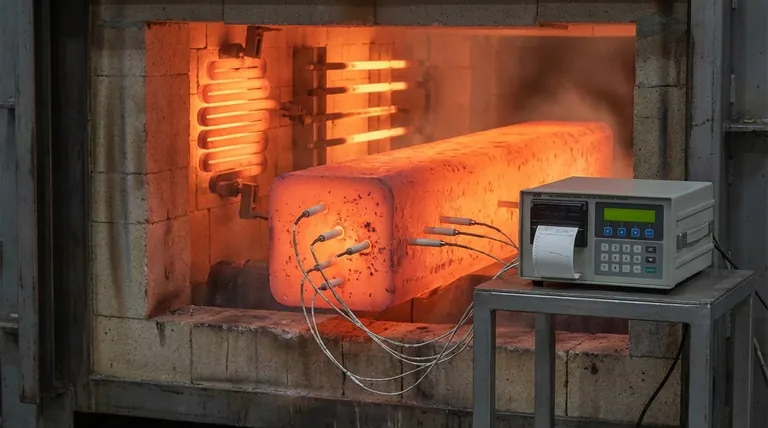
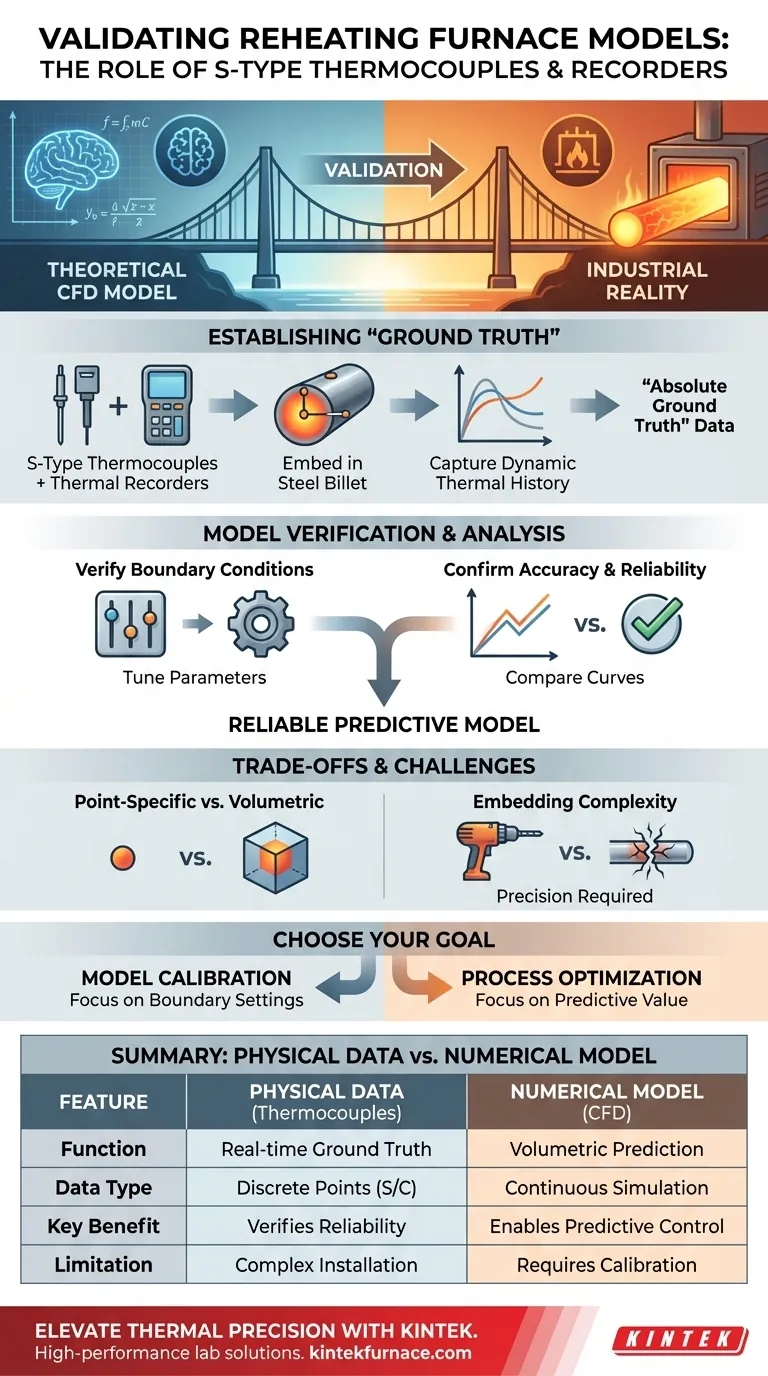
The primary purpose of utilizing embedded S-type thermocouples paired with high-temperature resistant thermal recorders is to capture precise, real-time thermal profiles of steel billets as they traverse furnace heating zones. This physical data serves as the absolute ground truth against which Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) models are benchmarked, allowing engineers to rigorously verify the simulation's reliability, accuracy, and the correctness of its physical boundary conditions.
