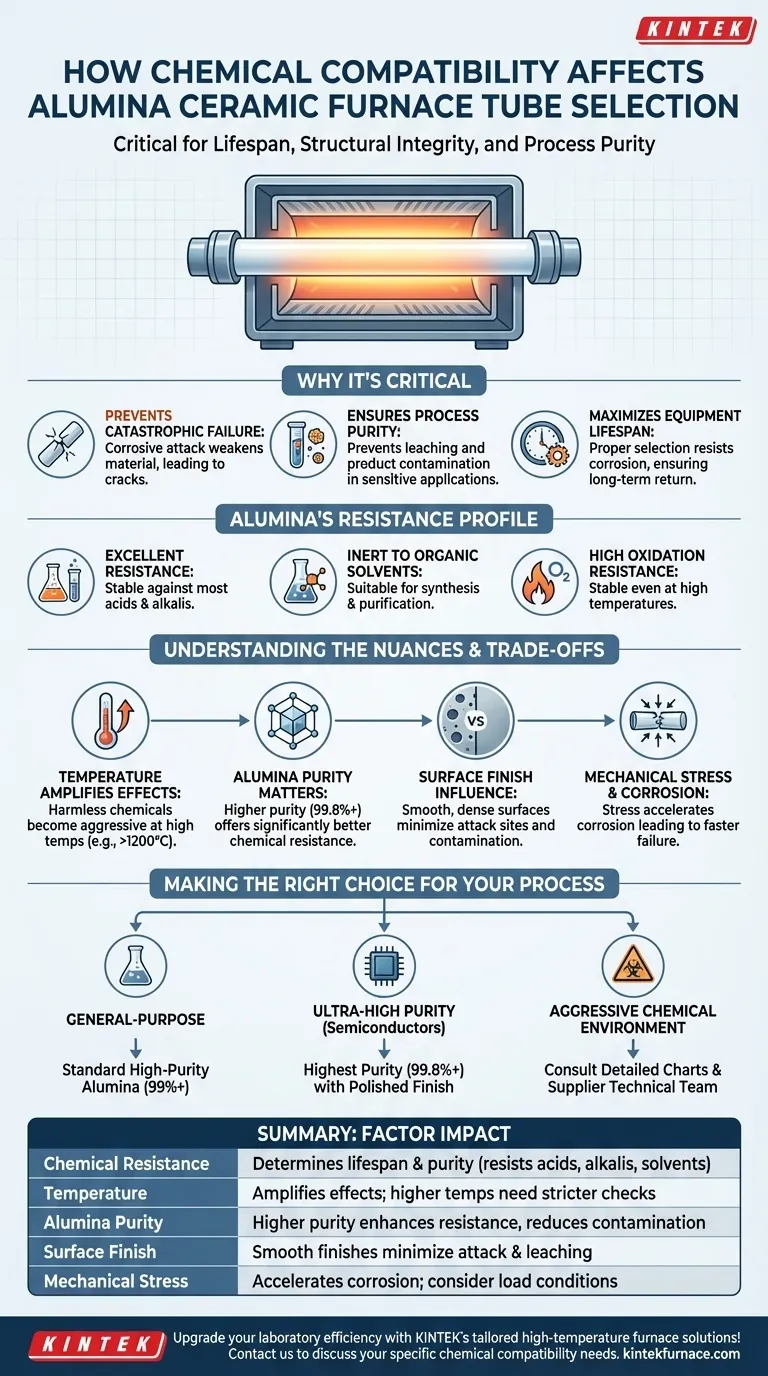
In selecting an alumina ceramic furnace tube, chemical compatibility is a critical factor that directly determines the tube's lifespan, structural integrity, and the purity of your process. Alumina is known for its excellent general resistance to most acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, making it a default choice for many applications. However, this general resilience does not eliminate the need for careful verification against the specific chemicals and temperatures present in your unique environment.
