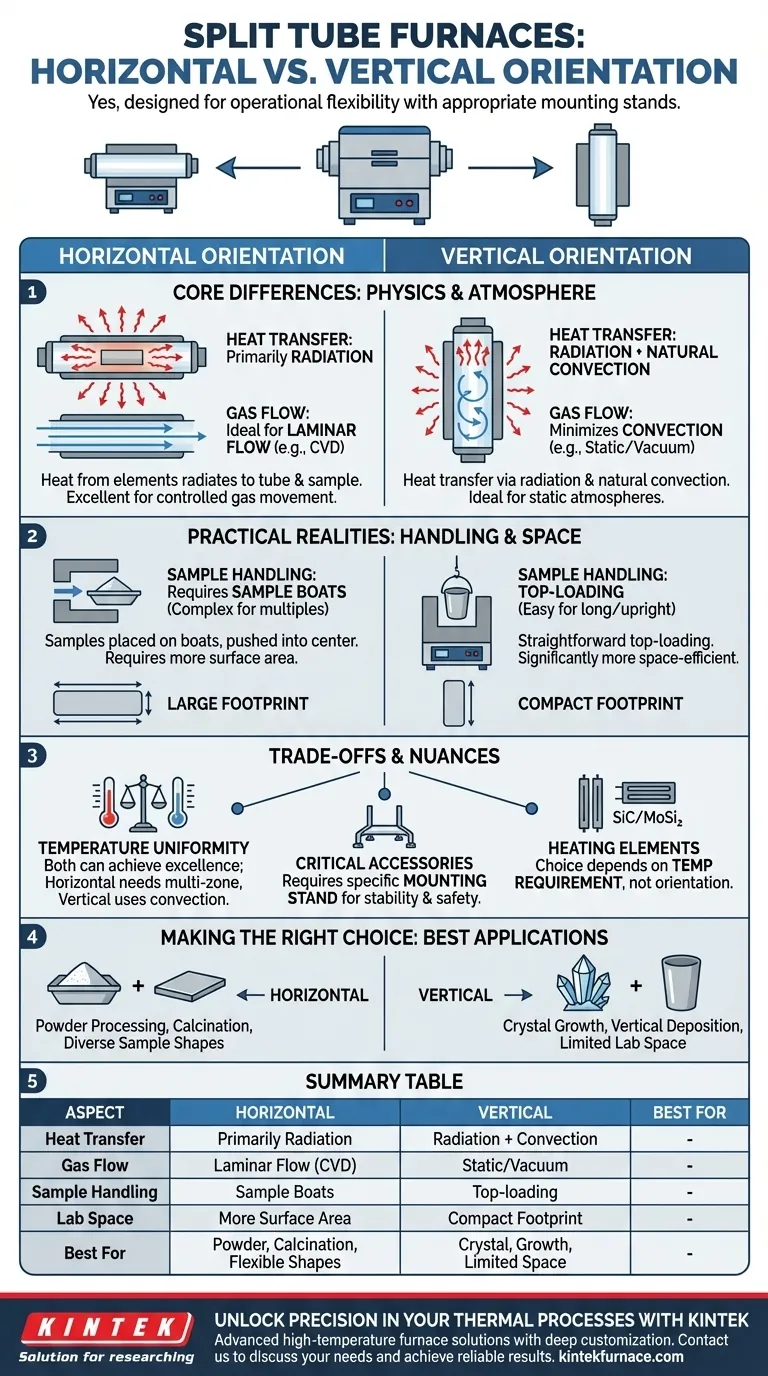
Yes, a split tube furnace is designed for operational flexibility. It can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations, but this versatility depends on having the appropriate mounting stands and support accessories. The ability to reorient the furnace allows you to tailor the thermal processing environment to the specific demands of your experiment.
The choice between a horizontal or vertical orientation is not about which is "better," but which is strategically correct for your application. The furnace's orientation directly impacts heat transfer, gas flow dynamics, and the practicalities of handling your sample.
