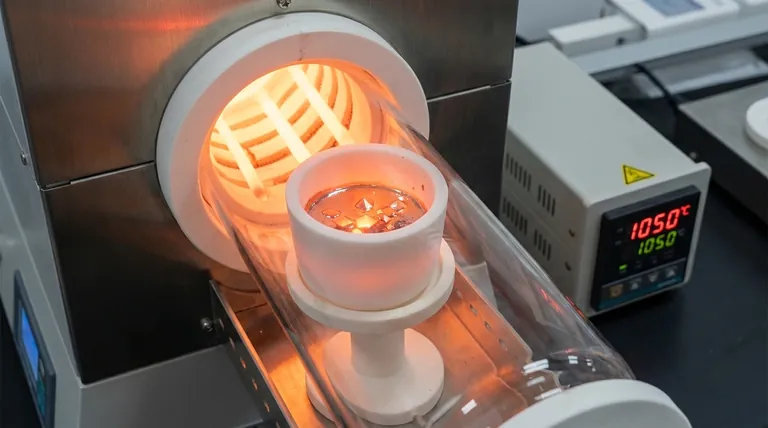
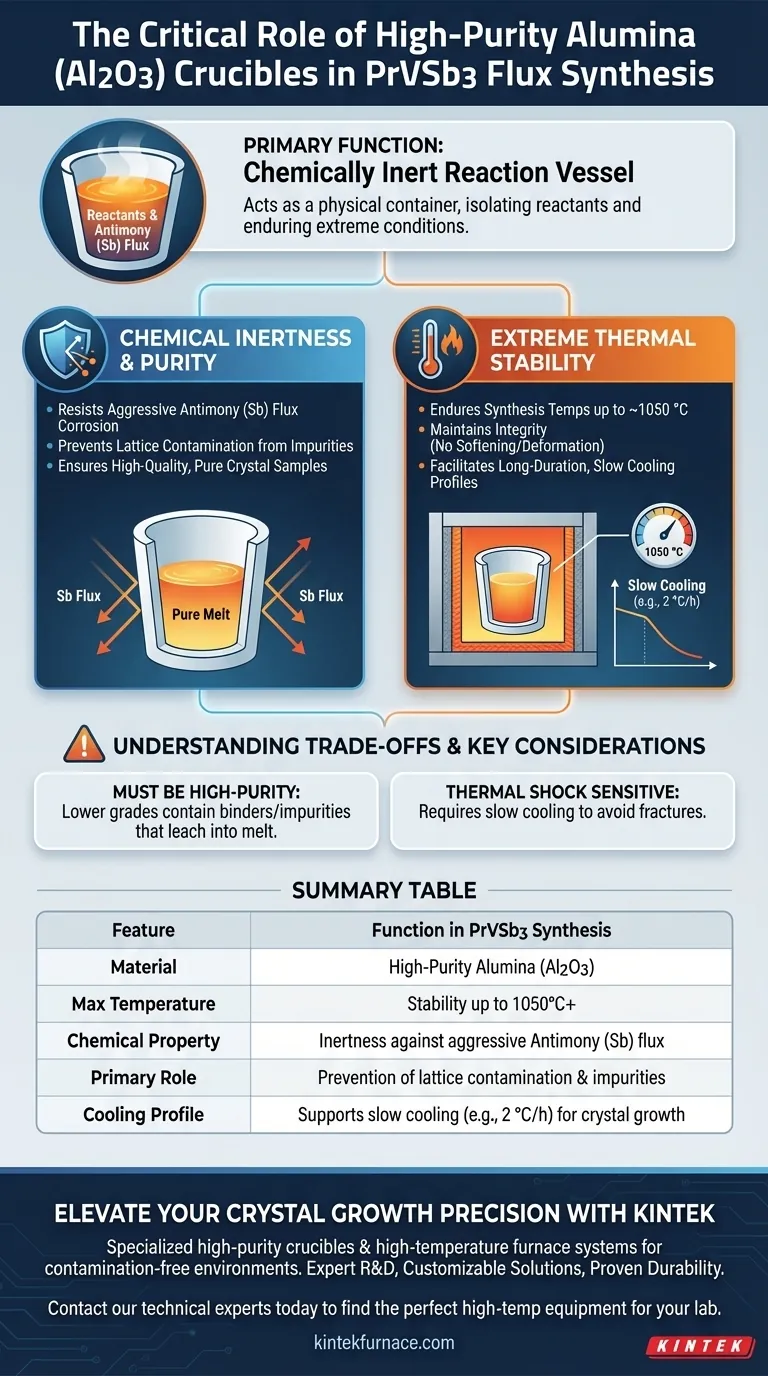
The primary function of a high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucible in this context is to serve as a chemically inert reaction vessel. It acts as the physical container for the raw materials during the flux method synthesis of PrVSb3 single crystals. Its specific role is to isolate the reactants from the external environment while enduring extreme thermal conditions.
