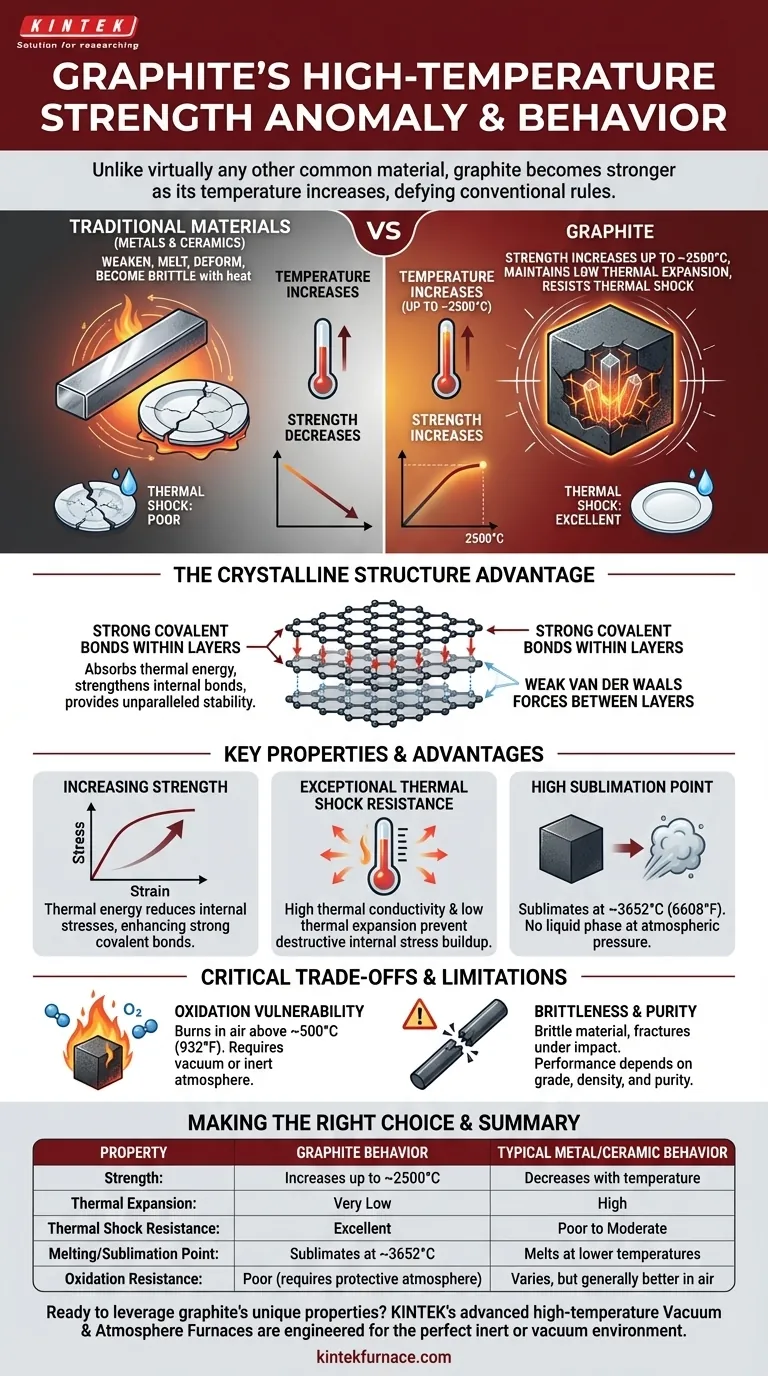
Unlike virtually any other common material, graphite possesses the unique and counter-intuitive property of becoming stronger as its temperature increases. Where metals weaken and ceramics become brittle, graphite's structural integrity improves up to approximately 2500°C, all while maintaining an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it exceptionally resistant to thermal shock.
The core reason for graphite's remarkable high-temperature performance lies in its layered atomic structure. This structure allows it to absorb thermal energy and strengthen its internal bonds, giving it unparalleled stability when most other materials would deform, melt, or fracture.

The Anomaly of Graphite: Why It Defies Conventional Rules
To understand graphite's value, we must first appreciate how its behavior contradicts that of traditional high-temperature materials like metals and ceramics.
The Crystalline Structure Advantage
Graphite consists of stacked layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. The bonds within each layer are incredibly strong covalent bonds. The bonds between the layers are much weaker van der Waals forces.
This dual structure is the key. It allows graphite to manage thermal energy in a way other materials cannot.
Increasing Strength with Temperature
In most materials, heat increases atomic vibration, weakening the bonds and causing the material to soften and expand. In graphite, increased thermal energy actually reduces internal stresses and allows the strong covalent bonds within its layers to become even more effective.
This results in a measurable increase in tensile strength as it heats up, a phenomenon that continues until it reaches extreme temperatures (around 2500°C or 4500°F).
Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is what causes a ceramic plate to crack if you pour cold water on it while it's hot. The rapid temperature change creates immense internal stress.
Graphite is highly resistant to this failure. Its high thermal conductivity allows it to dissipate heat quickly and evenly, while its low thermal expansion means it doesn't change shape dramatically when its temperature changes. This combination prevents the buildup of destructive internal stress.
A High Sublimation Point, Not Melting Point
At atmospheric pressure, graphite does not melt into a liquid. Instead, it sublimates, turning directly from a solid into a gas at an incredibly high temperature of around 3652°C (6608°F).
This is a significant advantage over even the most robust refractory metals like tungsten, which melts at 3422°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Graphite's properties are not universally superior. Its primary weakness is a critical consideration for any real-world application.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Graphite's single greatest vulnerability is oxidation. In the presence of oxygen, it will begin to burn away at temperatures as low as 500°C (932°F).
This means graphite's high-temperature strength can only be utilized in a vacuum, an inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen), or when protected by a special coating. For applications in open air, it is not a viable choice without such protection.
Brittleness Compared to Metals
While exceptionally strong, graphite is a brittle material. Unlike a metal, it will not bend or deform under load; it will fracture. This lack of ductility must be accounted for in component design to avoid failure from impact or sharp stress concentrations.
Purity and Porosity
The performance of a graphite component is highly dependent on its manufacturing process. The grade, density, and purity of the graphite will dictate its ultimate strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance. Lower-quality, porous graphite will not perform as well as a high-density, isotropic grade.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires balancing its strengths against the demands of the environment. Graphite is an exceptional tool, but only for the right job.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is often the superior choice for applications like furnace elements, casting molds, or rocket nozzles.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation in open air: A technical ceramic (like alumina) or a coated refractory metal is the necessary choice, as unprotected graphite will rapidly oxidize and fail.
- If your primary focus is toughness and resisting mechanical impact: A refractory metal like tungsten or molybdenum is a better choice due to its ductility, as graphite's brittleness is a significant liability.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select a material not just for its ideal properties, but with a clear strategy for mitigating its inherent weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| Property | Graphite Behavior | Typical Metal/Ceramic Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Increases up to ~2500°C | Decreases with temperature |
| Thermal Expansion | Very Low | High |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Poor to Moderate |
| Melting/Sublimation Point | Sublimates at ~3652°C | Melts at lower temperatures |
| Oxidation Resistance | Poor (requires protective atmosphere) | Varies, but generally better in air |
Ready to leverage graphite's unique high-temperature properties in your lab? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces, including our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, are engineered to create the perfect inert or vacuum environment needed to utilize graphite's full potential. Our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities allow for deep customization to meet your specific experimental requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior thermal processing results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















