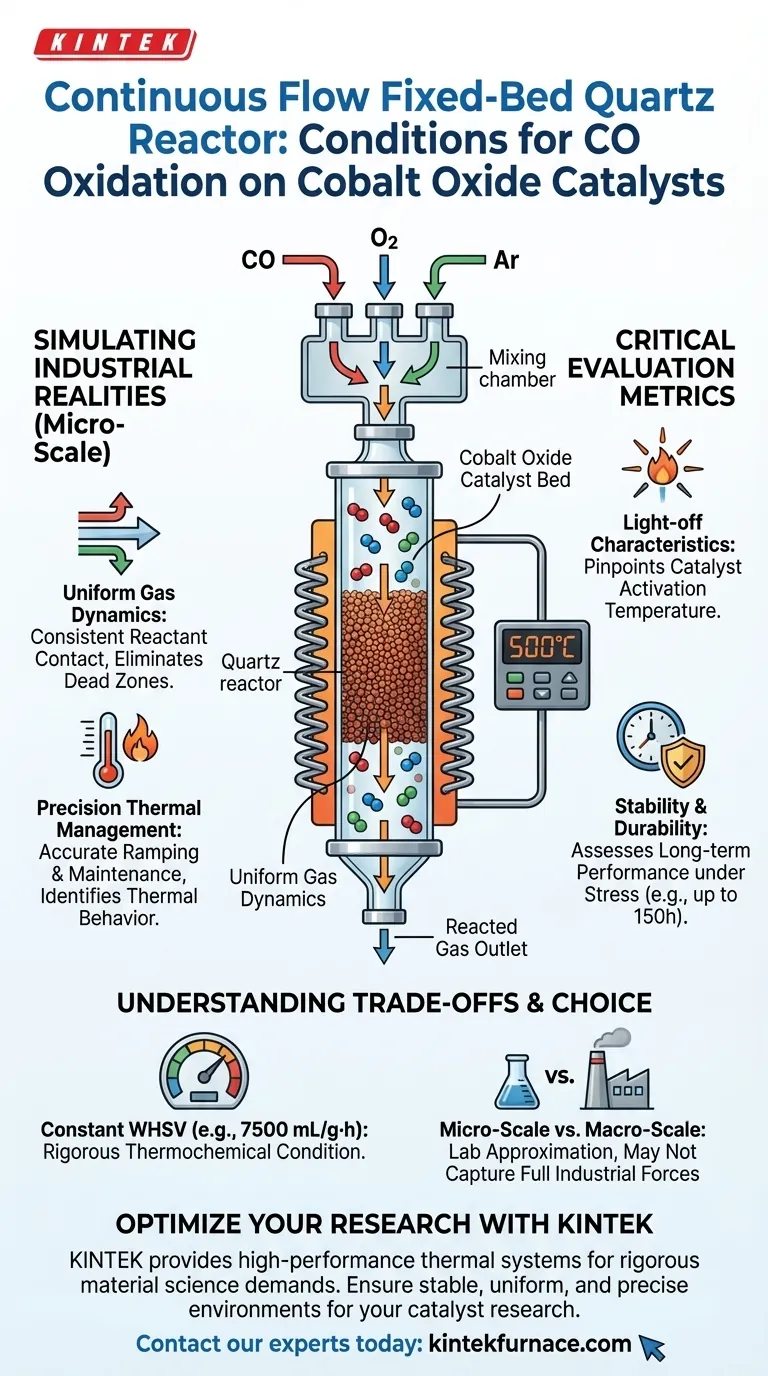
A continuous flow fixed-bed quartz reactor provides a highly controlled micro-reaction environment designed to replicate industrial realities. This setup ensures that critical reaction gases—specifically carbon monoxide (CO), oxygen, and argon—flow uniformly through the cobalt oxide catalyst bed. By integrating a high-precision temperature control system, the reactor creates the stable conditions necessary to accurately measure catalyst efficiency and durability.
The reactor's primary value lies in its ability to simulate actual industrial operating conditions on a micro-scale. This allows researchers to isolate specific performance variables, such as light-off temperature and structural stability, without the interference of environmental fluctuations.

Simulating Industrial Realities
Uniform Gas Dynamics
The reliability of your data depends entirely on the consistency of the reactant contact. This reactor type ensures that the gas mixture (CO, O2, and Ar) flows uniformly through the fixed bed.
