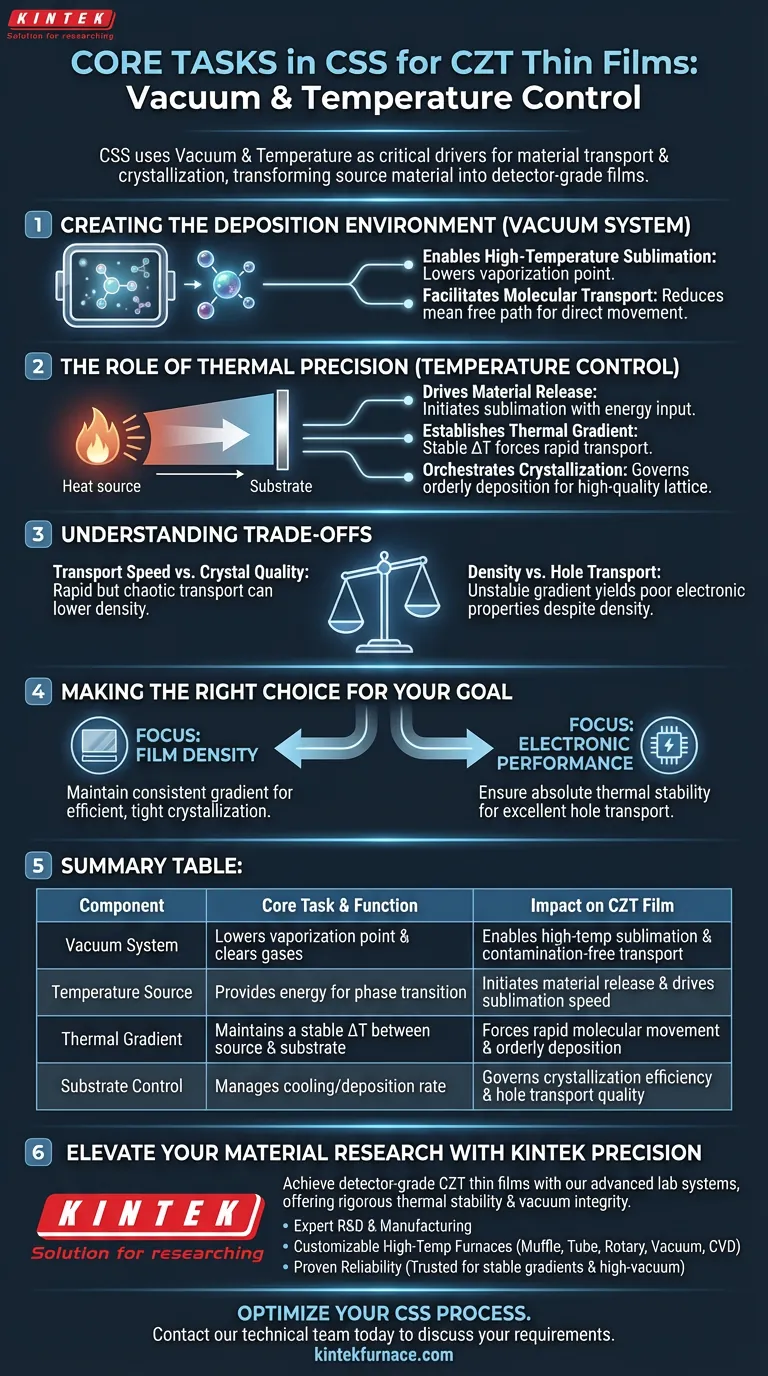
In the fabrication of Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CZT) thin films using Close-Spaced Sublimation (CSS), the vacuum and temperature control systems function as the critical drivers for material transport and crystallization. The vacuum system creates the necessary low-pressure environment to enable sublimation, while the temperature control system establishes a precise thermal gradient between the source and substrate to force the rapid movement and orderly deposition of molecules.
By maintaining a stable temperature difference in a vacuum, CSS equipment transforms raw source material into dense, detector-grade thin films characterized by excellent hole transport capabilities.
