spikes can cause the "gel network" or pore structure to collapse.
By adhering to a steady 120°C, the oven allows for the slow removal of volatiles. This preserves the internal architecture of the precursor, which is vital for the catalyst's final surface area and reactivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Rapid Heating
It is tempting to increase temperatures to speed up production. However, deviating from the controlled 120°C protocol introduces significant risks.
Rapid heating or temperature fluctuations can lead to non-uniform component distribution. Once the components segregate during the drying phase, this heterogeneity is permanent and will negatively affect the catalyst's performance.
Isothermal vs. Vacuum Drying
While some precursors (as noted in supplementary contexts) benefit from vacuum drying at lower temperatures (e.g., 50–90°C) to prevent oxidation, Co-Mg precursors specifically require the thermal energy of 120°C.
Using a vacuum method at lower temperatures might not effectively crystallize the mixed nitrates in the specific manner required for this catalyst type. The specific 120°C isothermal condition is tuned to the chemistry of the nitrates involved.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Co-Mg catalyst precursors, ensure your drying equipment aligns with the specific chemical needs of the substrate.
- If your primary focus is component uniformity: Ensure your oven has verified isothermal capabilities to prevent local overheating and component segregation.
- If your primary focus is physical stability: Adhere strictly to the 120°C protocol to allow for gradual crystallization, establishing a robust foundation for calcination.
Controlled drying is not a passive waiting period; it is the active engineering of the catalyst's internal structure.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification/Role | Impact on Catalyst Precursor |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temp | 120°C (Isothermal) | Prevents local overheating and component segregation. |
| Phase Change | Liquid to Solid | Facilitates gradual crystallization of mixed nitrates. |
| Structural Role | Stabilization | Creates physical integrity for high-temp calcination. |
| Uniformity | Homogeneous Heating | Ensures even distribution of Cobalt and Magnesium. |
| Risk Mitigation | Controlled Volatility | Prevents pore structure collapse and structural failure. |
Optimize Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't let uneven drying compromise your research outcomes. At KINTEK, we understand that catalyst performance starts with thermal precision. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance laboratory ovens and specialized high-temp systems designed for the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our equipment offers the isothermal stability required to prevent component segregation and ensure structural integrity. Every unit is fully customizable to meet your unique chemical protocols.
Ready to elevate your lab's efficiency and precision?
Visual Guide
References
- Magira Zhylkybek, Yermek Aubakirov. Cobalt–Magnesium Oxide Catalysts for Deep Oxidation of Hydrocarbons. DOI: 10.3390/catal14020136
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a continuous annealing furnace? Optimize Silicon Steel Normalization & Performance
- Why is a silicone oil bath preferred for T5 aging of HPDC magnesium alloys? Precision Heat for Peak Strength
- What is the function of a forced air drying oven for biochar? Optimize Moringa Oleifera Shell Pre-treatment
- How does oxygen flow at 2 to 8 SLPM regulate PS-PVD coating quality? Master Thermal Barrier Integrity
- What conditions are required for grafting norbornene functional groups onto S-glass fiber surfaces? Expert Protocol
- What is the significance of pre-equilibrating samples in silicate studies? Maximize Experimental Efficiency
- Why is a mixture of Argon (Ar) and Hydrogen (H2) required during beryl heat treatment? Master Color Transformation
- What is the objective of setting temperature gradients of 40 °C, 50 °C, and 60 °C? Optimize Yogurt Drying Viability



















