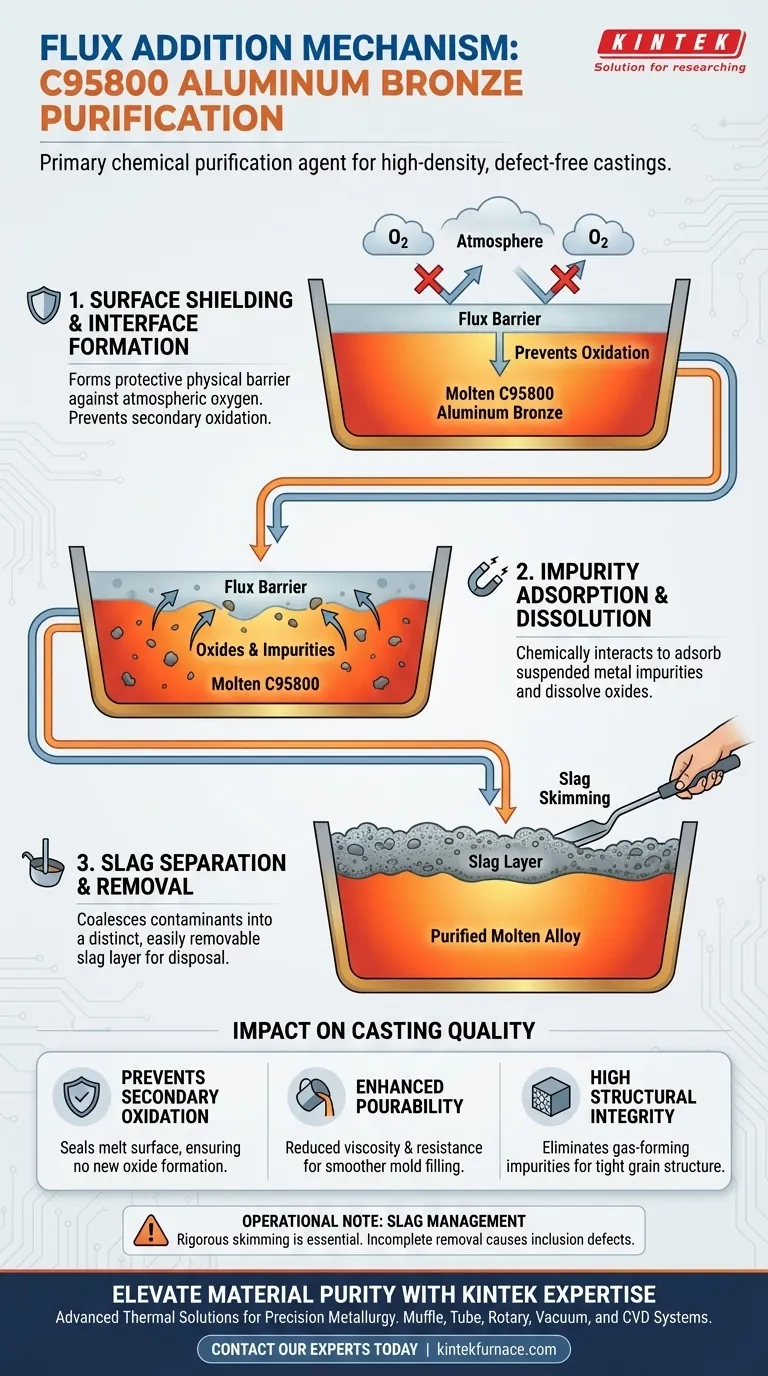
Flux addition serves as the primary chemical purification agent in C95800 aluminum bronze melts. Its fundamental mechanism works by establishing a protective barrier on the melt surface that actively adsorbs and dissolves metal impurities and oxides. This reaction facilitates the separation of contaminants from the liquid metal, coalescing them into a slag layer that can be easily skimmed off before casting.
The core function of flux in C95800 processing is to simultaneously shield the melt from atmospheric oxygen and extract existing impurities, directly enabling high-density, defect-free castings.