The crucible serves as a critical barrier against contamination, combining thermal stability with resistance to Antimony (Sb) flux corrosion. This ensures that impurities are excluded from the crystal lattice, guaranteeing the production of high-quality samples.

The Critical Role of Material Inertness
Resisting Chemical Corrosion
In the flux method, the reaction environment involves aggressive metal melts. Specifically, the Antimony (Sb) flux used in PrVSb3 synthesis is highly reactive.
Maintaining Chemical Stability
The high-purity alumina crucible exhibits excellent chemical inertness. It effectively resists corrosion that would otherwise occur when in contact with the molten flux and metal components.
Preventing Lattice Contamination
By resisting degradation, the crucible prevents foreign material from leaching into the melt. This is vital for ensuring that impurities do not enter the crystal lattice during the growth phase.
Withstanding Extreme Thermal Conditions
Enduring High Synthesis Temperatures
The synthesis of PrVSb3 requires heating the materials to approximately 1050 °C. The alumina crucible is selected for its ability to maintain structural integrity at these elevated temperatures without softening or deforming.
Facilitating Long-Duration Thermal Profiles
The growth process involves a complex thermal profile, including a slow cooling phase down to 750 °C. The crucible must remain stable throughout this extended cycle to allow solutes to precipitate and grow into large single crystals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of High Purity
Not all alumina crucibles are created equal. You must specifically utilize high-purity alumina for this process. Lower-grade ceramics may contain binders or impurities that could leach into the sensitive PrVSb3 melt, negating the benefits of the flux method.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
While alumina is excellent for high heat, it can be sensitive to rapid temperature changes. The slow-cooling rate (e.g., 2 °C/h) mentioned in the thermal profile is not only for crystal growth but also helps protect the crucible from thermal shock fractures.
Ensuring Success in Crystal Growth
To maximize the quality of your PrVSb3 single crystals, consider the following regarding your vessel selection:
- If your primary focus is Sample Purity: Ensure the crucible is certified as high-purity Al2O3 to eliminate any risk of interaction with the Antimony flux.
- If your primary focus is Process Stability: Verify that the crucible's thermal rating comfortably exceeds 1050 °C to maintain containment integrity during the peak melting phase.
Ultimately, the choice of the correct vessel is the foundational step that dictates the chemical fidelity of your final crystal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in PrVSb3 Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Material | High-Purity Alumina (Al2O3) |
| Max Temperature | Stability up to 1050°C+ |
| Chemical Property | Inertness against aggressive Antimony (Sb) flux |
| Primary Role | Prevention of lattice contamination and impurities |
| Cooling Profile | Supports slow cooling (e.g., 2 °C/h) for crystal growth |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth Precision with KINTEK
High-quality PrVSb3 single crystals demand a contamination-free environment. KINTEK provides the specialized high-purity Al2O3 crucibles and high-temperature furnace systems necessary to maintain chemical fidelity at 1050°C and beyond.
Why Choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Our laboratory solutions, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems, are engineered for demanding thermal profiles.
- Customizable Solutions: We offer tailored high-temperature furnaces and vessels to meet your specific research parameters.
- Proven Durability: Our materials are designed to resist aggressive flux corrosion and thermal shock.
Ready to ensure the success of your next synthesis? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temp equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are alumina crucibles and mother-powder necessary for LLZO sintering? Ensure High Ionic Conductivity
- Why must rare earth-based halide solid electrolytes be handled in a glove box? Protect Your Materials from Degradation
- Why is a laboratory-grade high-pressure reactor essential for TiO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Purity and Efficiency
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- What role does a high-precision mass flow controller play in assessing the gas selectivity of Gallium Sulfide sensors?
- How does chemical compatibility affect the selection of alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure Longevity and Purity
- How do quartz crucibles and quartz cover plates protect the substrate? Optimize TiO2 Nanowire Growth
- What are the functions of alumina crucibles and quartz sleeve encapsulation in the synthesis of calcium perrhenates?



















