In vacuum induction melting, operator safety is primarily ensured through a multi-layered system that combines inherent process design, robust engineering controls, and specific operational protocols. The furnace is physically contained, often within a tunnel or enclosure, to isolate personnel from extreme heat and potential melt-related incidents, while operators are required to wear specialized protective clothing for specific tasks.
The extreme heat and vacuum conditions of Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) present significant operational risks. However, safety is not merely an added precaution; it is an inherent design principle of the process, where the furnace's vacuum chamber and the physics of induction heating provide the primary layers of protection.

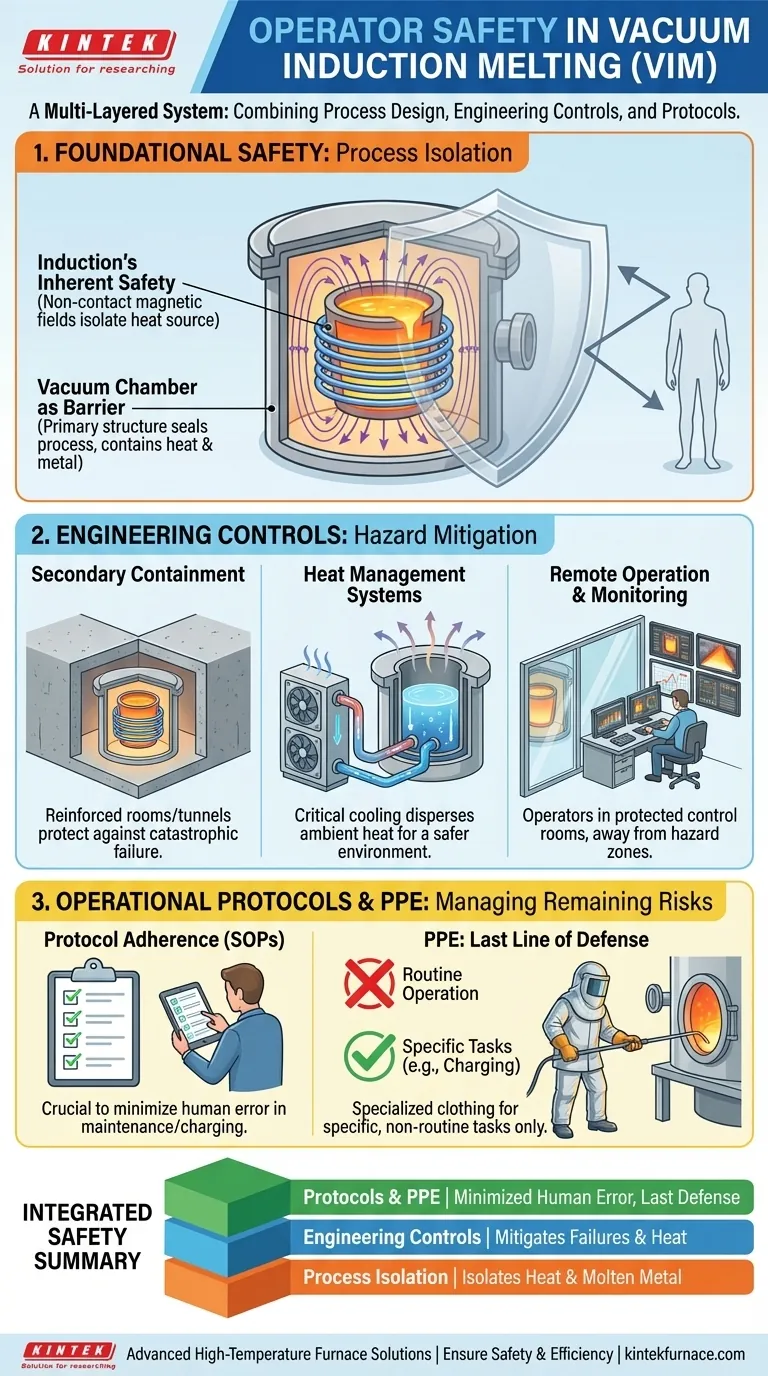
The Foundational Safety Principle: Process Isolation
The safest way to handle a hazard is to isolate it. The VIM process is built around this core concept, using both the laws of physics and the vacuum chamber itself as the first lines of defense.
