In induction furnace operations, the most common protective gases are inert gases, specifically argon and, to a lesser extent, helium. These gases are chosen for their chemical inactivity, which prevents the molten metal from reacting with the surrounding atmosphere during the high-temperature melting process.
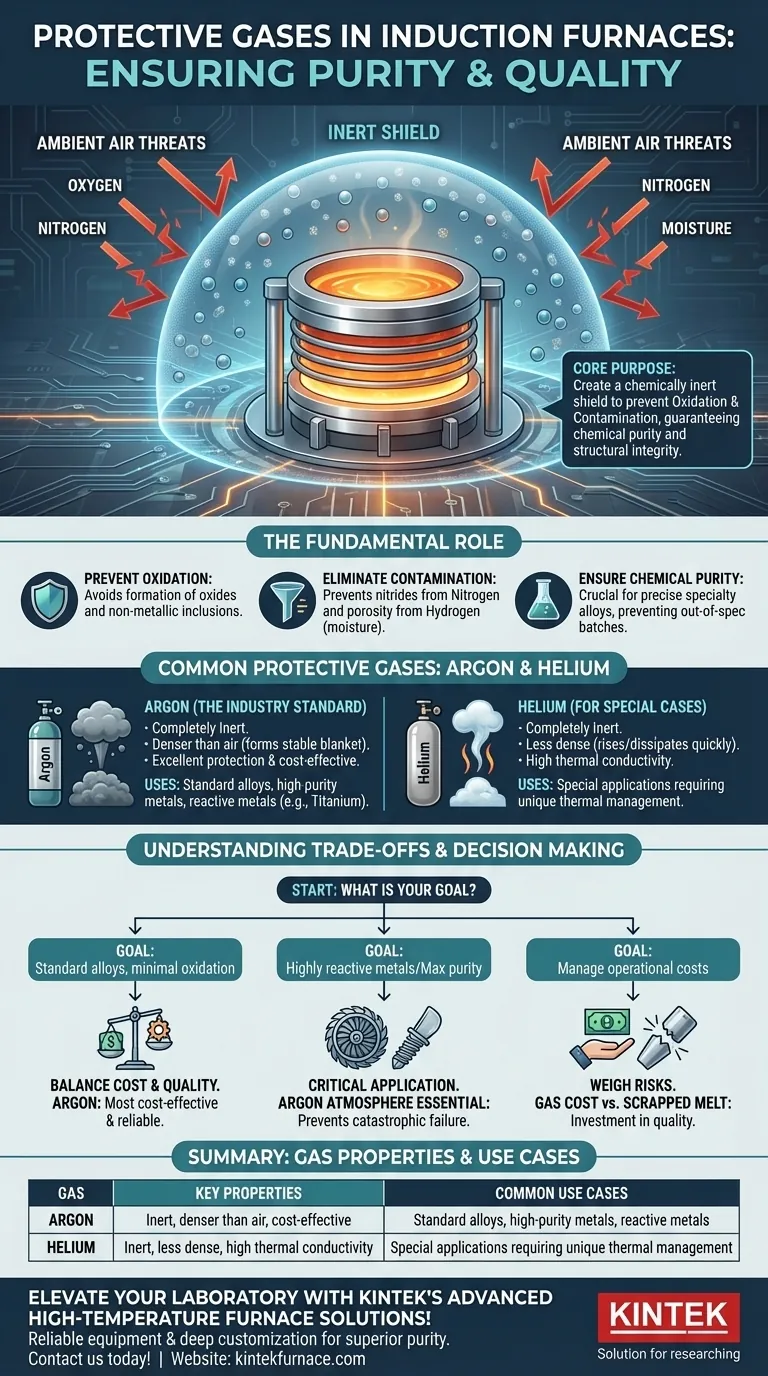
The core purpose of using a protective gas is to create a chemically inert shield around the molten metal. This shield is not merely for preventing surface rust; it is a critical control measure to prevent oxidation and contamination, thereby guaranteeing the chemical purity and structural integrity required for high-specification materials.
