In short, high vacuum furnaces are indispensable in industries where material failure is not an option, including aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and advanced electronics. These systems are used for processes like heat treatment and brazing to create components that require exceptional purity, strength, and reliability by processing them in a controlled, contaminant-free environment.
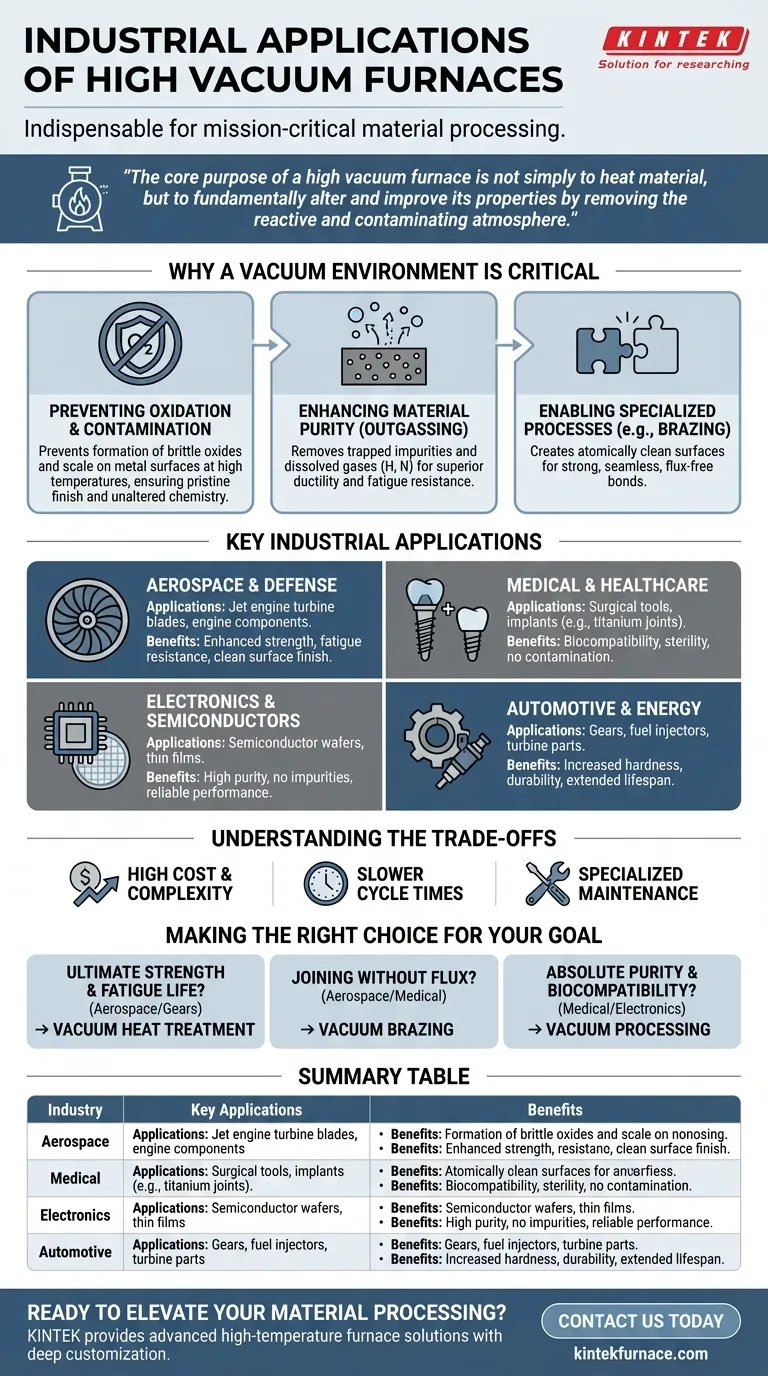
The core purpose of a high vacuum furnace is not simply to heat material, but to fundamentally alter and improve its properties by removing the reactive and contaminating atmosphere that would otherwise compromise its integrity at high temperatures.