Validation is the bridge between theoretical mathematics and industrial reality. By strictly comparing measured surface and center temperatures against simulated results, you confirm that your numerical model possesses the predictive value necessary for actual process control.

Establishing the "Ground Truth" in Reheating Furnaces
To validate a complex numerical model, you must first obtain indisputable physical data from the environment the model attempts to simulate.
Capturing the Thermal History
The combination of S-type thermocouples and thermal recorders allows for the continuous measurement of temperature as the steel moves.
This is not a static measurement; it captures the dynamic heating curve of the material as it passes through various heating zones.
Differentiating Surface and Center
A robust model must accurately predict the temperature gradient within the steel, not just the skin temperature.
By embedding sensors to measure both surface and center temperatures, engineers can validate the model’s ability to calculate internal heat conduction, which is critical for ensuring the billet is heated uniformly.
The Mechanics of Model Verification
Collecting the data is only the first step; the core purpose is the comparative analysis that follows.
Verifying Boundary Conditions
Numerical models rely on input parameters known as boundary conditions (e.g., heat transfer coefficients or radiation emissivity).
If the measured data deviates from the simulation, it often indicates that these boundary settings are incorrect. The physical data allows you to tune these parameters until the digital twin matches reality.
Confirming Simulation Accuracy
CFD simulations involve complex fluid dynamics and combustion physics.
Comparing the experimental data with the simulation results provides a quantitative metric of reliability. Only when the curves align can the model be trusted to predict outcomes for scenarios that have not yet been physically tested.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While this validation method is the industry standard, it is essential to recognize the inherent challenges in the process.
Point-Specific Data vs. Volumetric Modeling
Thermocouples provide data at discrete points (the specific location of the sensor tip).
A potential pitfall is assuming this point represents the entire region. The CFD model offers a volumetric view, but it is only validated at the specific coordinates where the physical sensors were placed.
The Complexity of Embedding
Accurately embedding S-type thermocouples into solid steel requires precision.
If the contact between the sensor and the steel is poor, the "ground truth" data will be flawed. This can lead to the erroneous adjustment of a correct model to match incorrect physical data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ultimate goal of this validation is to transition from experimental observation to predictive control.
- If your primary focus is Model Calibration: Prioritize the adjustment of boundary condition settings until your simulation's heating curves perfectly overlay the measured thermocouple data.
- If your primary focus is Process Optimization: Use the now-verified model to simulate new heating strategies, confident that the predictive value of the simulation reflects the actual physics of your furnace.
The value of a numerical model is determined entirely by its fidelity to the physical world; S-type thermocouples provide the proof required to trust that fidelity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Data (Thermocouples) | Numerical Model (CFD) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides real-time thermal ground truth | Predicts volumetric heat distribution |
| Data Type | Discrete point measurement (Surface/Center) | Continuous fluid & thermal simulation |
| Key Benefit | Verifies boundary conditions & reliability | Enables predictive process control |
| Accuracy | High precision S-type sensor readings | Dependent on physical validation |
| Limitation | Complex installation & point-specific | Requires calibration to match reality |
Elevate Your Thermal Precision with KINTEK
Transition from theoretical models to industrial excellence. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance laboratory solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are validating complex CFD simulations or optimizing heat treatment cycles, our customizable high-temperature furnaces are designed to meet your unique research and production needs.
Ready to bridge the gap between simulation and reality? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect thermal solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Minsheng Zhao, Xianzhong Hu. Study on Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Reheating Furnaces Under Oxygen-Enriched Conditions. DOI: 10.3390/pr13082454
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does graphite behave under high temperatures compared to other materials? Discover Its Unique Strengths
- What is thermal shock resistance, and why is it important? Ensure Material Durability in Extreme Temperatures
- What are the primary advantages of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements? Unmatched High-Temp Performance & Lifespan
- What critical information does a high-speed pyrometer provide during reactive film evaluation? Optimize Thermal Dynamics
- What are ceramic heating elements and what are their key characteristics? Discover High-Performance Heating Solutions
- What are the ideal applications for MoSi2 heating elements? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Performance
- How do MoSi2 heating elements resist oxidation? Unlock the Secret to High-Temperature Durability
- What are the common materials used for heating elements in industrial furnaces? Optimize Your Furnace Performance



















