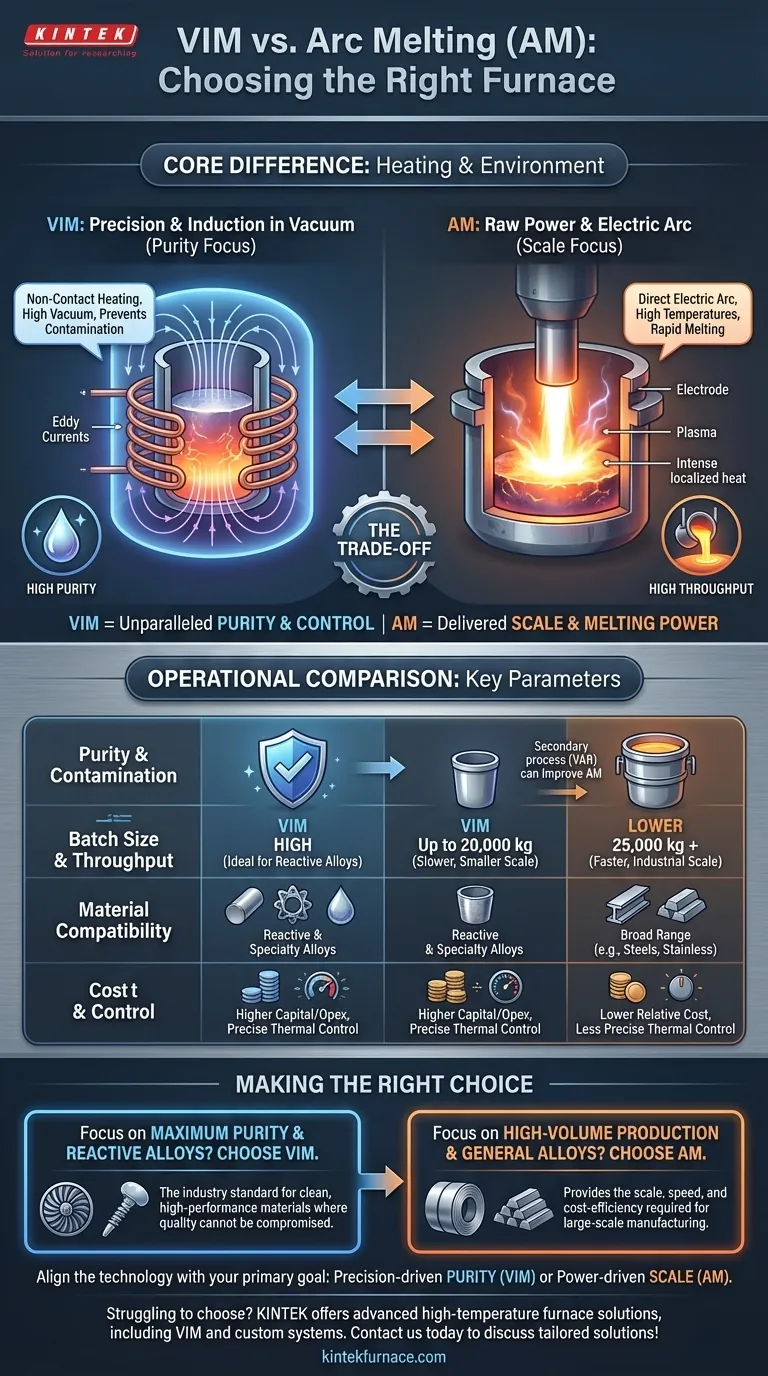
At their core, Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) and Arc Melting (AM) are distinguished by their fundamental heating mechanisms and operating environments. VIM uses electromagnetic induction within a high-vacuum chamber to achieve exceptional purity and control, making it ideal for reactive and high-performance alloys. In contrast, Arc Melting employs a high-energy electric arc to rapidly melt materials, prioritizing throughput and scale for a broader range of metals.
The decision between VIM and Arc Melting is not about which is superior, but about aligning the technology with your primary goal. The choice hinges on a fundamental trade-off: VIM offers unparalleled purity and control, while AM delivers scale and raw melting power.
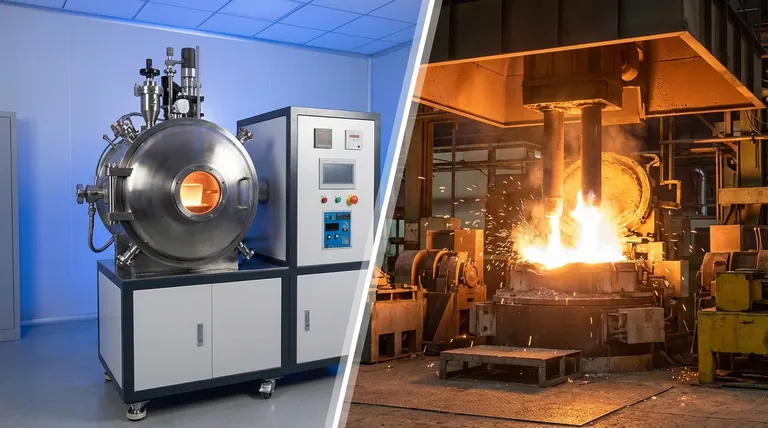

The Fundamental Difference: Heat Source and Environment
To understand the practical applications of each furnace, you must first grasp how they generate heat and control the melting environment. These two factors dictate everything from material purity to production volume.
