In essence, vacuum melting furnaces are indispensable in industries where material failure is not an option. Their primary applications are in the manufacturing of high-performance components for the aerospace, defense, energy, and medical sectors, where the absolute purity and specific mechanical properties of metals and alloys are critical for safety and performance.
The core value of vacuum melting is not merely melting metal, but fundamentally re-engineering it. By removing the corrupting influence of atmospheric gases, the process creates materials with a level of purity, strength, and consistency that is unattainable through conventional methods.

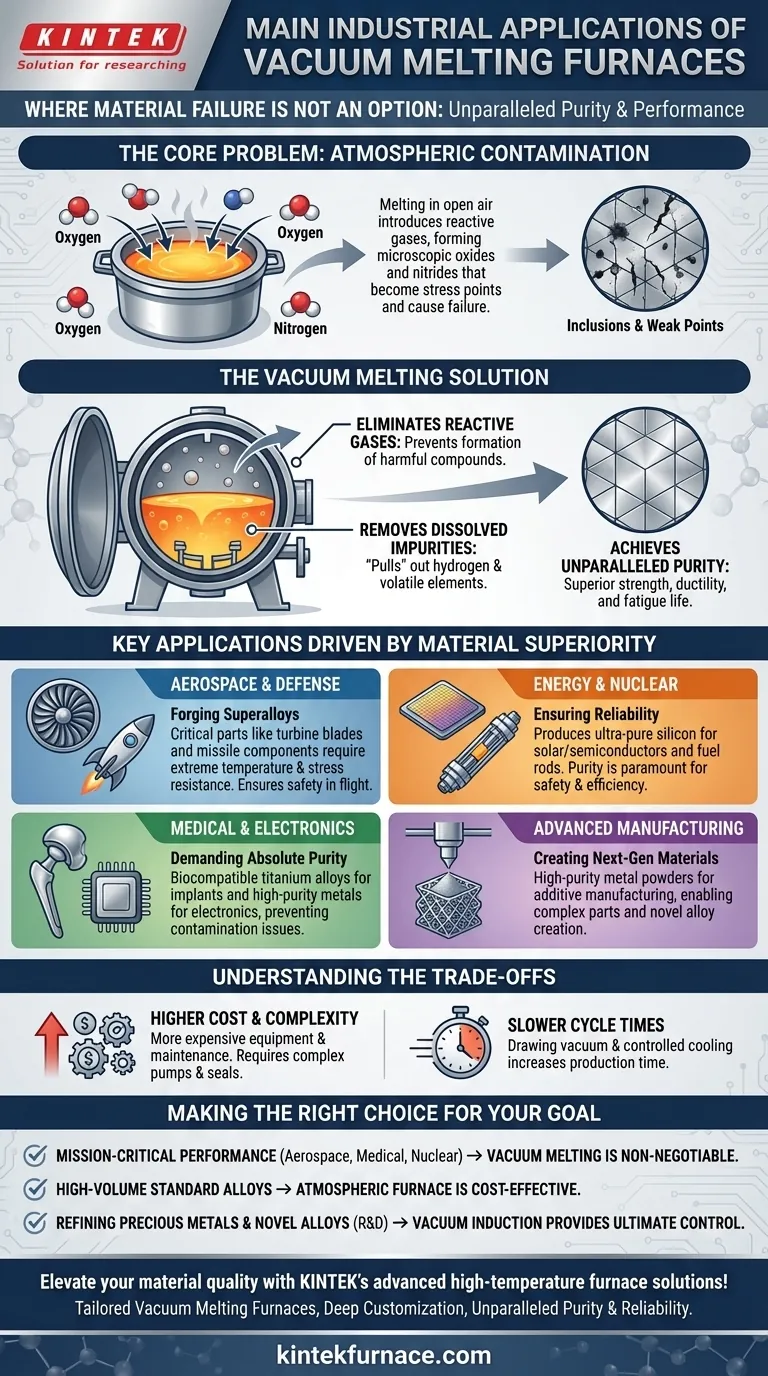
The Core Problem: Atmospheric Contamination
Melting metal in the open air or even a standard furnace introduces a host of problems. The atmosphere, composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen, is highly reactive with molten metals, compromising their final structure and properties.
