At their core, ceramic heating elements are advanced components that convert electrical energy into heat using a specialized ceramic material as the resistive conductor. They are prized for their ability to achieve high temperatures quickly, transfer heat with exceptional uniformity, and operate reliably in demanding conditions where traditional metallic elements might falter.
The true value of ceramic heating elements isn't just their ability to get hot, but their capacity to deliver precise, stable, and inherently safe heat. This makes them the definitive choice for applications where performance, efficiency, and long-term reliability are non-negotiable.

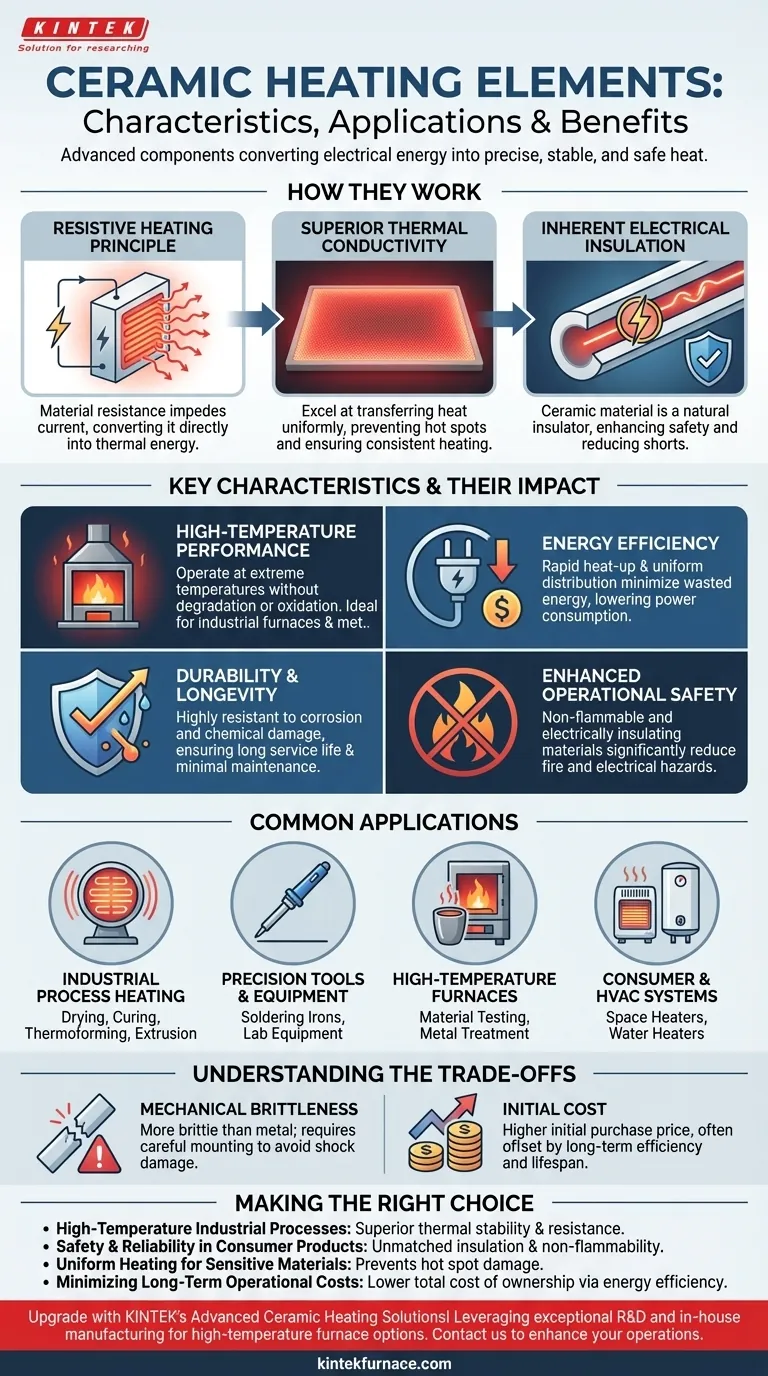
How Ceramic Heaters Generate Heat
The operation of a ceramic heater is based on a simple principle executed with an advanced material, offering distinct advantages over older technologies.