Creating the Deposition Environment
The vacuum system is the foundational element of the CSS process. It clears the stage for the physical physics of sublimation to occur without interference.
Enabling High-Temperature Sublimation
The primary task of the vacuum environment is to lower the vaporization point of the material. This allows the CZT source to sublime—transition directly from solid to vapor—effectively when subjected to high temperatures.
Facilitating Molecular Transport
By removing atmospheric gases, the vacuum reduces the mean free path necessary for the molecules to travel. This ensures that the vapor moves directly from the source to the substrate with minimal scattering or contamination.
The Role of Thermal Precision
While the vacuum enables the process, the temperature control system acts as the engine. It dictates the speed, quality, and structure of the film growth.
Driving Material Release
The system must generate sufficiently high temperatures at the source material. This energy input is what initiates the sublimation process, releasing CZT molecules into the gap between the plates.
Establishing the Thermal Gradient
The most critical task of the thermal system is maintaining a stable temperature difference between the source and the substrate. Because the source and substrate are placed in extremely close proximity, this gradient must be tightly controlled to prevent thermal equilibrium.
Orchestrating Crystallization
The temperature difference drives the transport of vapor toward the cooler substrate. The precision of this control governs the efficient crystallization of the material upon arrival, ensuring the atoms arrange themselves into a high-quality lattice structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving "detector-grade" quality requires balancing speed with stability. It is not enough to simply heat the material; the parameters must be tuned for specific outcomes.
Transport Speed vs. Crystal Quality
The thermal setup is designed to facilitate rapid transport of molecules. However, if the transport is too chaotic due to unstable temperatures, the film density may suffer.
Density vs. Hole Transport
The ultimate goal is to produce dense films with excellent hole transport capabilities. A system that cannot maintain a stable gradient may produce films that look physically dense but lack the electronic properties required for high-performance detection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of the CSS method, you must align your equipment settings with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Film Density: Prioritize a temperature control system that can maintain a consistent gradient to ensure efficient, tight crystallization.
- If your primary focus is Electronic Performance: Ensure the thermal stability is absolute, as this directly influences the hole transport capabilities of the final detector-grade film.
Success in CSS fabrication depends on the rigorous stability of the thermal gradient within the vacuum environment.
Summary Table:
| System Component | Core Task & Function | Impact on CZT Film |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers vaporization point & clears atmospheric gases | Enables high-temp sublimation & contamination-free transport |
| Temperature Source | Provides energy for phase transition | Initiates material release and drives sublimation speed |
| Thermal Gradient | Maintains a stable ΔT between source and substrate | Forces rapid molecular movement and orderly deposition |
| Substrate Control | Manages cooling/deposition rate | Governs crystallization efficiency and hole transport quality |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving detector-grade CZT thin films requires the absolute thermal stability and vacuum integrity found in KINTEK’s advanced laboratory systems. Whether you are focused on maximizing film density or enhancing hole transport capabilities, our equipment provides the rigorous control necessary for successful Close-Spaced Sublimation.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Precision-engineered solutions for high-performance material deposition.
- Customizable High-Temp Furnaces: Choose from Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your unique research needs.
- Proven Reliability: Trusted by global labs for maintaining stable thermal gradients and high-vacuum environments.
Ready to optimize your CSS process? Contact our technical team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab’s efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Z. J. Li, Zeqian Wu. Research on the Technological Progress of CZT Array Detectors. DOI: 10.3390/s24030725
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- Can you describe a process example using a vacuum hardening furnace? Achieve Clean, Precise Metal Hardening
- What are the main industrial applications of vacuum melting furnaces? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is a laboratory vacuum furnace and what environment does it create? Achieve Purity in High-Temp Processing
- What are some industrial applications of high vacuum furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Electronics
- How can the cooling rate of vacuum sintering be increased? Boost Efficiency with Gas-Assisted Cooling
- What is the maximum temperature a vacuum furnace can reach? Up to 2600°C for Advanced Materials Processing
- What is the purpose of using vacuum testing equipment? Achieve 100% Casting Quality via Density Index



