Induction's Inherent Safety
The power of induction heating lies in its use of non-contact magnetic fields. The induction coil, which generates the heat, remains outside the crucible containing the molten metal.
This means the primary heat source is physically isolated from the workpiece. This fundamental separation allows the entire melting process to be sealed within a robust containment vessel.
The Vacuum Chamber as a Physical Barrier
The vacuum chamber is not just for creating a pure melting environment; it is a primary safety structure. It is designed to contain the immense heat and the molten metal itself.
By sealing the process, the chamber protects operators from direct exposure to heat, radiation, and potential splashes during routine operation.
Engineering Controls for Hazard Mitigation
Beyond the inherent safety of the process, specific engineering controls are implemented to manage residual risks and protect against system failures.
Secondary Structural Containment
High-capacity furnaces are often located inside a reinforced concrete tunnel or a dedicated, segregated room.
This structure acts as a secondary containment barrier. In the event of a catastrophic failure of the primary vacuum chamber, this enclosure is designed to protect the surrounding facility and personnel.
Heat Management Systems
A VIM furnace radiates an enormous amount of heat. Sophisticated cooling systems for the chamber walls and power components are critical for equipment longevity.
These systems also serve a safety function by helping to disperse ambient heat, creating a more controlled and safer environment for any personnel who may need to be in the area.
Remote Operation and Monitoring
Modern VIM systems are operated remotely from a protected control room. This removes the operator from the immediate vicinity of the furnace during the most hazardous phases of melting and pouring.
Continuous monitoring via sensors and cameras allows operators to oversee the process without direct physical exposure, making immediate adjustments from a position of safety.
Understanding the Remaining Risks
No industrial process is without risk. Understanding the limitations and potential points of failure is critical for comprehensive safety management.
The Limits of Containment
The primary risk is a "burn-through," where molten metal breaches the crucible and the vacuum chamber. While rare, this is a severe event that secondary containment is designed to handle.
The Human Element
System integrity relies on proper maintenance and adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs). Human error during charging, sample-taking, or maintenance can introduce risks that engineering controls alone cannot prevent.
The Last Line of Defense: PPE
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as aluminized heat-resistant clothing, is not meant to protect during routine, remote operation.
Instead, it is the last line of defense for workers performing specific tasks that require closer proximity to the furnace, such as charging materials, maintenance, or responding to an off-normal condition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these integrated layers of protection is key to effectively managing risk in any role associated with VIM operations.
- If your primary focus is process engineering: Recognize that the vacuum chamber serves a dual purpose as both a process environment and a primary safety barrier.
- If your primary focus is facility safety: Your priority should be verifying the integrity of secondary containment structures, like tunnels or blast walls, and ensuring heat management systems are always functional.
- If your primary focus is operational management: Emphasize rigorous training on SOPs, as remote operation can mask developing issues if operators are not vigilant and well-trained.
By appreciating safety as a deeply integrated aspect of the technology, you can ensure the integrity and security of your vacuum melting operations.
Summary Table:
| Safety Layer | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Process Isolation | Vacuum chamber, non-contact induction heating | Isolates heat and molten metal, reducing direct exposure |
| Engineering Controls | Secondary containment, cooling systems, remote operation | Mitigates risks from failures and heat dispersion |
| Operational Protocols | SOPs, PPE for specific tasks | Minimizes human error and provides last-line defense |
Ensure unparalleled safety and efficiency in your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability tailors each solution to your unique experimental needs, enhancing operator protection and process integrity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your vacuum induction melting and other high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace and Arc Melting Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of using vacuum melting furnaces? Achieve Superior Purity and Control for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the key features and benefits of a Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace? Achieve High-Purity Metal Production
- What are the advantages of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Superior Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the main applications of vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces? Achieve Unmatched Metal Purity for Critical Industries
- What industries benefit from Vacuum Induction Melting Furnaces? Unlock High-Purity Metals for Aerospace, Medical, and More



















