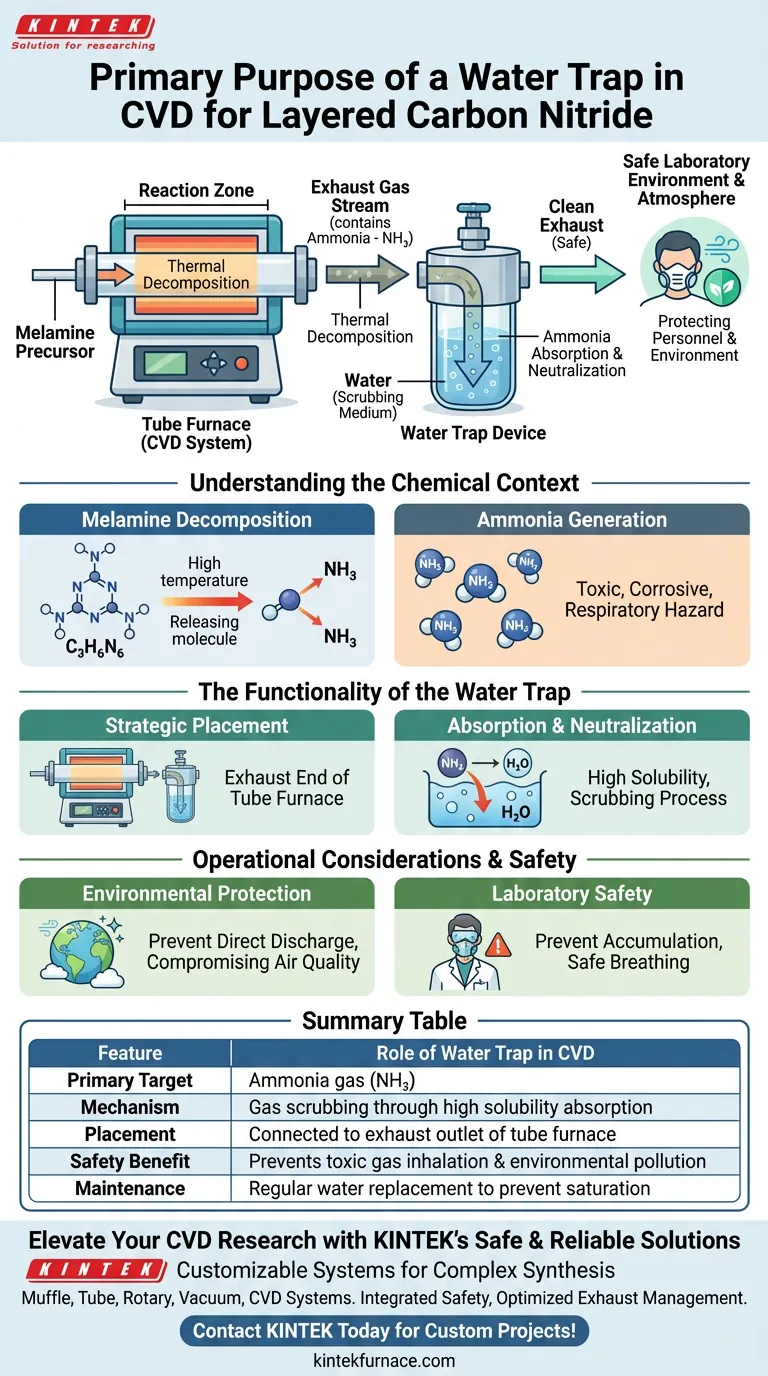
The primary purpose of a water trap device in the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of layered carbon nitride is to serve as a safety filtration system that captures hazardous exhaust gases. Specifically, it is connected to the tube furnace's outlet to absorb and neutralize ammonia byproducts generated during the thermal decomposition of precursors like melamine, preventing their release into the laboratory or atmosphere.
During the high-temperature synthesis of carbon nitride, toxic waste gases are an unavoidable byproduct. The water trap acts as a critical environmental shield, scrubbing these gases from the exhaust stream to ensure operator safety and preventing atmospheric pollution.
Understanding the Chemical Context
To understand the necessity of the water trap, one must first look at the chemical reactions occurring inside the furnace. The device is not merely an accessory; it addresses a specific chemical by-product of the synthesis process.
