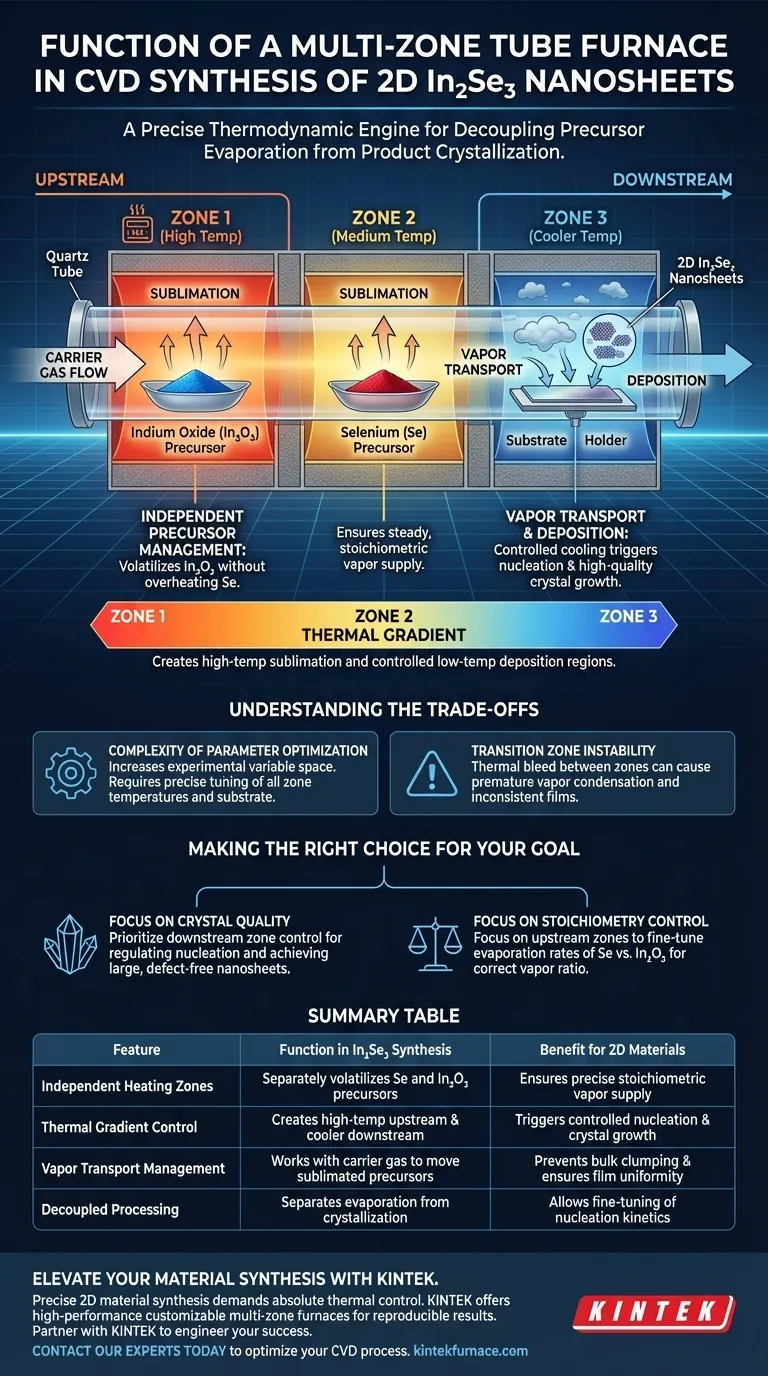
A multi-zone tube furnace serves as the precise thermodynamic engine required to synthesize two-dimensional beta-prime In2Se3 nanosheets via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Its primary function is to provide independent, isolated heating environments for different precursors—specifically selenium and indium oxide powders—while maintaining a distinct thermal gradient for deposition. This architecture ensures that precursors volatilize at high upstream temperatures and are transported by a carrier gas to crystallize on substrates in cooler downstream zones.
