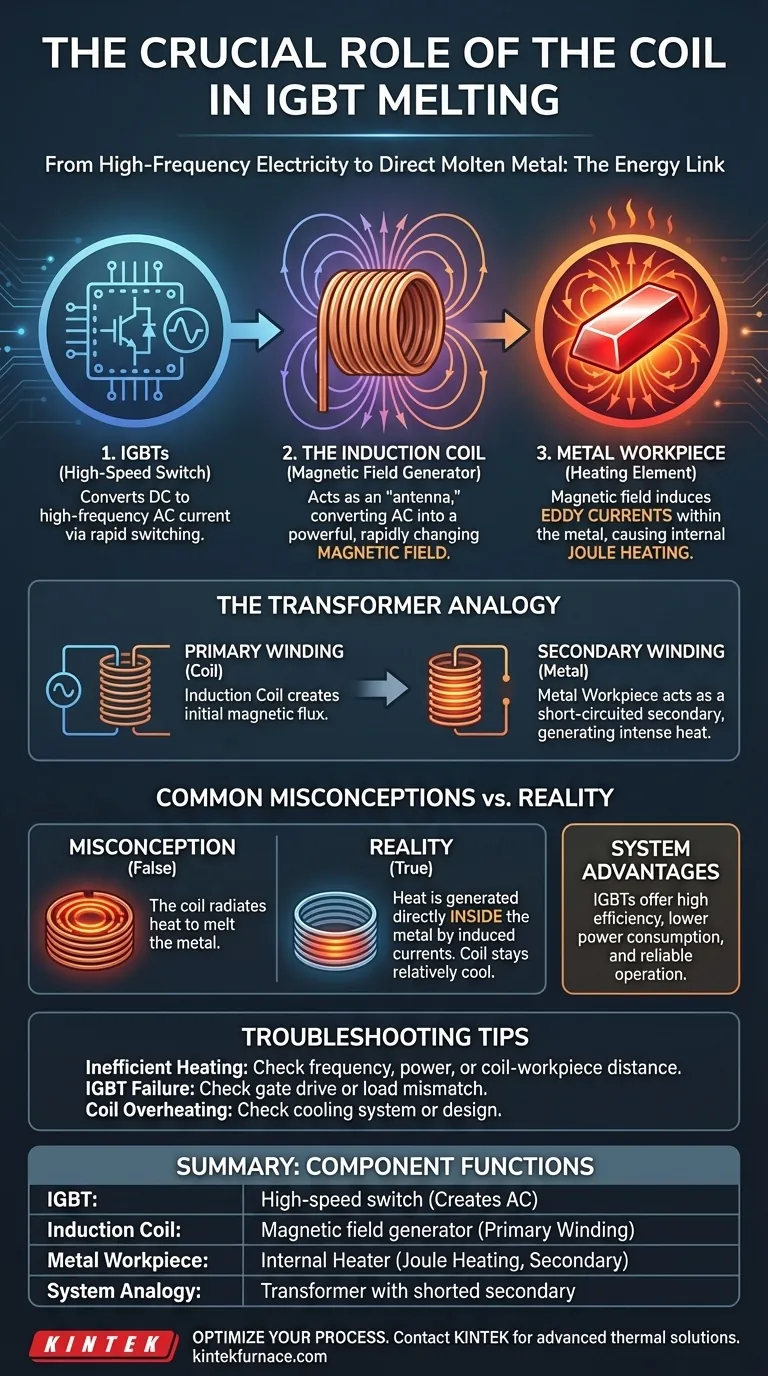
In an IGBT-based induction melting system, the coil's primary role is to act as an antenna, converting high-frequency electrical current from the IGBT circuit into a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. This magnetic field is what induces heat directly within the metal being melted, without any physical contact. The coil itself does not get hot by design; it is the crucial link that transfers energy from the power supply to the workpiece.
