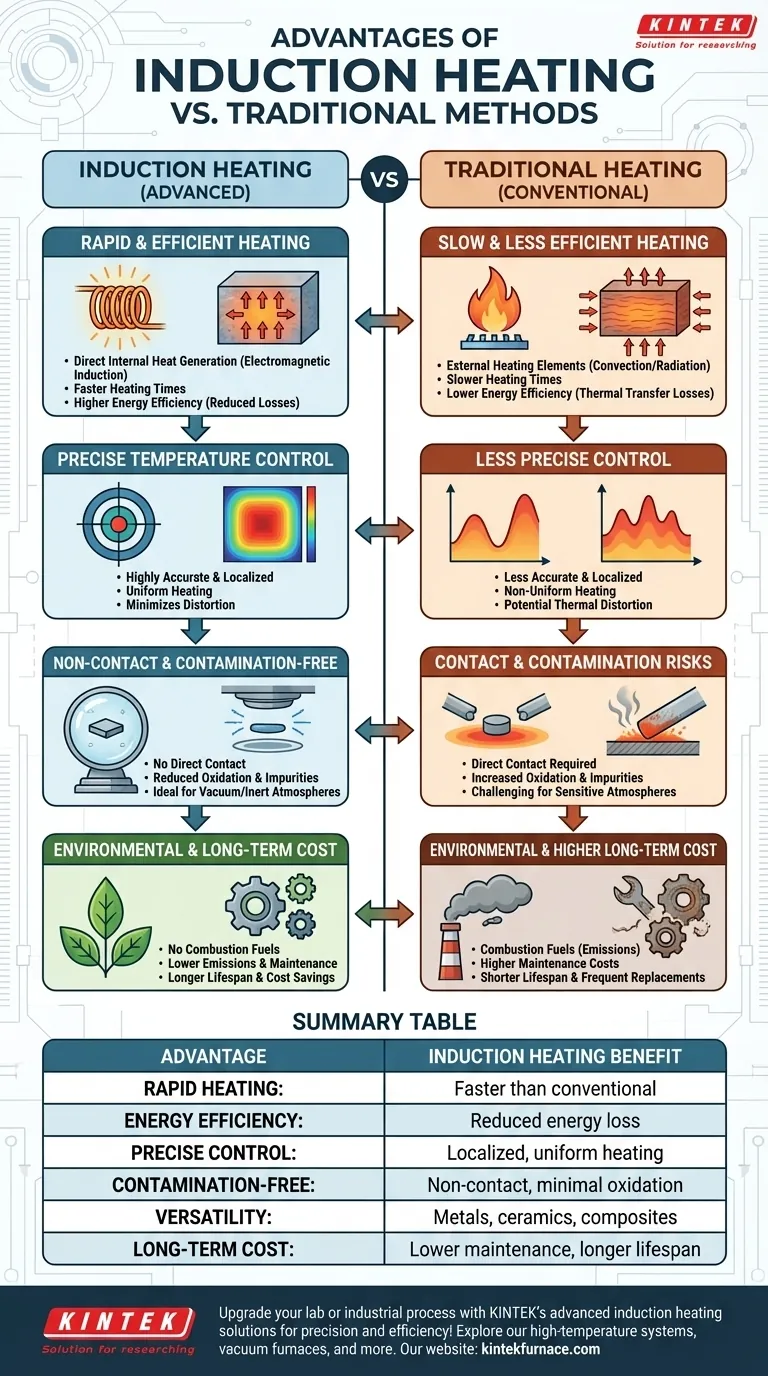
Induction heating provides significant advantages over traditional heating methods, including faster heating times, better energy efficiency, precise temperature control, and reduced contamination risks. It is particularly beneficial in industrial and laboratory settings where speed, accuracy, and cleanliness are critical. The technology's ability to operate in vacuum or inert atmospheres further enhances its suitability for sensitive applications, such as metal processing and high-temperature material treatments.

Key Points Explained:
-
Rapid and Efficient Heating
- Induction heating generates heat directly within the material via electromagnetic induction, eliminating the need for external heating elements.
- This results in faster heating times compared to conventional methods like gas or resistance heating.
- Energy efficiency is improved since heat is produced internally, reducing losses associated with thermal transfer.
-
Precise Temperature Control
- The process allows for highly accurate and localized heating, minimizing thermal distortion in workpieces.
- Automated control systems ensure uniform heating, critical for applications like metal hardening or semiconductor processing.
-
Non-Contact and Contamination-Free
- Since induction heating does not require direct contact between the heating element and the material, contamination risks (e.g., oxidation or impurities) are reduced.
- This makes it ideal for vacuum or inert atmosphere applications, such as in a vacuum furnace price-sensitive environment.
-
Environmental and Operational Benefits
- No combustion fuels are needed, reducing emissions and improving workplace safety.
- Lower energy consumption leads to cost savings over time, despite potentially higher initial setup costs.
-
Versatility in Industrial Applications
- Suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and composites.
- Used in processes like melting, brazing, annealing, and sintering, where traditional methods may be too slow or imprecise.
-
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
- Reduced maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and no direct heating element wear.
- Longer operational lifespans compared to traditional furnaces, making it a more economical choice over time.
By leveraging these advantages, induction heating stands out as a superior solution for industries requiring high precision, efficiency, and cleanliness in thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Heating | Direct electromagnetic induction heats materials faster than conventional methods. |
| Energy Efficiency | Internal heat generation reduces energy loss, lowering operational costs. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables localized, uniform heating for critical applications like metal hardening. |
| Contamination-Free | Non-contact process minimizes oxidation and impurities, ideal for vacuum use. |
| Versatility | Works with metals, ceramics, and composites for melting, brazing, and sintering. |
| Long-Term Cost Savings | Lower maintenance and longer lifespan compared to traditional furnaces. |
Upgrade your lab or industrial process with KINTEK’s advanced induction heating solutions. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures tailored high-temperature systems, including vacuum and atmosphere furnaces, CVD/PECVD reactors, and more. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing with precision and efficiency!
Products You Might Be Looking For:
Explore ultra-high vacuum components for contamination-free heating
Shop high-performance heating elements for electric furnaces
Discover precision vacuum valves for controlled environments
Learn about advanced CVD systems for material processing
View high-vacuum observation windows for real-time monitoring
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















