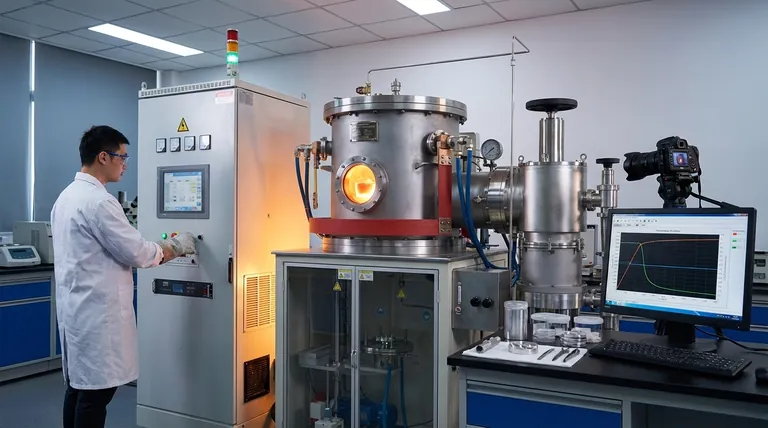
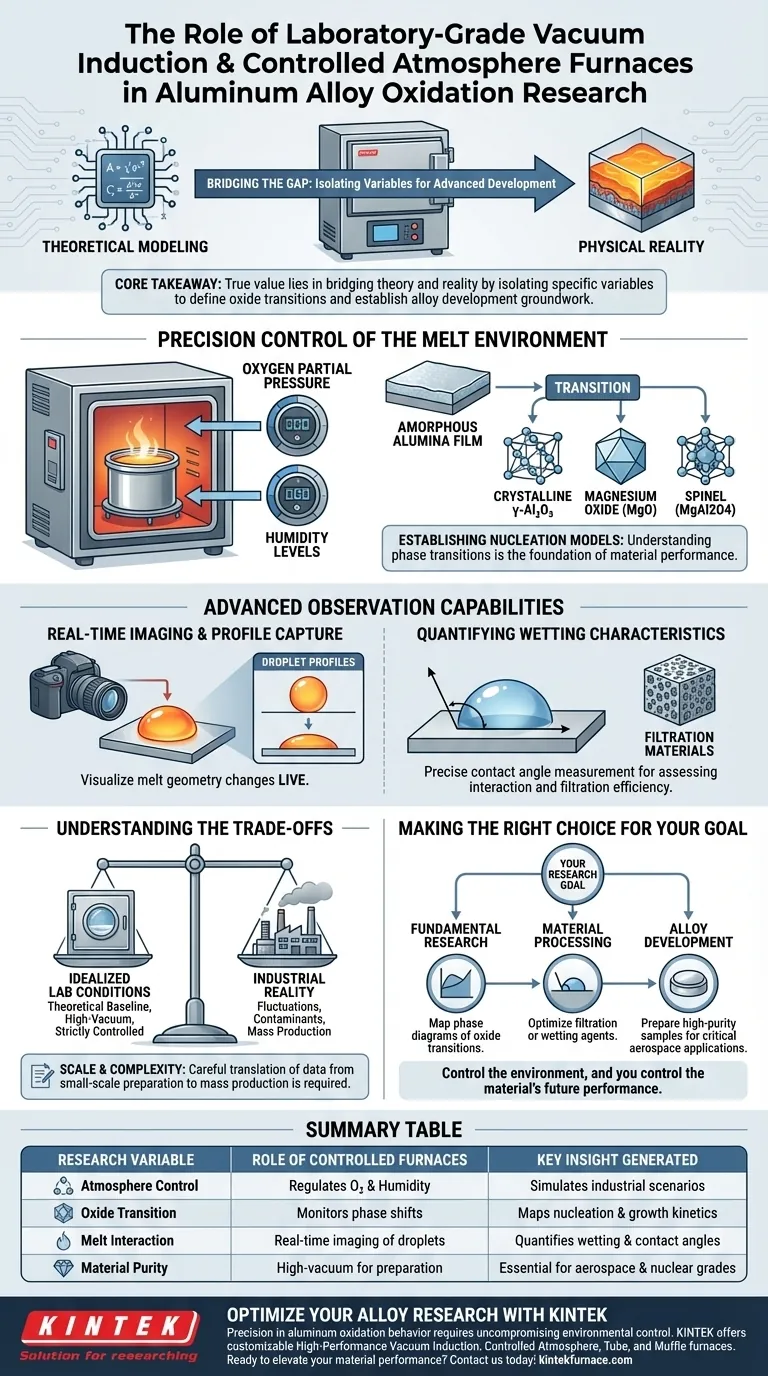
Laboratory-grade vacuum induction and controlled atmosphere furnaces serve as the primary tools for precisely regulating the environment surrounding molten aluminum. By enabling the exact control of oxygen partial pressure and humidity, these systems allow researchers to simulate diverse production conditions to observe how oxide films initiate, grow, and transform.
