In short, induction melting furnaces offer significant advantages in speed, energy efficiency, safety, and metal quality compared to traditional fuel-fired methods. The technology uses electromagnetic induction to generate intense heat directly within the metal itself, leading to a faster, cleaner, and more controllable melting process.
The core advantage of induction melting is not just one feature, but how its integrated benefits—speed, control, and safety—compound to fundamentally lower operational costs while simultaneously improving the final product's quality.
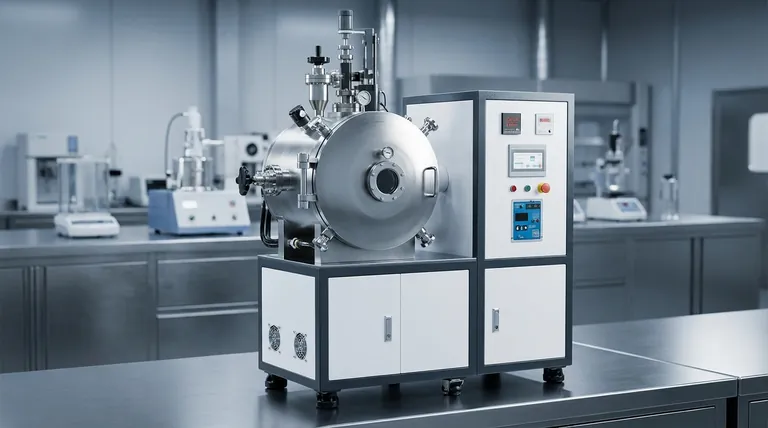

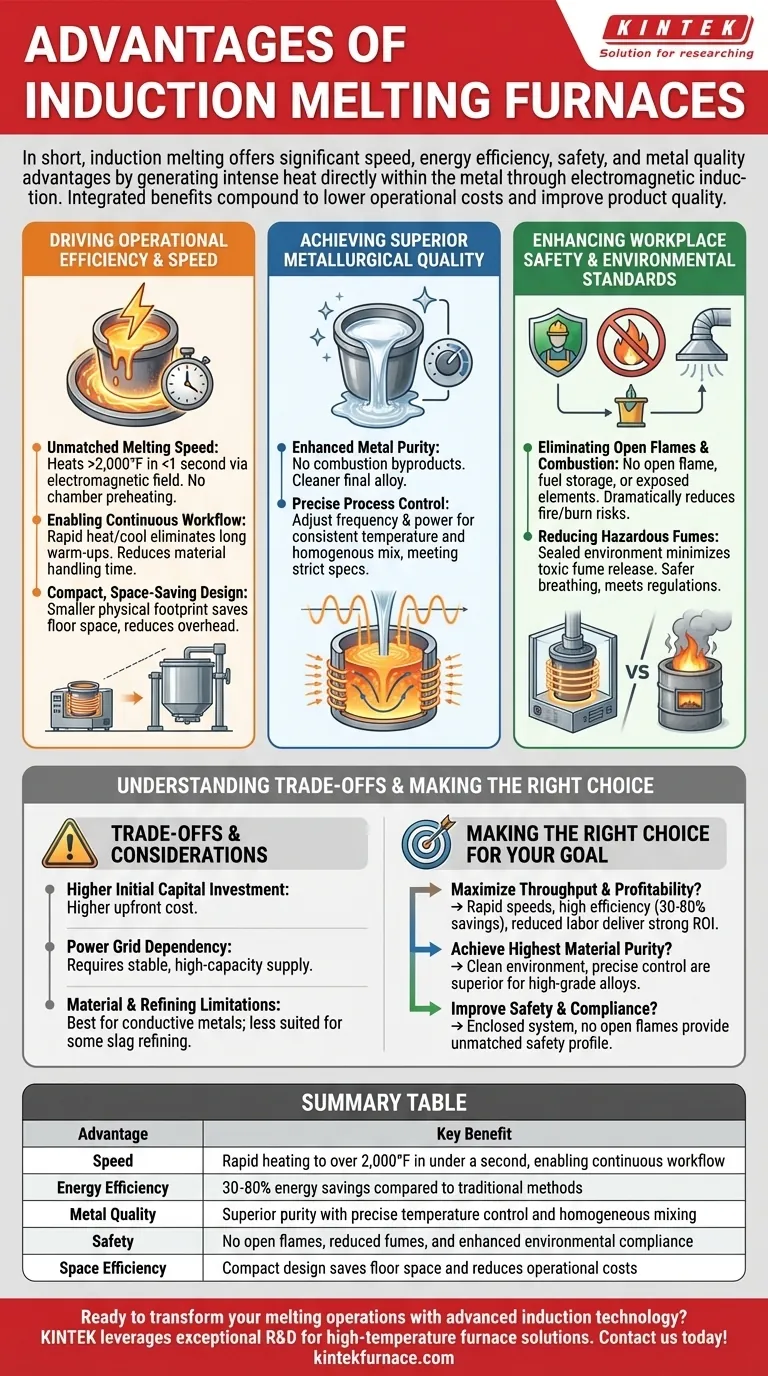
Driving Operational Efficiency and Speed
Induction furnaces are engineered for high-performance production environments. They eliminate many of the delays and inefficiencies inherent in conventional melting systems.
