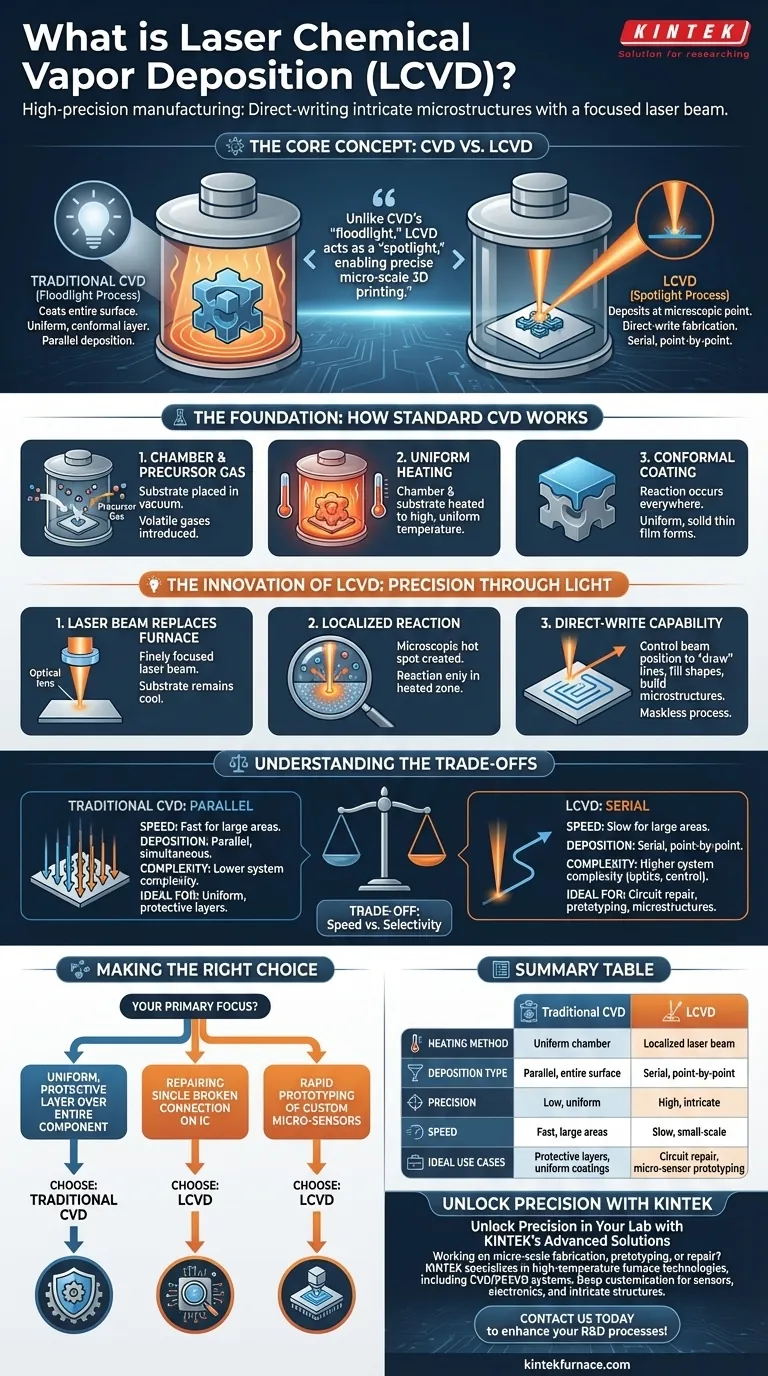
At its core, Laser Chemical Vapor Deposition (LCVD) is a high-precision manufacturing technique that uses a focused laser beam to deposit material onto a surface. Unlike traditional methods that coat an entire object, the laser heats a microscopic spot, causing a chemical reaction to occur and material to deposit only in that specific location. This allows for the direct "writing" or fabrication of intricate microstructures.
While conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a "floodlight" process that coats an entire surface, LCVD acts as a "spotlight." It provides the unique ability to deposit materials with extreme precision, essentially functioning like a micro-scale 3D printer for thin films.