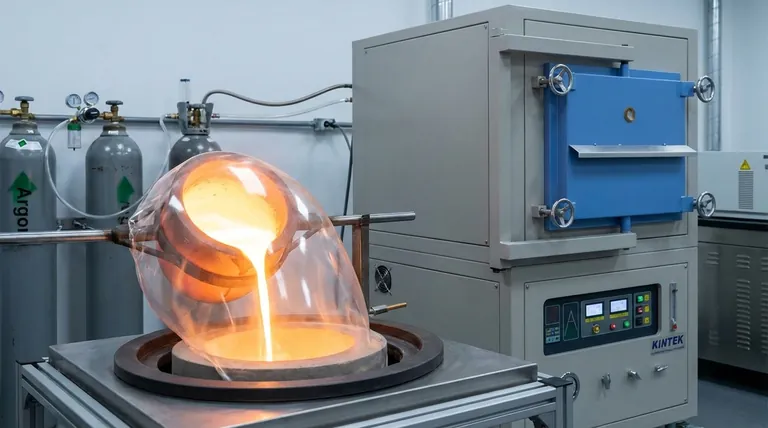

The Fundamental Role of a Protective Atmosphere
When metals are heated to their melting point, they become highly reactive. The ambient air, composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen, becomes a significant source of contamination. A protective atmosphere directly counteracts this threat.
Preventing Oxidation
At high temperatures, oxygen aggressively reacts with most metals to form oxides. This process is not just a surface-level issue; it can introduce non-metallic inclusions into the melt, which compromise the material's final mechanical properties, such as strength and ductility.
Eliminating Contamination
Beyond oxygen, other atmospheric gases like nitrogen and water vapor can also be detrimental. Nitrogen can form unwanted nitrides in certain alloys, while moisture can introduce hydrogen, leading to porosity or hydrogen embrittlement in the solidified metal.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
For industries producing specialty alloys, the chemical composition must be controlled with extreme precision. Unwanted reactions with atmospheric gases can alter this delicate balance, shifting the alloy out of specification and rendering the entire batch useless.
A Closer Look at Common Protective Gases
The choice of gas is dictated by its properties, effectiveness, and cost. While several inert gases exist, one stands out as the industry standard.
Argon: The Industry Standard
Argon is the most widely used protective gas in induction furnaces. It is completely inert and will not react with the molten metal, even at extreme temperatures.
Because argon is denser than air, it can effectively form a stable "blanket" over the surface of the melt, displacing the reactive atmosphere. It provides excellent protection and is relatively cost-effective compared to other inert gases.
Helium: For Special Cases
Helium is another inert gas that can be used. While it provides the same inertness as argon, its physical properties are quite different.
Helium is much less dense than air, so it will rise and dissipate quickly rather than forming a stable blanket. It also has a much higher thermal conductivity. These properties make it less common for general use but potentially valuable for very specific applications where its unique thermal characteristics are desired.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Implementing a protective gas atmosphere is a decision that involves balancing cost, complexity, and quality requirements.
Cost vs. Quality
The primary trade-off is the cost of the gas and the required delivery system versus the value of the material being produced. For low-cost, non-critical metals, the expense may not be justified. For high-purity or reactive alloys, the cost of the gas is negligible compared to the cost of a failed or rejected melt.
Application Determines Necessity
Industries such as aerospace, medical manufacturing, and electronics rely on materials with zero defects. For components like turbine blades or biomedical implants, any contamination can lead to catastrophic failure. In these contexts, using a protective argon atmosphere is not a choice but a mandatory process requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a protective gas, and which one to use, should be directly tied to your final product requirements.
- If your primary focus is producing standard alloys with minimal oxidation: Argon provides the most cost-effective and reliable protection for most applications.
- If your primary focus is working with highly reactive metals (like titanium) or achieving maximum purity: A strictly controlled argon atmosphere is essential for meeting material specifications and preventing catastrophic batch failure.
- If your primary focus is managing operational costs: You must weigh the expense of the inert gas against the much higher financial risk of a scrapped melt or a component failure.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is a direct investment in the quality and reliability of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Key Properties | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Argon | Inert, denser than air, cost-effective | Standard alloys, high-purity metals, reactive metals like titanium |
| Helium | Inert, less dense, high thermal conductivity | Special applications requiring unique thermal management |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior metal purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