The Principle of Resistive Heating
When electricity flows through the ceramic material, the material's natural resistance impedes the current. This opposition forces the electrical energy to convert directly into thermal energy, or heat.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Once heated, the ceramic excels at transferring thermal energy uniformly across its entire surface. This prevents "hot spots" and ensures that the target object or space receives consistent, even heating.
Inherent Electrical Insulation
A key differentiator is that the ceramic material itself is an excellent electrical insulator. This means the heating element is intrinsically safe, significantly reducing the risk of electrical shorts or hazards common with metal-sheathed elements that rely on separate insulation layers.
Key Characteristics and Their Impact
The material properties of ceramics translate directly into tangible performance benefits across a wide range of uses.
High-Temperature Performance
Ceramic elements can operate at extremely high temperatures without degrading, oxidizing, or losing structural integrity. This makes them essential for industrial furnaces, metallurgy, and high-performance soldering equipment.
Energy Efficiency
Due to their rapid heat-up times and uniform heat distribution, ceramic heaters waste very little energy. Heat is generated and delivered precisely where it is needed, leading to lower overall power consumption.
Durability and Longevity
Ceramics are highly resistant to corrosion and chemical damage. This quality is critical for applications like water heaters or industrial processes involving corrosive substances, resulting in a longer service life and minimal maintenance.
Enhanced Operational Safety
Beyond their insulating properties, ceramic materials are non-flammable. This characteristic dramatically reduces the risk of fire and thermal runaway incidents, making them a fundamentally safer choice for both industrial and household products.
Common Applications
The unique combination of features makes ceramic heaters the preferred solution in many critical applications.
Industrial Process Heating
Ceramic infrared emitters are used for drying, curing, and thermoforming processes. Band and cartridge heaters are vital in plastic extrusion and packaging machinery where controlled, direct-contact heat is required.
Precision Tools and Equipment
The ability to maintain a precise and stable temperature makes ceramic elements ideal for soldering irons and scientific laboratory equipment.
High-Temperature Furnaces
In material testing and metal treatment, high-temperature furnaces rely on ceramic elements to reach and hold extreme temperatures reliably for extended periods.
Consumer and HVAC Systems
Ceramic heaters are found in portable space heaters, providing safe and fast warmth. Their corrosion resistance also makes them a durable option for modern water heaters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, it's important to understand the specific considerations for using ceramic technology.
Mechanical Brittleness
Compared to ductile metals, ceramic is a brittle material. The elements must be designed and mounted to protect them from significant mechanical shock or vibration, which could cause them to crack.
Initial Cost
The manufacturing process for advanced ceramic components can be more complex than for simple metallic wire heaters. This can sometimes lead to a higher initial purchase price, though it is often offset by a longer lifespan and greater energy efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processes: Ceramic heaters are the superior choice for their thermal stability and resistance to degradation.
- If your primary focus is safety and reliability in consumer products: The inherent electrical insulation and non-flammable nature of ceramics provide an unmatched level of safety.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating for sensitive materials: The even heat distribution of ceramic elements prevents damage from hot spots and ensures consistent quality.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: The energy efficiency and low maintenance needs of ceramic heaters deliver a lower total cost of ownership over their extended service life.
Ultimately, choosing a ceramic heating element is an investment in precision, safety, and long-term performance.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Impact |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Performance | Essential for industrial furnaces and metallurgy without degradation |
| Energy Efficiency | Rapid heat-up and uniform distribution reduce power consumption |
| Durability and Longevity | Resistant to corrosion, leading to longer service life |
| Enhanced Operational Safety | Inherent electrical insulation and non-flammable properties minimize hazards |
Upgrade your heating systems with KINTEK's advanced ceramic heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