VIM: Precision Through Induction and Vacuum
A Vacuum Induction Melting furnace uses alternating current passed through a coil to create a powerful magnetic field. This field induces eddy currents within the metallic charge, generating heat from the inside out without any direct contact.
This entire process occurs under a high vacuum. The vacuum environment is critical because it prevents airborne contaminants like oxygen and nitrogen from reacting with the molten metal. It also helps pull dissolved gases out of the melt, resulting in a cleaner, higher-quality final product.
AM: Raw Power Through an Electric Arc
An Arc Melting furnace generates heat using a much more direct method: a sustained electric arc. This arc is struck between an electrode and the metallic charge, creating a plasma that reaches extremely high temperatures.
This intense, localized heat is highly effective at melting materials with very high melting points. While some arc melting processes are performed under a vacuum (like Vacuum Arc Remelting or VAR), the primary goal of the arc itself is sheer thermal energy and melting speed, not the gentle, controlled heating of VIM.
Comparing Key Operational Parameters
The differences in heating and environment lead to distinct operational outcomes. Your choice depends on which of these parameters is most critical to your project.
Purity and Contamination Control
VIM is the unequivocal choice for achieving the highest levels of purity. The combination of non-contact induction heating and a high-vacuum atmosphere minimizes the introduction of impurities and actively refines the metal by removing gases. This is essential for aerospace superalloys, medical implants, and electronic materials where even trace elements can cause failure.
Arc Melting, particularly in its large-scale, non-vacuum configurations, is more susceptible to contamination from the atmosphere and the electrodes. While secondary processes like VAR can significantly improve purity, the inherent design of VIM is built around contamination avoidance from the start.
Batch Size and Throughput
Arc Melting is designed for industrial scale. These furnaces are workhorses of the steel industry, capable of processing batches starting at 25,000 kg and going much higher. Their rapid melting cycles are optimized for high-volume production.
VIM operates on a smaller, more precise scale. Typical batch sizes range from a few hundred kilograms up to around 20,000 kg. The process is inherently slower due to the time required to achieve and maintain a high vacuum, making it better suited for lower-volume, high-value materials.
Material Compatibility
VIM excels at melting reactive alloys like titanium, zirconium, and nickel-based superalloys. These materials would be ruined by exposure to oxygen at high temperatures, making VIM's vacuum environment a necessity.
Arc Melting is a versatile process capable of melting a vast range of metals, including steels, stainless steels, and various common alloys. Its primary strength is its ability to efficiently melt large quantities of material with high melting points.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a perfect solution for all scenarios. Acknowledging their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Cost of Purity (VIM)
The precision of VIM comes at a price. The equipment is complex, requiring sophisticated vacuum pumps and control systems, which leads to higher capital and operational costs. The process cycles are also longer, reducing overall throughput compared to AM.
The Limitations of Power (AM)
The primary strength of Arc Melting—its raw power—is also a source of its limitations. The intense heat of the arc provides less precise thermal control over the melt compared to induction. Furthermore, in its most common forms, AM offers minimal protection against atmospheric contamination, making it unsuitable for alloys where purity is the primary driver of performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology requires a clear understanding of your end goal. The material you are processing and the required properties of the final product will guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and reactive alloys: Choose VIM. It is the industry standard for producing clean, high-performance superalloys, titanium for medical and aerospace use, and other specialty metals where quality cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and general alloys: Choose AM. It provides the scale, speed, and cost-efficiency required for large-scale steelmaking and the production of large forgings or bulk ingots.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental trade-off between precision-driven purity and power-driven scale is the key to selecting the right melting technology for your metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Arc Melting (AM) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Electromagnetic induction in high vacuum | Electric arc for rapid melting |
| Purity Control | High, ideal for reactive alloys | Lower, suitable for general alloys |
| Batch Size | Up to 20,000 kg | 25,000 kg and above |
| Material Compatibility | Reactive alloys (e.g., titanium, superalloys) | Broad range (e.g., steels, stainless steels) |
| Key Advantage | Precision and purity | Scale and throughput |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's metal melting needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need the purity of VIM or the scale of Arc Melting. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