The core principle is not about the coil generating heat, but about the coil generating a magnetic field. The IGBT's job is to feed the coil a high-frequency current, and the coil's job is to use that current to create the field that induces heat-generating eddy currents within the target metal.

How the System Works: From Electricity to Molten Metal
An IGBT melting system is a highly efficient method for converting electrical energy into thermal energy. This process can be broken down into a few key steps, with the coil playing a central role in the energy transfer.
The IGBT as a High-Speed Switch
The process starts with the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT). An IGBT is a powerful semiconductor device that acts as an extremely fast and efficient electronic switch.
A control circuit, known as a gate driver, tells the IGBT to switch on and off thousands of times per second. This rapid switching is what generates a high-frequency alternating current (AC).
The Coil as a Magnetic Field Generator
This high-frequency AC is then fed into the induction coil, which is typically made of hollow copper tubing. As the current flows through the coil, it generates a strong and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around it.
The metal piece to be melted (the "workpiece" or "charge") is placed inside this magnetic field, but it does not touch the coil.
The Metal as the Heating Element
According to the laws of electromagnetic induction, this changing magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents within the conductive metal workpiece. These are known as eddy currents.
Because the metal has electrical resistance, these swirling eddy currents generate immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This is the same principle that makes a stove's heating element glow red. The heat is generated inside the metal itself, leading to rapid and efficient melting.
Understanding the Key Analogy: A Transformer
The relationship between the coil and the workpiece is best understood as a transformer. This provides a clear mental model for the entire system.
The Coil is the Primary Winding
The induction coil, connected to the IGBT power supply, acts as the primary winding of the transformer. Its job is to create the initial magnetic flux.
The Metal is the Secondary Winding
The metal workpiece acts as the secondary winding. The magnetic field from the primary coil "links" to the workpiece, inducing the eddy currents.
The Metal is Also the Resistor
Crucially, the workpiece also acts as its own resistor. It's as if you took the secondary winding of a transformer and short-circuited it. The induced current flows against the metal's inherent resistance, which is what produces the intense heat needed for melting.
Common Misconceptions and System Advantages
Understanding the distinct roles of each component helps clarify the efficiency and advantages of this technology.
Misconception: The Coil Heats the Metal
A common mistake is to think the coil radiates heat like a conventional burner. In reality, the coil stays relatively cool and is often water-cooled to dissipate its own small amount of resistive heat. The heat is generated directly and internally within the workpiece by the eddy currents.
The Advantage of IGBTs
Using IGBTs to power the coil offers significant benefits. Their high switching speed and efficiency mean less energy is wasted as heat within the control electronics themselves. This leads to lower power consumption and simpler, more reliable driver circuits compared to older technologies.
Applying This to Your System
Understanding these principles allows you to better diagnose issues and optimize performance.
- If you are experiencing inefficient heating: The problem may not be the coil itself but the frequency or power being supplied by the IGBT circuit, or an improper coupling distance between the coil and the workpiece.
- If your IGBTs are failing: This could point to issues in the gate drive circuit or a mismatch between the power supply and the load presented by the coil and workpiece combination.
- If your coil is overheating: This is a serious issue, indicating either a failure in its cooling system or a design flaw causing excessive resistive losses.
By viewing the system as an IGBT-driven transformer, you can correctly attribute functions to components and troubleshoot problems far more effectively.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function in IGBT Melting |
|---|---|
| IGBT | Acts as a high-speed switch to create high-frequency AC current. |
| Induction Coil | Converts high-frequency current into a rapidly changing magnetic field. |
| Metal Workpiece | Heats internally via induced eddy currents (Joule heating) from the magnetic field. |
| System Analogy | Functions as a transformer, with the coil as the primary winding and the metal as a short-circuited secondary. |
Struggling with inefficient heating or component failure in your melting process?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal solutions. Our expertise in high-temperature systems, including custom induction heating setups, ensures you get precisely the performance your application demands.
Let us help you optimize your process with reliable, high-efficiency equipment. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