Core Takeaway The true value of these furnaces lies in their ability to bridge the gap between theoretical modeling and physical reality. They allow for the isolation of specific variables—such as humidity or gas composition—to determine how initial amorphous films transition into complex crystalline structures, establishing the groundwork for advanced alloy development.

Precision Control of the Melt Environment
Simulating Production Conditions
In standard environments, aluminum oxidation is chaotic and difficult to measure. Vacuum and controlled atmosphere furnaces solve this by allowing you to define the exact oxygen partial pressure and humidity levels above the melt.
This capability is essential for replicating specific industrial scenarios in a controlled laboratory setting. It transforms anecdotal observation into repeatable, scientific data.
Tracking Oxide Film Transitions
The primary research application is studying the evolution of the oxide film itself.
You can observe how an initial, amorphous alumina film transforms over time. Researchers use these controlled environments to pinpoint the exact conditions required for the transition into crystalline gamma-alumina ($\gamma$-Al2O3), magnesium oxide (MgO), or spinel (MgAl2O4).
Establishing Nucleation Models
Understanding these phase transitions is not just an academic exercise; it is the foundation of material performance.
By characterizing these oxide films, researchers can establish experimental models for using natural oxides as nucleation substrates. This leads to a better understanding of how intermetallic compounds form and interact within the alloy.
Advanced Observation Capabilities
Real-Time Imaging and Profile Capture
Beyond atmospheric control, these furnaces are often equipped with high-resolution imaging systems.
This allows for the real-time capture of droplet profiles as the alloy melts on a ceramic substrate. You can visualize changes in the melt geometry as they happen, rather than relying solely on post-mortem analysis.
Quantifying Wetting Characteristics
The imaging capabilities enable the precise measurement of contact angles.
This data is critical for evaluating the wetting characteristics of the material. For example, it allows researchers to assess how molten aluminum interacts with filtration materials, such as manganese oxide, which is vital for industrial filtration efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Idealized Conditions vs. Industrial Reality
While these furnaces offer precision, they create a "perfect" environment that rarely exists on a factory floor.
Data gathered under high-vacuum or strictly controlled inert gas conditions represents a theoretical baseline. You must account for the fact that real-world casting involves fluctuations and contaminants that a laboratory furnace might intentionally exclude.
Scale and Complexity
These systems are generally designed for small-scale sample preparation.
While they are excellent for developing special alloys for demanding fields like aerospace and nuclear industries, scaling these precise oxidation parameters to mass production requires careful translation of the data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of these furnaces, align their capabilities with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Fundamental Research: Utilize the precise oxygen and humidity controls to map the phase diagrams of oxide transitions (amorphous to crystalline).
- If your primary focus is Material Processing: Leverage the high-resolution imaging to measure contact angles and optimize filtration or wetting agents.
- If your primary focus is Alloy Development: Use high-temperature vacuum conditions to prepare high-purity samples for testing in critical applications like aerospace.
Control the environment, and you control the material's future performance.
Summary Table:
| Research Variable | Role of Controlled Furnaces | Key Insight Generated |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Regulates oxygen partial pressure and humidity | Simulates industrial production scenarios |
| Oxide Transition | Monitors amorphous to crystalline ($\gamma$-Al2O3) phase shifts | Maps nucleation and growth kinetics |
| Melt Interaction | Real-time imaging of droplet profiles on substrates | Quantifies wetting and contact angles |
| Material Purity | High-vacuum environment for alloy preparation | Essential for aerospace and nuclear grades |
Optimize Your Alloy Research with KINTEK
Precision in aluminum oxidation behavior requires uncompromising environmental control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum Induction, Controlled Atmosphere, Tube, and Muffle furnaces—all customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are modeling phase transitions or developing high-purity aerospace materials, our systems provide the stability and accuracy your data deserves.
Ready to elevate your material performance? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Gábor Gyarmati, Ján Erdélyi. Intermetallic Phase Control in Cast Aluminum Alloys by Utilizing Heterogeneous Nucleation on Oxides. DOI: 10.3390/met15040404
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is an induction-heated vacuum furnace and what is its primary use? Achieve Ultimate Metal Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What industries commonly use vacuum or protective atmosphere induction furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and More
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Which protective gases are commonly used in induction furnaces? Boost Metal Purity and Performance
- What role does a medium-frequency induction vacuum furnace play in melting S30403? Achieve Pure Alloy Integrity
- How is operator safety ensured during the vacuum induction melting process? Discover Multi-Layered Protection for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using induction melting furnaces? Boost Efficiency, Quality, and Safety
- What are the advantages of induction heating over traditional heating methods? Faster, Cleaner, and More Efficient



