Unmatched Melting Speed
An induction system can heat metal to over 2,000°F in under a second. This rapid heating is due to the electromagnetic field generating heat directly within the charge material, bypassing the need to first heat a chamber and then transfer that heat via convection or radiation.
Enabling Continuous Workflow
The system’s ability to heat and cool quickly eliminates the need for long warm-up cycles or batch processing delays. Operations can often be performed directly on the main work floor, reducing material handling time between different stages of production.
Compact, Space-Saving Design
Induction furnaces have a smaller physical footprint compared to traditional furnaces. This compact design saves valuable floor space, which can directly reduce facility overhead and operational costs.
Achieving Superior Metallurgical Quality and Control
The quality of the final cast product is directly tied to the precision of the melting process. Induction technology provides a level of control that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
Enhanced Metal Purity
Because the heat is generated within the metal itself, there are no combustion byproducts like those from burning coke or gas. This eliminates a primary source of contamination, resulting in superior metal purity and a cleaner final alloy.
Precise Process Control
Operators can precisely manage the melting process by adjusting the frequency and power of the electromagnetic field. This constant power output ensures a consistent temperature and a homogenous mix, which is critical for meeting strict metallurgical specifications.
Enhancing Workplace Safety and Environmental Standards
Induction melting represents a fundamental shift toward a safer and cleaner foundry environment.
Eliminating Open Flames and Combustion
The entire process operates without an open flame, fuel storage, or exposed heating elements. This dramatically reduces the risk of fires, explosions, and severe burns associated with traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
Reducing Hazardous Fumes
Operating in a sealed or controlled environment, an induction furnace significantly minimizes the release of toxic fumes and smoke. This creates a safer breathing environment for operators and helps facilities meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While the advantages are significant, a truly objective assessment requires understanding the associated trade-offs. Adopting induction technology is a strategic decision with specific requirements.
Higher Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost for an induction furnace system is often higher than for a conventional cupola or resistance furnace. This investment must be weighed against the long-term operational savings.
Power Grid Dependency
These systems require a stable, high-capacity electrical supply. Facilities may need to invest in upgrading their power infrastructure to support the furnace's demands, adding to the initial project cost.
Material and Refining Limitations
Induction is most effective on electrically conductive metals. Furthermore, while it excels at clean melting, it is less suited for certain types of refining processes that rely on slag chemistry to remove specific impurities, which can be managed more easily in other furnace types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to adopt an induction furnace should be aligned with your primary operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput and profitability: The combination of rapid melting speeds, high energy efficiency (30-80% savings), and reduced labor for material handling will deliver a strong return on investment.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity: The clean, contaminant-free melting environment and precise temperature control make induction the superior choice for producing high-grade alloys for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is improving workplace safety and environmental compliance: The enclosed system, which eliminates open flames and drastically reduces fume exposure, provides an unmatched safety profile.
Ultimately, investing in induction technology empowers you to achieve a faster, cleaner, and more cost-effective melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Speed | Rapid heating to over 2,000°F in under a second, enabling continuous workflow |
| Energy Efficiency | 30-80% energy savings compared to traditional methods |
| Metal Quality | Superior purity with precise temperature control and homogeneous mixing |
| Safety | No open flames, reduced fumes, and enhanced environmental compliance |
| Space Efficiency | Compact design saves floor space and reduces operational costs |
Ready to transform your melting operations with advanced induction technology? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can boost your efficiency, quality, and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















