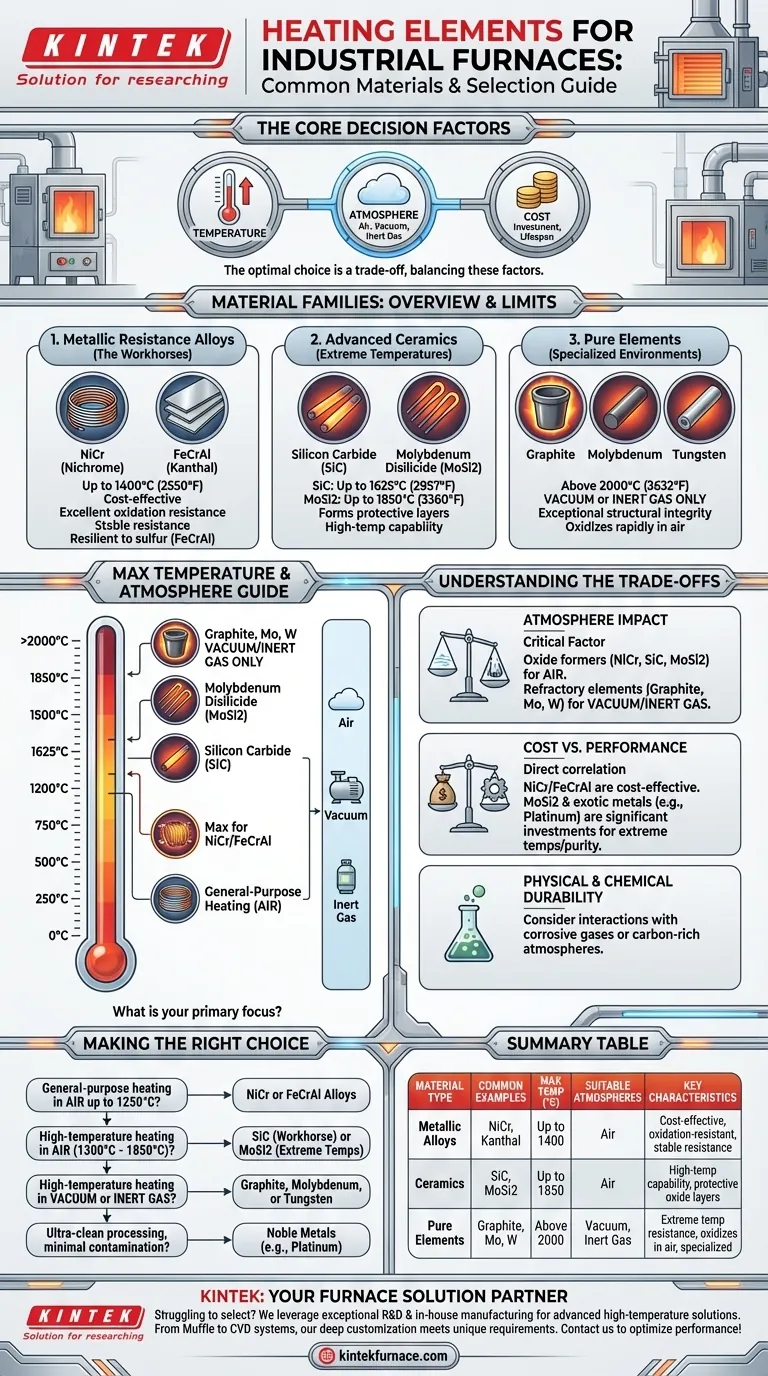
At its core, the selection of a heating element material for an industrial furnace is a precise engineering choice driven by three factors: temperature, atmosphere, and cost. The most common materials fall into three distinct families: metallic resistance alloys like Nichrome (NiCr) and Kanthal (FeCrAl), advanced ceramics like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), and pure elements like Graphite, Molybdenum, and Tungsten for specialized environments.
The "best" material does not exist. Instead, the optimal choice is always a trade-off, balancing the required operating temperature and furnace atmosphere against the material's cost, lifespan, and chemical stability.