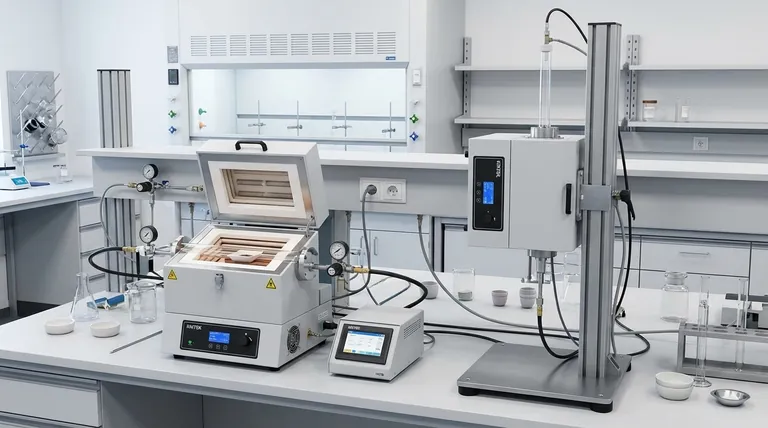

The Core Difference: How Orientation Impacts Your Process
Choosing an orientation is a fundamental decision that affects the physics inside the furnace tube. Understanding these differences is key to achieving repeatable and accurate results.
The Physics of Heat Transfer
In a vertical furnace, the heating elements surround the process tube, and heat is transferred through both radiation and natural convection. Hot air or gas naturally rises, creating a thermal current that can help promote temperature uniformity along the sample's length.
In a horizontal furnace, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation from the elements to the process tube and sample. While highly effective, this can sometimes lead to slight temperature variations along the length of the sample if not properly calibrated, as natural convection plays a lesser role.
Controlling the Atmosphere
A horizontal orientation is often superior for processes requiring controlled gas movement. It allows for a laminar gas flow from one end to the other, making it ideal for applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) where precursor gases must flow evenly over a substrate.
A vertical orientation excels at minimizing gas movement. It is ideal for static atmosphere or vacuum applications where you want to reduce the effects of convection currents, such as in certain crystal growth or annealing processes.
Practical Realities: Sample Handling and Lab Space
Beyond the thermal science, the physical layout and usability of the furnace are critical factors in a daily laboratory setting.
Sample Loading and Positioning
Vertical furnaces offer straightforward top-loading, which is highly advantageous for long samples or crucibles that need to sit upright. Samples can be easily lowered into and lifted out of the hot zone.
Horizontal furnaces require samples to be placed on a "boat" or holder and pushed into the center of the tube. This can be more complex, especially when positioning multiple samples or ensuring they don't touch the tube walls.
Footprint and Laboratory Layout
Vertical furnaces have a significantly more compact footprint. Their tower-like design makes them perfect for labs with limited bench or floor space.
Horizontal furnaces are longer and require more dedicated surface area or floor space. Their layout can be beneficial for integrating with other linear processing equipment but is less space-efficient overall.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
A split tube furnace's flexibility comes with considerations that must be managed to ensure successful operation.
The Myth of Temperature Uniformity
While the physics differs, both orientations can achieve excellent temperature uniformity. A vertical furnace's natural convection can be an advantage, but a well-designed horizontal furnace with multi-zone heating control can produce an exceptionally stable and uniform hot zone.
The Critical Role of Accessories
You cannot simply turn a furnace on its side. Switching from horizontal to vertical (or vice versa) requires the manufacturer-specified mounting stand. This ensures stability, proper airflow for cooling the furnace body, and operator safety.
Heating Elements and Temperature
The choice of heating element—such as silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) —is determined by your maximum temperature requirement, not the furnace's orientation. Both horizontal and vertical models can be equipped with high-temperature elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your furnace orientation based on your primary experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is powder processing or calcination: A horizontal orientation is often preferred for spreading material evenly in a sample boat.
- If your primary focus is crystal growth or vertical deposition: A vertical orientation provides gravitational stability and minimizes unwanted convective currents.
- If your primary focus is simple annealing with diverse sample shapes: A horizontal furnace provides flexibility for placing samples of varying dimensions.
- If your lab space is extremely limited: A vertical orientation is the clear and practical choice for its smaller footprint.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select a furnace configuration that serves as a precise tool for your scientific goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Horizontal Orientation | Vertical Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Primarily radiation; may have slight variations | Radiation and natural convection for better uniformity |
| Gas Flow Control | Ideal for laminar flow (e.g., CVD processes) | Minimizes convection; good for static/vacuum applications |
| Sample Handling | Requires sample boats; can be complex for multiple samples | Top-loading; easy for long or upright samples |
| Lab Space | Requires more surface area | Compact footprint; space-efficient |
| Best For | Powder processing, calcination, flexible sample shapes | Crystal growth, vertical deposition, limited space labs |
Unlock Precision in Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need a split tube furnace for horizontal or vertical use, we ensure optimal performance, safety, and efficiency tailored to your specific applications like powder processing, crystal growth, or CVD.
Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's capabilities and achieve reliable, repeatable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