Eliminating Reactive Gases
At high temperatures, molten metal readily reacts with oxygen to form oxides and with nitrogen to form nitrides. These compounds create microscopic inclusions, or impurities, within the metal's crystalline structure.
These inclusions act as stress points, becoming the origin of cracks and failures. A vacuum furnace removes freien gases, preventing these harmful reactions from ever occurring.
Removing Dissolved Impurities
A vacuum environment does more than just prevent new contamination; it actively cleanses the molten metal. The low-pressure atmosphere helps to "pull" volatile impurities and dissolved gases, like hydrogen, out of the melt.
Removing these elements is crucial. Hydrogen, for instance, can cause embrittlement in steel, while other impurities like sulfur can degrade corrosion resistance and ductility.
Achieving Unparalleled Purity
The combined effect is a finished metal with significantly improved mechanical properties. By minimizing oxides, nitrides, and other dissolved impurities, the final product exhibits superior tensile strength, ductility, and fatigue life.
Key Applications Driven by Material Superiority
The demand for these superior materials dictates where vacuum furnaces are used. The application is a direct consequence of the need for uncompromising quality.
Aerospace and Defense: Forging Superalloys
This is the largest and most critical application. Jet engine turbine blades, rocket nozzles, and missile components operate under extreme temperature and stress.
Vacuum melting is used to produce superalloys (like nickel-based Inconel) and ultra-high strength steels. The process ensures these parts are free from the microscopic weak points that could lead to catastrophic failure in flight.
Energy and Nuclear: Ensuring Reliability
In proposto generation, vacuum-melted materials are vital. This includes the production of ultra-pure silicon for semiconductors and solar cells, where impurities disrupt electrical performance.
In the nuclear industry, vacuum furnaces are used to produce fuel rods and other critical components. The purity and predictable behavior of these materials are paramount for safety and operational efficiency.
Medical and Electronics: Demanding Absolute Purity
The human body is an aggressive environment. Medical implants, such as hip joints or dental posts, must be made from biocompatible materials like titanium alloys that will not corrode or leach harmful elements.
Vacuum melting is the only way to achieve the required purity. In electronics, the process is used to refine high-purity metals for sputtering targets and other components where any contamination 이슈s performance.
Advanced Manufacturing: Creating Next-Generation Materials
Vacuum induction furnaces are also central to modern manufacturing. They are used to create high-purity metal powders for 3D printing (additive manufacturing), enabling the creation of complex parts with superior material properties.
Other applications include casting intricate parts for the jewelry industry, producing specialized valves for harsh chemical environments, and in research and development for creating novel alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum melting produces superior materials, it is not the default choice for all applications. The benefits come with practical and economic considerations.
The Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than their atmospheric counterparts. The systems require complex vacuum pumps, seals, and control instrumentation.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of drawing a vacuum, melting, and cooling under controlled conditions is inherently slower than a simple atmospheric melt. This reduces throughput and increases the cost per part.
Selective Element Removal
The vacuum that is so effective at removing unwanted impurities can also remove desirable, volatile alloying elements if not managed carefully. This requires precise control over pressure and temperature to maintain the target alloy composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum melting is a strategic balance between cost and required performance. It is a solution for problems where material quality is the primary driver.
- If your primary focus is producing mission-critical, high-performance components: Vacuum melting is non-negotiable for aerospace, medical, or nuclear-grade materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume casting of standard alloys: A conventional atmospheric or induction furnace is almost always more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is refining precious metals or developing novel alloys: Vacuum induction melting provides the ultimate combination of purity and process control.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum melting is a strategic decision to trade higher initial costs and slower production for materials of unparalleled quality and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Application Sector | Key Materials Produced | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Superalloys, Ultra-high strength steels | Enhanced strength, fatigue resistance, safety in extreme conditions |
| Energy & Nuclear | Ultra-pure silicon, Nuclear fuel rods | High purity, reliability, improved electrical and safety performance |
| Medical & Electronics | Titanium alloys, High-purity metals | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, contamination-free components |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Metal powders for 3D printing, Novel alloys | Superior material properties, complex part creation, innovation in R&D |
Elevate your material quality with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored vacuum melting furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering unparalleled purity, strength, and reliability for critical applications in aerospace, medical, energy, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















