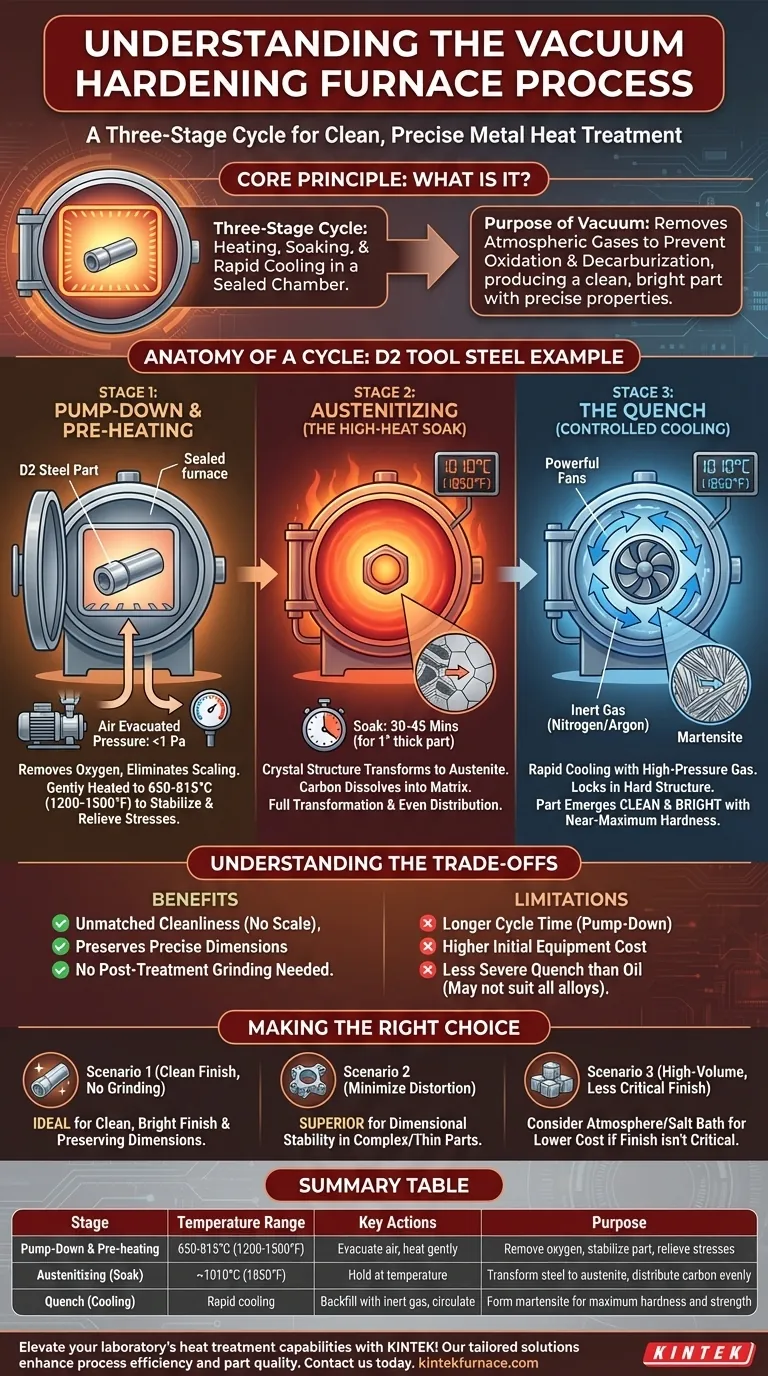
At its core, a vacuum hardening process is a three-stage cycle performed in a sealed chamber. First, metal components are heated to a specific hardening temperature under a deep vacuum. Second, they are held at this temperature (a step called "soaking") to ensure the entire part transforms its internal structure. Finally, they are rapidly cooled using high-pressure inert gas to lock in the desired hardness and strength.
The fundamental purpose of using a vacuum is not the vacuum itself, but what it prevents. By removing atmospheric gases, the process eliminates surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization, producing a clean, bright part with precise and predictable mechanical properties.
