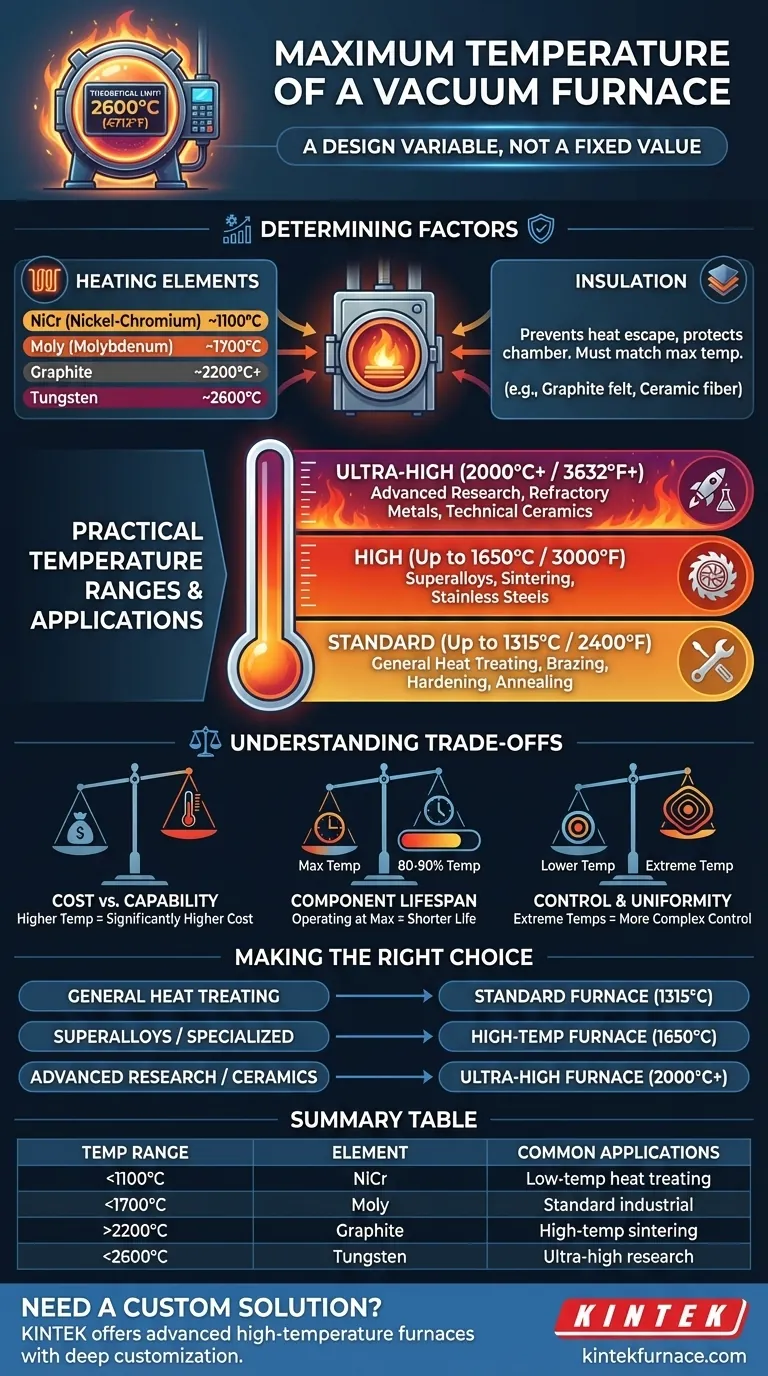
In principle, a vacuum furnace can be designed to reach temperatures as high as 2600°C (4712°F). However, the vast majority of industrial and laboratory furnaces operate within specific, lower temperature ranges determined by their construction and intended application.
The maximum temperature of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but a design variable. It is dictated by the materials used for its heating elements and insulation, with different models engineered for specific thermal processing needs from standard annealing to advanced ceramics sintering.

What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The theoretical temperature limit is a function of the materials used in the furnace's "hot zone"—the internal area that reaches the target temperature. Two components are the primary limiting factors.
The Role of Heating Elements
Heating elements are the heart of the furnace, converting electrical energy into heat. The material used for these elements directly determines the maximum achievable temperature.
- Nickel-Chromium (NiCr): Common for lower-temperature applications, typically maxing out around 1100°C.
- Molybdenum (Moly): Used for standard and high-temperature furnaces, capable of reaching up to 1700°C.
- Graphite: The standard for many high-temperature applications, reliably operating up to 2200°C and even higher in specialized designs.
- Tungsten: Employed for ultra-high temperature needs, enabling furnaces to exceed 2200°C and approach the 2600°C limit.
The Importance of Insulation
Insulation prevents heat from escaping the hot zone and protects the water-cooled vacuum chamber walls. The choice of insulation must be compatible with the maximum operating temperature.
Common insulation materials include layered graphite felt, rigid graphite fiberboard, or ceramic fiber materials. An insulation package rated for only 1300°C cannot be used in a furnace with graphite elements designed for 2000°C.
Common Temperature Ranges in Practice
Commercially available vacuum furnaces are typically offered in series, with each series defined by its maximum temperature and designed for specific industrial processes.
Standard Industrial Furnaces (Up to 1315°C / 2400°F)
This is the most common range, covering a huge number of heat-treating processes. These furnaces are workhorses for applications like brazing, hardening, tempering, and annealing of standard steels and alloys.
High-Temperature Furnaces (Up to 1650°C / 3000°F)
This range is required for processing more specialized materials, such as stainless steels, superalloys, and certain ceramics. They provide the higher thermal energy needed for processes like sintering and stress-relieving high-performance components.
Ultra-High Temperature Furnaces (2000°C+ / 3632°F+)
Reserved for the most demanding applications, these furnaces are used for advanced materials research, sintering of refractory metals (like tungsten and tantalum), and firing technical ceramics. Reaching these temperatures requires specialized graphite or tungsten elements and robust insulation packages.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace based on its maximum temperature involves significant trade-offs in cost, longevity, and operational complexity.
Cost vs. Capability
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its cost. The exotic materials required for ultra-high temperature elements (tungsten) and insulation are significantly more expensive than standard molybdenum and ceramic fiber systems.
Component Lifespan
Continuously operating a furnace at its absolute maximum rated temperature will drastically shorten the life of its heating elements and insulation. For optimal longevity and reliability, it is best to choose a furnace where your target process temperature is around 80-90% of its maximum rating.
Control and Uniformity
While modern systems offer exceptional process control (often to within +/- 1°C), maintaining strict temperature uniformity becomes more challenging at extreme temperatures. High-temperature furnaces require sophisticated designs to ensure the entire workload reaches the same temperature, which is critical for process repeatability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The "best" furnace is the one that meets your specific process requirements without being over-engineered. Consider your primary goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating of steels and common alloys: A standard furnace with a maximum temperature around 1315°C (2400°F) offers the best balance of capability and cost.
- If your primary focus is processing superalloys or specialized materials: You will require a high-temperature model, likely in the 1650°C (3000°F) range.
- If your primary focus is advanced research, ceramics, or refractory metals: You must specify an ultra-high temperature furnace capable of 2000°C (3632°F) or more.
Ultimately, defining your material and process requirements is the critical first step to selecting a furnace with the appropriate temperature capability.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Heating Elements | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1100°C | Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) | Low-temperature heat treating |
| Up to 1700°C | Molybdenum (Moly) | Standard industrial processes |
| Up to 2200°C+ | Graphite | High-temperature sintering |
| Up to 2600°C | Tungsten | Ultra-high temperature research |
Need a custom vacuum furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior thermal processing results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