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
To understand the applications, you must first understand the problem a vacuum solves. At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, metals become highly reactive. A vacuum furnace creates an environment that prevents these unwanted reactions.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At elevated temperatures, oxygen and other trace gases in the air will aggressively react with a metal's surface, forming oxides. This creates a brittle, discolored scale that weakens the component and ruins its surface finish.
A high vacuum environment removes these reactive gases. This ensures the material's surface remains pristine and its internal chemistry is unaltered, which is critical for performance.
Enhancing Material Purity
Beyond preventing surface reactions, a vacuum can actively purify the material itself. The process, known as outgassing, pulls trapped impurities and dissolved gases (like hydrogen and nitrogen) out from within the metal's structure.
This purification process leads to materials with superior mechanical properties, such as increased ductility and fatigue resistance.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain manufacturing processes are only possible in a vacuum. For example, vacuum brazing joins two components using a filler metal that melts and flows between them.
This process requires atomically clean surfaces to form a strong, seamless bond. A vacuum provides the perfect environment, eliminating the need for corrosive chemical fluxes used in atmospheric brazing.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The principles of purity and control directly enable the manufacturing of mission-critical components across several key sectors.
Aerospace and Defense
Components like jet engine turbine blades operate under extreme stress and temperatures. Vacuum heat treatment ensures they have the required structural consistency and strength to prevent catastrophic failure.
The process produces a bright, clean surface finish that requires no subsequent cleaning, preserving the precise dimensions of the aerodynamically-shaped blades.
Medical and Healthcare
Surgical tools and implants, such as titanium hip joints or dental posts, must be perfectly biocompatible. Any surface contamination or oxide layer could be rejected by the human body.
Vacuum furnaces create the ultra-clean, sterile, and passive surfaces necessary for these devices to function safely and effectively inside the body.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The production of semiconductor wafers and other electronic components demands the highest level of purity. Even microscopic contaminants can disrupt electrical pathways and ruin an entire batch of microchips.
Vacuum processing provides the stringently controlled environment needed for depositing thin films and annealing components without introducing performance-degrading impurities.
Automotive and Energy
High-performance gears, fuel injectors, and components for power generation turbines are subjected to intense wear and pressure.
Vacuum heat treatment and carburizing enhance the surface hardness and core strength of these parts, dramatically increasing their lifespan and reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are a specialized technology with specific operational considerations.
High Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. They are complex systems requiring sophisticated pumps, seals, and control instrumentation.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a high vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber, run the thermal cycle, and cool the load under vacuum can be significantly longer than for atmospheric processes.
Specialized Maintenance
The components that create and maintain the vacuum, such as pumps and seals, require regular and specialized maintenance to ensure the system performs to specification and avoids costly downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven entirely by the required final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material strength and fatigue life: Vacuum heat treatment is non-negotiable for mission-critical parts like turbine blades or high-performance gears.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, sensitive components without flux: Vacuum brazing provides the clean environment needed for strong, void-free bonds in aerospace and medical assemblies.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity and biocompatibility: Vacuum processing is the only way to guarantee the inert, contaminant-free surfaces required for medical implants and electronics.
Ultimately, adopting high vacuum technology is a commitment to creating materials with properties that are simply unattainable in a standard atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Turbine blades, engine components | Enhanced strength, fatigue resistance, clean surface finish |
| Medical & Healthcare | Surgical tools, implants (e.g., titanium joints) | Biocompatibility, sterility, no contamination |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Semiconductor wafers, thin films | High purity, no impurities, reliable performance |
| Automotive & Energy | Gears, fuel injectors, turbine parts | Increased hardness, durability, extended lifespan |
Ready to elevate your material processing with high vacuum solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs in aerospace, medical, electronics, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable, contaminant-free furnaces can enhance your component performance and drive innovation in your industry!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