The Purification Mechanism Explained
Formation of a Protective Interface
Upon addition, the flux melts to create a continuous layer over the surface of the molten aluminum bronze. This physical barrier is critical for isolating the reactive liquid metal from the surrounding atmosphere.
Adsorption and Dissolution
The flux does not merely sit on top of the melt; it interacts chemically with the solution. It works by adsorbing metal impurities and dissolving oxides that are suspended within the melt.
Slag Separation
As the flux captures these impurities, it facilitates their physical separation from the desirable molten alloy. The contaminants are bound together to form a distinct slag, which floats on the surface for easy removal.
Impact on Casting Quality
Prevention of Secondary Oxidation
One of the most critical roles of the flux barrier is preventing "secondary oxidation." By sealing the melt surface, the flux ensures that no new oxides are formed during the holding or pouring phases.
Enhancing Pourability
The removal of particulate oxides and impurities significantly reduces the viscosity and resistance of the melt. This purification ensures the metal pours smoothly, reducing turbulence and potential defects during the mold-filling process.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
The ultimate result of this chemical cleansing is high casting density. By eliminating gas-forming impurities and oxide films, the flux allows the C95800 alloy to solidify with a tight, uniform grain structure.
Operational Considerations
The Requirement for Slag Management
While flux is essential for cleaning the metal, it generates a byproduct that must be managed. The formation of slag is a deliberate outcome, but it necessitates a rigorous skimming process.
Consequences of Incomplete Removal
If the slag formed by the flux is not completely removed, it can become re-entrained in the melt during pouring. This transforms the captured impurities into inclusions, potentially compromising the mechanical strength of the final part.
Optimizing the C95800 Casting Process
To maximize the benefits of flux addition in your aluminum bronze casting operations, consider your specific quality targets:
- If your primary focus is Casting Density: Prioritize the flux's ability to dissolve oxides to prevent internal porosity and voids.
- If your primary focus is Surface Finish: Rely on the flux barrier to prevent secondary oxidation, ensuring the metal remains clean during the pour for a smoother exterior.
Effective flux application transforms a reactive melt into a stable, high-quality liquid ready for precision casting.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism Phase | Primary Action | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Shielding | Creates a physical barrier against oxygen | Prevents secondary oxidation and gas absorption |
| Impurity Adsorption | Dissolves suspended oxides and metal impurities | Reduces viscosity and improves melt pourability |
| Slag Formation | Coalesces contaminants into a removable layer | Eliminates inclusions for high structural integrity |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK Expertise
Don’t let impurities compromise the structural integrity of your C95800 aluminum bronze castings. KINTEK provides the advanced thermal solutions necessary for precision metallurgy. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other high-temperature laboratory furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique purification and casting needs.
Ready to optimize your melt quality and achieve defect-free results?
Contact Our Experts Today to discover how KINTEK’s precision equipment can transform your lab or production efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Chawanan Thongyothee, Sombun Chareonvilisiri. The Effect of Gas Venting on the Mechanical Properties of C95800 Aluminum Bronze Castings. DOI: 10.48084/etasr.10993
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials and specifications are typically used in vacuum casting? Master High-Fidelity Prototyping with PU Resins
- What role does the coil play in the IGBT melting process? It's the Key to Efficient Induction Heating
- What are the advantages of industrial-grade induction furnaces for aluminum alloy production? Scale Your Mass Production
- How does the IGBT induction melting furnace maintain constant power output? Achieve Faster, More Efficient Melting
- What is the role of vacuum induction furnaces in aluminum alloy oxidation research? Mastering Melt Environment Control
- What are the main differences between VIM and Arc Melting furnaces? Choose the Right Melting Tech for Your Alloys
- What is the critical function of a vacuum induction furnace in the preparation of Fe-Cu-Nb-Mo-Si-B master alloys?
- How do induction melting furnaces ensure superior metal quality? Achieve Purity, Homogeneity & Control



