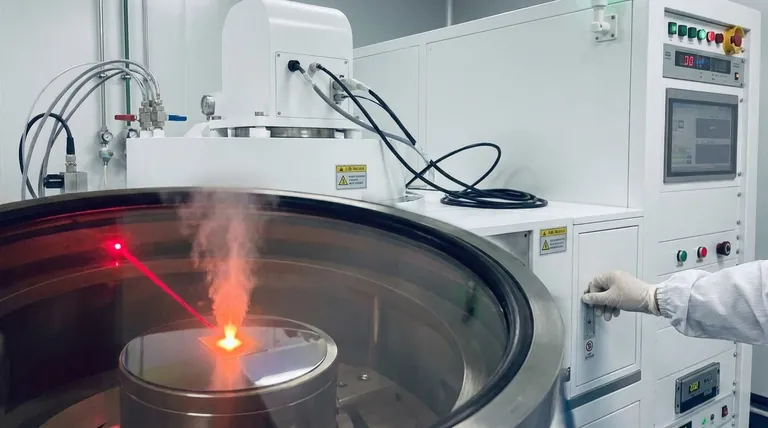

The Foundation: How Standard CVD Works
To understand the innovation of LCVD, we must first understand the process it is built upon: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The Chamber and Precursor Gas
The standard CVD process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. A substrate (the object to be coated) is placed inside, and one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced. These gases contain the atoms of the material you wish to deposit.
The Role of Uniform Heating
The entire chamber and substrate are heated to a high, uniform temperature. This heat provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction or decomposition of the precursor gases on the substrate's surface.
The Result: A Conformal Coating
Because the entire substrate is hot, the deposition occurs everywhere at once. The result is a high-quality, solid thin film that coats all exposed surfaces uniformly. This is ideal for creating durable, protective layers across a whole component.
The Innovation of LCVD: Precision Through Light
LCVD fundamentally alters the CVD process by changing how energy is delivered. It moves from a global heating approach to a highly localized one.
Replacing the Furnace with a Laser
Instead of heating the entire chamber, LCVD uses a finely focused laser beam. This beam is aimed directly at the substrate, which remains at a much lower ambient temperature.
Localized Chemical Reaction
The intense energy of the laser creates a microscopic hot spot on the substrate surface. The precursor gas only reacts or decomposes within this tiny, heated zone. The rest of the surface is too cool for the deposition reaction to occur.
Direct-Write Capability
By controlling the position of the laser beam, you can move this hot spot across the surface. This allows you to "draw" lines, fill shapes, or build three-dimensional microstructures atom-by-atom. It is a maskless, direct-write process, offering tremendous flexibility for prototyping and repair.
Understanding the Trade-offs
LCVD provides unmatched precision, but this specialization comes with important limitations. It is not a universal replacement for traditional CVD.
Serial Processing vs. Parallel Deposition
The primary trade-off is speed versus selectivity. LCVD is a serial process; it builds features point-by-point. This makes it extremely slow for coating large areas compared to traditional CVD, which deposits material everywhere simultaneously (in parallel).
System Complexity
An LCVD system requires sophisticated optics to focus and steer the laser beam, as well as precise control over laser power and scan speed. This can make the equipment more complex and expensive than a standard CVD furnace.
Material and Substrate Constraints
The effectiveness of LCVD depends on the interaction between the laser and the materials. The substrate must efficiently absorb the laser's energy to create a hot spot, and the precursor gas must be thermally sensitive enough to react at that localized temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use LCVD or traditional CVD depends entirely on the scale and precision required for your application.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform, protective layer over an entire component: Traditional CVD is the superior and more efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is repairing a single broken connection on an integrated circuit: LCVD provides the necessary surgical precision that is otherwise impossible.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping of custom micro-scale sensors or electronics: LCVD's direct-write capability offers a significant advantage in speed and flexibility by avoiding mask production.
Ultimately, choosing between these methods depends on whether your goal requires coating an entire landscape or drawing a single, precise line.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional CVD | LCVD |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Uniform chamber heating | Localized laser beam heating |
| Deposition Type | Parallel, entire surface coating | Serial, point-by-point direct writing |
| Precision | Low, for uniform coatings | High, for intricate microstructures |
| Speed | Fast for large areas | Slow, ideal for small-scale applications |
| Ideal Use Cases | Protective layers, uniform coatings | Circuit repair, micro-sensor prototyping |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Solutions
Are you working on micro-scale fabrication, prototyping, or repair tasks that demand extreme accuracy? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace technologies, including CVD/PECVD systems, tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you're developing sensors, electronics, or other intricate structures.
Contact us today to discuss how our advanced solutions can enhance your research and development processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