The core challenge is not simply asking if alumina is "compatible," but understanding how temperature, chemical concentration, and material purity interact. While highly resistant, alumina's performance limits can be reached, and failure often occurs when one or more of these factors are pushed to an extreme without proper evaluation.

Why Chemical Compatibility Is Critical
Choosing a furnace tube with the wrong chemical resistance can lead to costly and dangerous outcomes. It's a foundational aspect of process design.
Preventing Catastrophic Failure
Continuous exposure to an incompatible chemical, especially at high temperatures, will corrode the ceramic. This attack weakens the material, leading to cracks, embrittlement, and eventual mechanical failure of the tube.
Ensuring Process Purity
For applications in semiconductor manufacturing or chemical synthesis, purity is paramount. A chemical reaction between the process atmosphere and the furnace tube can cause leaching, where elements from the ceramic contaminate the product.
Maximizing Equipment Lifespan
A properly selected tube can last for years, even under demanding conditions. Chemical corrosion is a primary driver of premature replacement, and ensuring compatibility from the start is the best way to maximize the return on your investment.
Understanding Alumina's Resistance Profile
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) is a chemically stable and robust material, but its compatibility has specific characteristics.
Excellent Resistance to Acids and Alkalis
High-purity alumina shows exceptional stability when exposed to a wide range of both acids and alkalis. This makes it a reliable choice for many chemical processing and laboratory applications where corrosive substances are common.
Stability with Organic Solvents
Alumina is largely inert to most organic solvents across a wide temperature range. This allows it to be used in processes involving organic synthesis or purification without risk of degradation.
High Resistance to Oxidation
The material itself is an oxide, meaning it is already in a highly stable oxidized state. This gives it superb resistance to oxidation, even in high-temperature air or oxygen-rich atmospheres where metals would quickly fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While broadly resistant, several factors can compromise alumina's performance. Ignoring these nuances is a common cause of failure.
The Amplifying Effect of Temperature
A chemical that is harmless to alumina at room temperature can become highly aggressive at 1200°C or higher. Chemical resistance data must always be considered in the context of your operating temperature.
The Critical Role of Alumina Purity
Not all alumina is the same. A 99.8% pure alumina tube will have significantly better chemical resistance than an 85% pure tube. The lower-purity ceramics contain other oxides and glassy phases that are often less resistant and can be selectively attacked.
The Influence of Surface Finish
A rough, porous surface has a much higher surface area than a smooth, dense one. This provides more sites for chemical attack to begin and can trap corrosive agents, accelerating degradation. A smooth surface finish minimizes contamination risk and enhances chemical resilience.
Mechanical Stress and Corrosion
A tube under significant mechanical stress (bending or compression) is more susceptible to stress corrosion cracking. The chemical attack concentrates at points of high stress, leading to failure much faster than would be expected from corrosion alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection must be based on a holistic view of your application. Use your specific process goals to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, high-temperature processing: A standard high-purity (99%+) alumina tube is an excellent and cost-effective starting point due to its broad chemical and thermal resistance.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity (e.g., semiconductors): Select the highest purity alumina available (99.8%+) with a polished surface finish to absolutely minimize the risk of leaching and contamination.
- If your primary focus is a highly aggressive chemical environment: Do not rely on general data. Consult detailed chemical compatibility charts and provide your supplier's technical team with the specific chemicals, concentrations, and operating temperatures for a definitive recommendation.
A thorough evaluation of your process chemistry is the foundation for a reliable and long-lasting high-temperature system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Selection |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Determines lifespan and purity; alumina resists acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Temperature | Amplifies chemical effects; higher temps require stricter compatibility checks |
| Alumina Purity | Higher purity (e.g., 99.8%) enhances resistance and reduces contamination |
| Surface Finish | Smooth finishes minimize attack and leaching risks |
| Mechanical Stress | Stress can accelerate corrosion; consider load conditions |
Upgrade your laboratory efficiency with KINTEK's tailored high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, including chemical compatibility for alumina ceramic tubes. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process purity and equipment lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity



