Thermal Decomposition of Melamine
The CVD process for creating layered carbon nitride often relies on specific precursors, such as melamine. When subjected to the high temperatures required for deposition, these precursors undergo thermal decomposition.
The Generation of Ammonia
As the melamine breaks down to form the desired carbon nitride structure, it releases volatile waste gases. The most significant byproduct in this reaction is ammonia. This gas is toxic, corrosive, and poses a respiratory hazard if left unmanaged.
The Functionality of the Water Trap
The water trap provides a simple yet effective physical and chemical barrier between the reaction chamber and the open environment.
Strategic Placement
The device is connected directly to the exhaust end of the tube furnace. This ensures that all gas leaving the reaction zone must pass through the trap before exiting the system.
Absorption and Neutralization
Ammonia is highly soluble in water. As the exhaust gases bubble through the water trap, the water absorbs the ammonia, effectively neutralizing the waste stream. This "scrubbing" process removes the harmful components from the gas flow.
Operational Considerations and Safety
While the concept is simple, the role of the water trap is vital for compliance and health standards in a research setting.
Environmental Protection
The primary goal is to prevent the direct discharge of harmful gases. Releasing untreated ammonia into the atmosphere violates environmental safety protocols and compromises air quality.
Laboratory Safety
By containing the exhaust, the trap protects laboratory personnel. It prevents the accumulation of noxious fumes within the workspace, maintaining a safe breathing environment for researchers handling the equipment.
Ensuring Process Integrity
Identifying Saturation Limits
While water is an effective solvent for ammonia, it has a finite capacity. Over time, the water in the trap will become saturated with ammonia, reducing its absorption efficiency.
Monitoring Precursor Loads
The amount of waste gas produced is directly proportional to the amount of melamine precursor used. Larger synthesis batches will require more vigilant monitoring of the trap to ensure it does not become overwhelmed.
Implementing Effective Exhaust Management
When setting up your CVD system for layered carbon nitride, consider your specific operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Laboratory Safety: Ensure the connection between the furnace exhaust and the water trap is completely airtight to prevent gas leakage before filtration occurs.
- If your primary focus is Environmental Compliance: Regularly refresh the water in the trap to maintain maximum absorption capacity for the specific volume of ammonia your process generates.
The water trap is the defining boundary between a controlled chemical reaction and an environmental hazard.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Water Trap in CVD |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | Ammonia gas (NH3) produced from melamine decomposition |
| Mechanism | Gas scrubbing through high solubility absorption |
| Placement | Connected to the exhaust outlet of the tube furnace |
| Safety Benefit | Prevents toxic gas inhalation and environmental pollution |
| Maintenance | Regular water replacement to prevent saturation |
Elevate Your CVD Research with KINTEK's Safe & Reliable Solutions
Don't let toxic byproducts compromise your laboratory safety or environmental compliance. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all precision-engineered to handle complex layered carbon nitride synthesis. Our systems are fully customizable to your unique research needs, ensuring integrated safety features like optimized exhaust management.
Ready to upgrade your high-temperature furnace setup?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom project!
Visual Guide
References
- Kota Higuchi, Yoshio Hashimoto. Layered carbon nitride films deposited under an oxygen-containing atmosphere and their electronic properties. DOI: 10.1063/5.0193419
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of chemical vapour deposition? To Grow High-Performance Materials from a Vapor
- How does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) work? Master Thin Film Fabrication for Superior Materials
- What is Laser Chemical Vapor Deposition (LCVD)? Precision Micro-Scale 3D Printing for Thin Films
- What is a major advantage of chemical vapor? It Sterilizes Without Rusting Your Metal Instruments
- What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and where is it commonly used? Key Applications and Benefits
- How does a dual-zone CVD furnace facilitate ISG of alpha-In2Se3? Optimize Thin Film Synthesis with Dual-Zone Control
- What are the advantages of using a tube furnace CVD system for Cu(111)/graphene? Superior Scalability and Quality
- What level of precision and control does CVD provide? Achieve Atomic-Level Mastery for Advanced Materials



