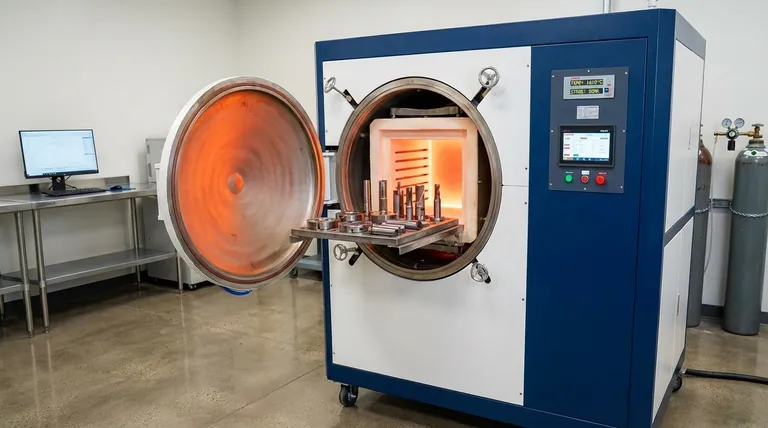

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Hardening Cycle
To make this tangible, let's walk through the hardening of a common tool steel, such as D2. This high-carbon, high-chromium steel is used for dies and cutting tools that require excellent wear resistance.
Stage 1: Pump-Down and Pre-heating
The cycle begins by loading the D2 steel parts into the cold furnace and sealing the chamber door.
A powerful vacuum system then removes the air, typically reaching a pressure level millions of times lower than the atmosphere outside. This crucial step removes oxygen, the primary cause of scaling and surface defects at high temperatures.
Once the vacuum is established, the parts are gently heated to a pre-heat temperature, often around 650-815°C (1200-1500°F). This step stabilizes the part, relieves internal stresses from prior machining, and ensures the component heats uniformly during the next critical stage.
Stage 2: Austenitizing (The High-Heat Soak)
From the pre-heat temperature, the furnace rapidly heats the parts to the specific austenitizing temperature for D2 steel, which is typically around 1010°C (1850°F).
At this temperature, the steel's crystal structure transforms into a phase called austenite, which has the unique ability to dissolve carbon into its matrix.
The parts are then "soaked"—held at this temperature for a predetermined time. This ensures the entire part, including its core, has fully transformed and the carbon and other alloying elements are evenly distributed. For a 1-inch thick D2 section, this soak might last 30-45 minutes.
Stage 3: The Quench (Controlled Cooling)
This is the "hardening" moment. To lock the hard structure in place, the steel must be cooled rapidly from the austenitizing temperature.
In a vacuum furnace, this is not done with oil or water. Instead, the heating elements are turned off, and the chamber is rapidly backfilled with a high-pressure, inert gas—usually Nitrogen or Argon.
Powerful fans circulate this gas at high velocity, pulling heat from the components rapidly and uniformly. This fast cooling forces the austenite to transform into martensite, a very hard, strong, but brittle crystal structure. The part emerges from the furnace with near-maximum hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum hardening is a superior process for many applications, but it is not the only solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Benefit: Unmatched Cleanliness and Precision
The primary advantage is the result: a clean, bright part with no surface scale. Because there is no oxidation or decarburization (loss of surface carbon), the hardened part often requires no subsequent cleaning or machining. This preserves the precise dimensions of the component.
The Cost: Cycle Time and Equipment
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines. The initial pump-down adds significant time to the overall process compared to an atmosphere furnace where parts can be loaded directly into a hot chamber. The equipment itself is more expensive to purchase and maintain.
The Limitation: Cooling Severity
While modern high-pressure gas quenching is very effective, it is generally a less severe quench than that provided by an aggressive oil bath. For some low-alloy steels or very thick parts that require extremely rapid cooling to achieve full hardness, a vacuum gas quench may not be sufficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heat treatment process depends entirely on the requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is a clean, bright finish and avoiding post-treatment grinding: Vacuum hardening is the ideal choice for preserving the part's surface and dimensions.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in complex or thin parts: The uniform heating and controlled gas quenching of a vacuum process offer superior dimensional stability.
- If your primary focus is high-volume hardening of simple carbon steels where surface finish is not critical: A more conventional and lower-cost atmosphere furnace or salt bath may be a more economical solution.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum hardening is an investment in process control for applications where final part quality and precision are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Key Actions | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pump-Down & Pre-heating | 650-815°C (1200-1500°F) | Evacuate air, heat gently | Remove oxygen, stabilize part, relieve stresses |
| Austenitizing (Soak) | ~1010°C (1850°F) | Hold at temperature | Transform steel to austenite, distribute carbon evenly |
| Quench (Cooling) | Rapid cooling | Backfill with inert gas, circulate | Form martensite for maximum hardness and strength |
Elevate your laboratory's heat treatment capabilities with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering clean, precise results for applications in tool steel hardening and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your process efficiency and part quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