The core value of a multi-zone furnace is the ability to decouple precursor evaporation from product crystallization. By managing these two processes in separate thermal zones, you can precisely tune vapor density and nucleation kinetics, which is impossible in a single-zone setup.

The Mechanics of Controlled Synthesis
Independent Precursor Management
In the synthesis of complex binary materials like In2Se3, the precursors often have vastly different volatility profiles. A multi-zone furnace allows you to place selenium and indium oxide in separate heating zones. You can heat the selenium to its specific volatilization point without overheating or prematurely reacting the indium source, ensuring a steady and stoichiometric vapor supply.
Establishing the Thermal Gradient
The defining feature of this equipment is the ability to maintain a specific temperature gradient along the length of the tube. The furnace creates a high-temperature region upstream to drive sublimation and a controlled lower-temperature region downstream. This spatial difference is critical for guiding the thermodynamic flow of the reaction.
Vapor Transport and Deposition
Once the precursors are volatilized, an inert carrier gas transports the vapor downstream. As the vapor enters the cooler deposition zone, the drop in temperature forces the material to supersaturate. This controlled cooling, enabled by the multi-zone design, triggers the nucleation and growth of high-quality two-dimensional crystals on the substrate rather than bulk, uncontrolled clumps.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Parameter Optimization
While multi-zone furnaces offer superior control, they significantly increase the experimental variable space. You must simultaneously optimize the temperature for the indium source, the selenium source, and the substrate. A slight misalignment in any zone can disrupt the vapor pressure balance, leading to poor stoichiometry or incomplete reactions.
Transition Zone Instability
The areas between heated zones can suffer from thermal bleed, where heat from a high-temperature zone affects a neighboring cooler zone. If the gradient is not sharp enough, vapors may condense prematurely in the transition region. This results in wasted precursor material and potentially inconsistent film thickness on the actual target substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a multi-zone furnace for In2Se3 synthesis, align your setup with your specific research priority:
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Prioritize precise temperature control in the downstream zone to strictly regulate nucleation kinetics and ensure large, defect-free nanosheets.
- If your primary focus is Stoichiometry Control: Focus on the upstream zones to fine-tune the evaporation rates of Selenium vs. Indium Oxide, ensuring the correct ratio of vapors reaches the substrate.
Mastering the thermal profile of your multi-zone furnace is the definitive step in transitioning from random deposition to the engineering of reproducible 2D materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in In2Se3 Synthesis | Benefit for 2D Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Independent Heating Zones | Separately volatilizes Se and In2O3 precursors | Ensures precise stoichiometric vapor supply |
| Thermal Gradient Control | Creates high-temp upstream and cooler downstream zones | Triggers controlled nucleation and crystal growth |
| Vapor Transport Management | Works with carrier gas to move sublimated precursors | Prevents bulk clumping and ensures film uniformity |
| Decoupled Processing | Separates evaporation from crystallization | Allows fine-tuning of nucleation kinetics |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise 2D material synthesis demands absolute thermal control. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous standards of modern laboratory research.
Whether you are synthesizing In2Se3 nanosheets or developing custom thin-film applications, our fully customizable multi-zone furnaces provide the thermal stability and gradient precision necessary for reproducible results. Don't let thermal instability compromise your research—partner with KINTEK to engineer your success.
Ready to optimize your CVD process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Fan Zhang, Chenggang Tao. Atomic-scale manipulation of polar domain boundaries in monolayer ferroelectric In2Se3. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44642-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of CVD tube furnace sintering systems? Achieve Superior Material Control and Purity
- How are hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) films processed using CVD tube furnaces? Optimize Growth for High-Quality 2D Materials
- What customization options are available for CVD tube furnaces? Tailor Your System for Superior Material Synthesis
- What are 2D heterostructures and how are they created using CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Atomic-Scale Material Engineering
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab



