This uniformity eliminates "hot spots" or dead zones within the catalyst bed. It guarantees that every particle of the cobalt oxide catalyst is subjected to the same chemical potential.
Precision Thermal Management
To evaluate catalysts derived from different microalgae sources or calcination temperatures, thermal accuracy is non-negotiable. The system utilizes high-precision temperature control, often employing components like K-type thermocouples.
This allows for the precise ramping and maintenance of heat. It enables you to determine exactly how the catalyst behaves across a spectrum of temperatures, rather than just at a single set point.
Critical Evaluation Metrics
Determining Light-off Characteristics
One of the most critical performance metrics for CO oxidation is the "light-off" temperature—the point at which the catalyst becomes active. The reactor's controlled environment allows you to pinpoint this threshold with high accuracy.
By ramping temperatures systematically, you can identify the exact moment oxidation begins. This data is essential for comparing the efficacy of catalysts prepared under different calcination conditions.
Assessing Stability and Durability
Beyond initial activity, the reactor allows for the evaluation of stability over time. It can simulate rigorous conditions to test if the catalyst maintains its structure and activity or degrades.
Supplementary data suggests these reactors can maintain conditions for extended periods (up to 150 hours) at high temperatures (500°C–550°C). This reveals the catalyst's resistance to thermal stress and structural collapse.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Rigor of Constant Space Velocity
While beneficial for standardization, these reactors often maintain a constant Weight Hourly Space Velocity (WHSV) (e.g., 7500 mL/g·h).
This imposes a rigorous thermochemical condition on the catalyst. If the catalyst has weak atomic synergistic active sites, this constant high-velocity flow may lead to rapid deactivation that might not occur under gentler conditions.
Micro-Scale vs. Macro-Scale
This equipment provides a micro-reaction environment. While it simulates industrial conditions effectively, it remains a lab-scale approximation.
Factors such as massive heat gradients or physical crushing forces present in a full-scale industrial reactor may not be fully captured in a quartz tube setup.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a continuous flow fixed-bed quartz reactor, align your testing parameters with your specific data requirements:
- If your primary focus is Activity Profiling: Prioritize the precision temperature control features to accurately map the light-off curve of the CO oxidation reaction.
- If your primary focus is Lifecycle Analysis: Utilize the system's ability to maintain constant WHSV and temperature over long durations (100+ hours) to stress-test the catalyst's structural stability.
By leveraging the precise control of gas flow and temperature, you transform raw chemical potential into actionable engineering data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Condition Provided | Benefit to CO Oxidation Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Dynamics | Uniform flow of CO, O2, and Ar | Eliminates dead zones; ensures consistent reactant contact. |
| Thermal Control | High-precision ramping & maintenance | Accurately identifies "light-off" temperature and thermal behavior. |
| Operating Mode | Continuous flow at constant WHSV | Simulates industrial environments to test durability and stability. |
| Environment | Controlled Micro-reaction (Quartz) | Isolates performance variables and prevents environmental interference. |
Optimize Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of reliable CO oxidation performance data. KINTEK provides high-performance, customizable thermal systems—including Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD reactors—engineered to meet the rigorous demands of modern material science.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our equipment ensures the stable, uniform, and high-precision environments your cobalt oxide catalysts require. Whether you need a standard setup or a bespoke reactor for unique research conditions, KINTEK delivers the durability and accuracy your lab deserves.
Ready to elevate your research efficiency? Contact our experts today to find your perfect solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Agnieszka Sidorowicz, Günther Rupprechter. Microalgae-derived Co<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub> nanomaterials for catalytic CO oxidation. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra00343h
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why use a tube furnace for TiO2–TiN/S heat treatment? Achieve Perfect Sulfur Infusion and Purity
- What is the function of a multi-zone tube furnace in CVD synthesis? Master 2D In2Se3 Nanosheet Precision
- Can split tube furnaces be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations? Maximize Your Lab's Efficiency with Flexible Setup
- What role does a tube furnace play in the one-step pyrolysis of Fe-BN-C catalysts? Precision Synthesis Explained
- Why is a tube high-temperature furnace required for Au@MoSe2/graphene composites? Precision Reaction Control
- What is the function of a tube furnace during the CVD growth of WS2 monolayers? Expert Thermal Control Guide
- Why is a high-purity argon environment required in a high-temperature tube furnace for ceramic scaffolds?
- What is the primary function of a CVD tube furnace in the preparation of Multi-Layer Graphene? Expert Guide



















