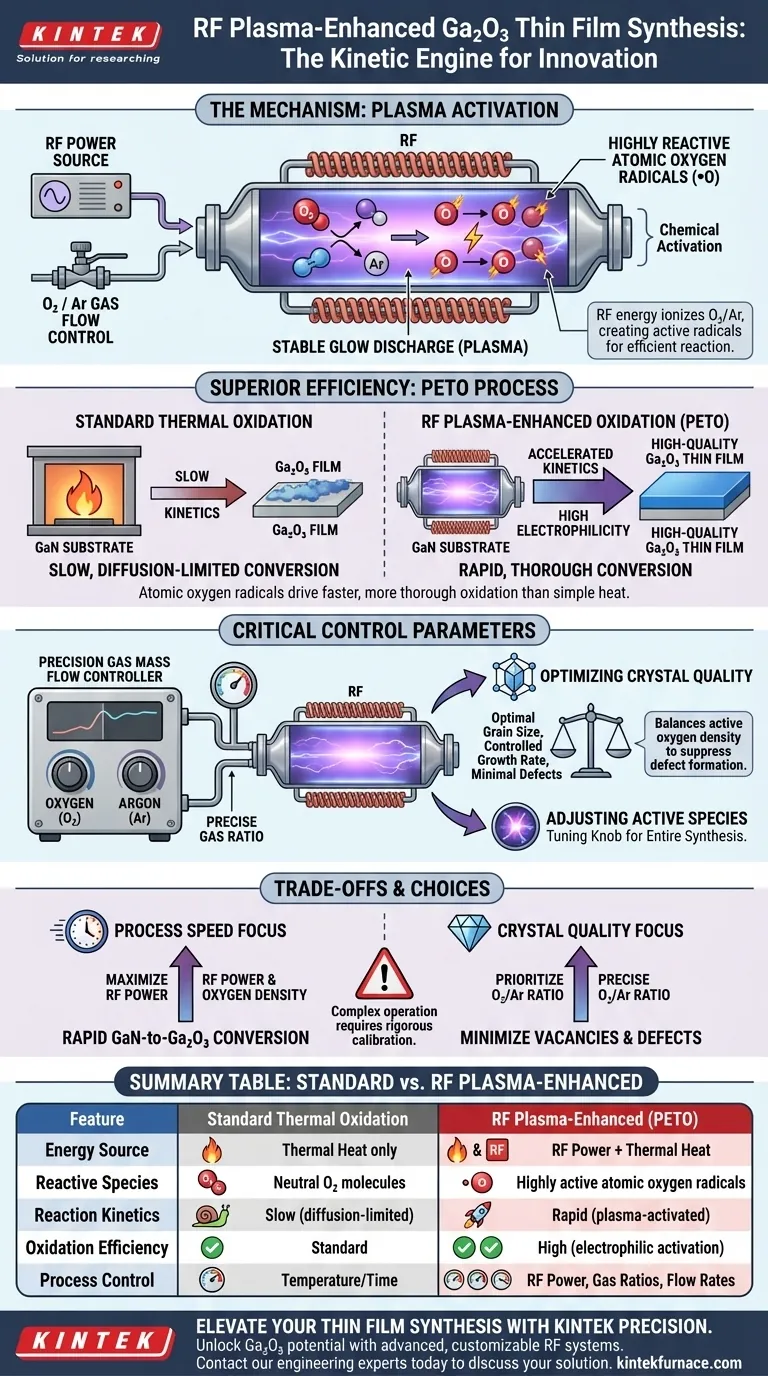
A Radio Frequency (RF) plasma-enhanced horizontal tube furnace acts as the kinetic engine for synthesizing Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3) thin films, specifically through the Plasma-Enhanced Thermal Oxidation (PETO) process.
By using an RF power source to generate a stable glow discharge, the furnace ionizes a mixture of oxygen and argon gases into a highly active plasma state. This process creates atomic oxygen radicals with high chemical activity, which drives the oxidation of Gallium Nitride (GaN) into Gallium Oxide far more efficiently than standard thermal methods.
Core Takeaway While traditional furnaces rely primarily on heat to drive reactions, this equipment uses RF energy to chemically activate the atmosphere. This allows for the rapid, high-quality conversion of materials by substituting simple thermal energy with highly reactive atomic oxygen radicals.

The Mechanism of Plasma Activation
Generating Stable Glow Discharge
The fundamental function of the furnace is to apply Radio Frequency (RF) power to the gas environment within the tube.