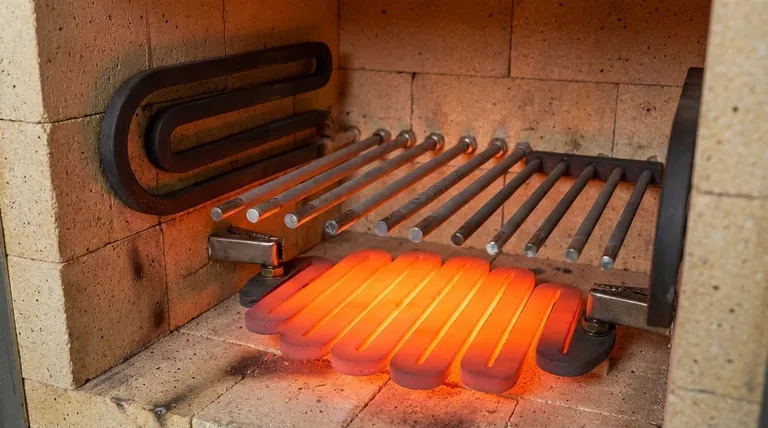

The Foundation: Metallic Resistance Alloys
These alloys are the workhorses for a vast range of industrial heating applications, especially in furnaces operating in normal air atmospheres up to around 1400°C (2550°F).
Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) Alloys
Often known by the trade name Nichrome, this alloy (typically 80% nickel, 20% chromium) is arguably the most common heating element material.
Its popularity stems from a superb combination of properties: a high melting point, excellent resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, and relatively stable electrical resistance as it heats up.
Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alloys
Commonly sold as Kanthal, this family of alloys serves a similar role to NiCr but can often reach slightly higher operating temperatures.
FeCrAl alloys form a very stable and protective aluminum oxide layer. This makes them particularly resilient in sulfur-containing atmospheres where nickel-based elements might struggle. However, they can become more brittle with age compared to NiCr.
For Extreme Temperatures: Non-Metallic Elements
When process temperatures need to exceed the limits of metallic alloys, engineers turn to robust ceramic or carbon-based materials.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide is a highly versatile ceramic material used for elements in furnaces operating up to 1625°C (2957°F).
SiC elements are self-supporting, mechanically strong, and can be used in a variety of furnace atmospheres, offering a great balance of performance and cost for high-temperature applications.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
For the highest temperatures in air, Molybdenum Disilicide is the premier choice, capable of operating reliably up to 1850°C (3360°F).
When heated, MoSi2 forms a protective, glass-like layer of silica on its surface that prevents further oxidation, allowing it to survive extreme heat.
Graphite
Graphite is the go-to material for many very high-temperature processes, but with a critical caveat: it must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere.
In the absence of oxygen, graphite has exceptional structural integrity at temperatures well above 2000°C (3632°F). If exposed to air at these temperatures, it will rapidly oxidize and fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element is never about a single specification. You must consider how the material interacts with its entire operational environment.
The Impact of Atmosphere
This is the most critical factor after temperature. Materials like NiCr, FeCrAl, SiC, and MoSi2 are designed to form protective oxide layers, making them perfect for use in air.
Conversely, materials like Graphite, Molybdenum, and Tungsten are known as refractory elements. They have extremely high melting points but will oxidize and fail catastrophically in air at high temperatures. They are reserved exclusively for vacuum or inert-gas furnaces.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost. NiCr and FeCrAl alloys are cost-effective solutions for the most common heat-treating ranges.
Materials like MoSi2 and exotic metals like Platinum (used in specialized lab furnaces for its purity and stability) represent a significant investment, justified only when extreme temperatures or process purity are non-negotiable.
Physical and Chemical Durability
Consider the chemical nature of your process. Will the elements be exposed to corrosive gases, carbon-rich atmospheres (carburizing), or anything that could react with the element itself? A material that thrives in one environment may degrade quickly in another.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
After defining your maximum temperature and furnace atmosphere, your choice becomes clear.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air up to 1250°C: NiCr or FeCrAl alloys provide the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating in air (1300°C - 1850°C): SiC is the workhorse, while MoSi2 is the solution for the most extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite, Molybdenum, or Tungsten are your only viable options.
- If your primary focus is ultra-clean processing with minimal contamination: Noble metals like Platinum are used despite their high cost.
Ultimately, matching the heating element material to its specific operational duty is the single most important decision in furnace design.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Max Temperature (°C) | Suitable Atmospheres | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Nichrome (NiCr), Kanthal (FeCrAl) | Up to 1400 | Air | Cost-effective, oxidation-resistant, stable electrical resistance |
| Ceramics | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1850 | Air | High-temperature capability, self-supporting, protective oxide layers |
| Pure Elements | Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten | Above 2000 | Vacuum or inert gas | Extreme temperature resistance, oxidizes in air, specialized use |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your industrial furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're dealing with extreme temperatures, specific atmospheres, or cost constraints, our experts can help you optimize performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