This energy input excites the gas molecules, creating a stable glow discharge. This state is the precursor to effective plasma processing.
Creating Highly Reactive Species
Inside the furnace, the RF energy ionizes a specific mixture of oxygen (O2) and argon (Ar).
This ionization breaks down stable oxygen molecules into atomic oxygen radicals. These radicals possess high electrophilicity and chemical activity, making them significantly more aggressive in driving chemical reactions than neutral oxygen molecules.
Superior Efficiency Over Standard Diffusion
Accelerating the Reaction
Standard diffusion furnaces rely heavily on high temperatures to force oxidation, which can be a slow process.
In contrast, the RF plasma-enhanced furnace utilizes the high energy of the atomic oxygen radicals to accelerate the reaction kinetics. This significantly speeds up the conversion of Gallium Nitride (GaN) substrates into Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3) thin films.
Enhanced Oxidation Efficiency
The "active" nature of the plasma ensures that the oxidation is not only faster but more thorough.
The high electrophilicity of the oxygen radicals ensures they react readily with the substrate, improving the overall efficiency of the oxidation process compared to passive thermal oxidation.
Critical Control Parameters
The Role of Gas Mass Flow
To harness the power of the plasma effectively, the furnace must be paired with a high-precision gas mass flow control system.
This system accurately regulates the flow ratios of oxygen and argon. This ratio is the "tuning knob" for the entire synthesis process.
Optimizing Crystal Quality
By finely adjusting the gas mixture, operators can control the density of active oxygen species within the plasma.
This precise control is essential for suppressing defect formation. A balanced gas ratio results in films with optimal grain size, controlled growth rates, and minimal oxygen vacancy concentrations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Balance of Reactivity vs. Quality
While the RF plasma enhances speed, the oxygen-to-argon ratio creates a critical dependency.
If the ratio is not optimized, the density of active oxygen species may become too high or too low. This imbalance can lead to increased oxygen vacancies or poor crystal structure, negating the benefits of the plasma enhancement.
Complexity of Operation
Unlike a simple thermal oven, this system introduces variables that must be actively managed.
Achieving the perfect "recipe" for grain size and growth rate requires rigorous calibration of the RF power and gas flow ratios, demanding a higher level of process control than standard diffusion methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of an RF plasma-enhanced furnace, align your process parameters with your specific output requirements:
- If your primary focus is Process Speed: Maximize the density of atomic oxygen radicals via RF power to accelerate the GaN-to-Ga2O3 conversion rate.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Prioritize the precision of the Oxygen/Argon ratio to minimize oxygen vacancies and suppress defect formation.
Success in this process relies not just on generating plasma, but on precisely controlling the chemical activity of the oxygen radicals it creates.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Thermal Oxidation | RF Plasma-Enhanced (PETO) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal Heat only | RF Power + Thermal Heat |
| Reactive Species | Neutral O2 molecules | Highly active atomic oxygen radicals |
| Reaction Kinetics | Slow (diffusion-limited) | Rapid (plasma-activated) |
| Oxidation Efficiency | Standard | High (electrophilic activation) |
| Process Control | Temperature/Time | RF Power, Gas Ratios, Flow Rates |
Elevate Your Thin Film Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3) research with KINTEK’s advanced RF plasma-enhanced systems. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific laboratory requirements. Whether you are optimizing crystal quality or accelerating reaction kinetics, our specialized high-temp furnaces provide the stability and control your innovations demand.
Ready to transform your material synthesis? Contact our engineering experts today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Ren-Siang Jiang, Qijin Cheng. O2-to-Ar Ratio-Controlled Growth of Ga2O3 Thin Films by Plasma-Enhanced Thermal Oxidation for Solar-Blind Photodetectors. DOI: 10.3390/nano15181397
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How are source gases delivered in PECVD systems? Ensure Uniform Film Growth with Precision
- What is the plasma deposition system? Build Advanced Materials Atom-by-Atom
- What are the advantages of PECVD for preparing 2D materials? Unlock Scalable, Low-Temp Fabrication
- What makes PECVD a cornerstone technology in modern fabrication processes? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What are capacitively coupled and inductively coupled plasmas in PECVD? Choose the Right Plasma for Superior Film Quality
- How is PECVD used in the food packaging industry? Extend Shelf Life with Transparent Barrier Films
- How did PECVD systems evolve over time? From Batch to Single-Wafer for Precision
- How are deposition rates and film properties controlled in PECVD? Master Key Parameters for Optimal Thin Films



















