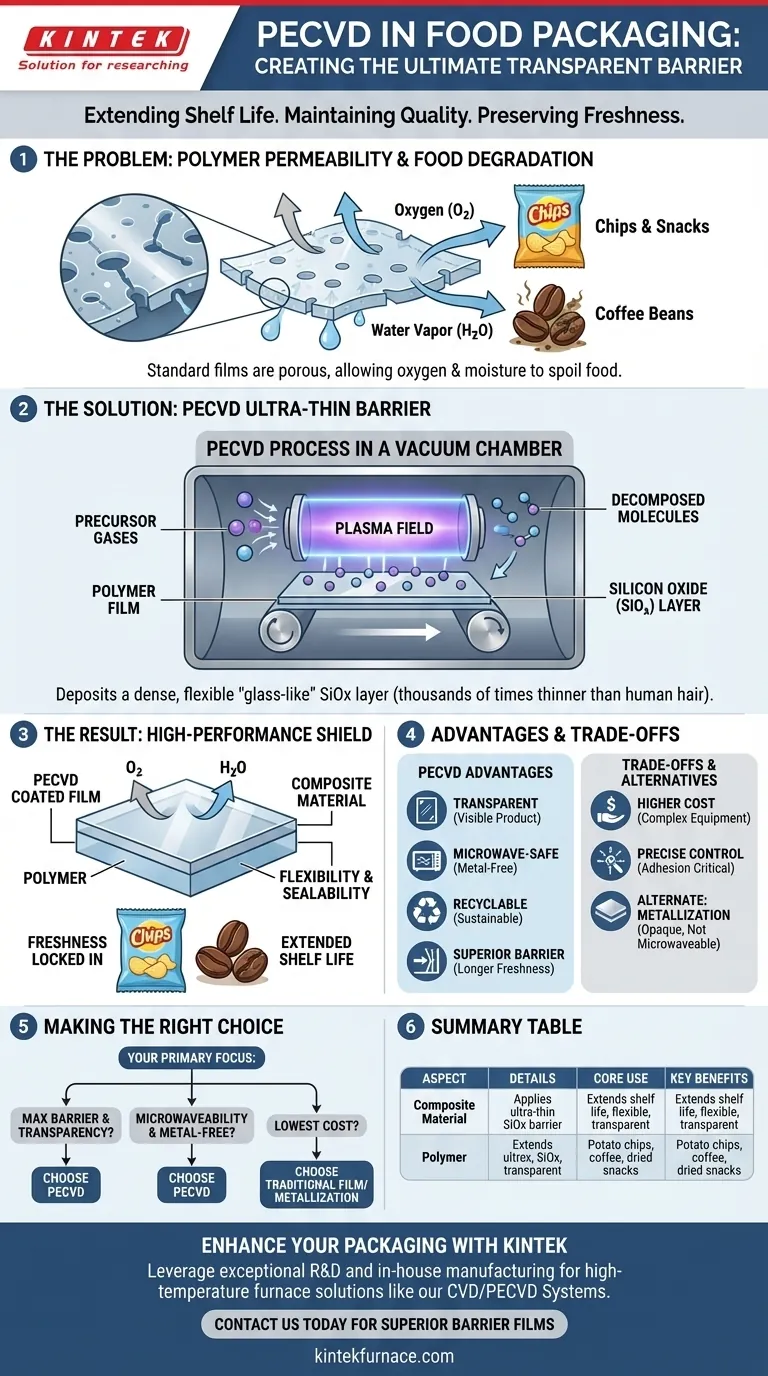
In the food packaging industry, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is used to apply an ultra-thin, transparent barrier layer onto flexible polymer films. This microscopic coating, often made of materials like silicon oxide, dramatically improves the packaging's ability to protect food from oxygen and moisture, thereby extending shelf life and maintaining product quality for items like potato chips, coffee, and dried snacks.
The core function of PECVD in food packaging is to solve a fundamental weakness of plastic: its permeability. By depositing a glass-like barrier that is thousands of times thinner than a human hair, PECVD transforms a standard polymer film into a high-performance material that keeps food fresh without sacrificing flexibility or transparency.

The Core Problem: Why Flexible Packaging Fails
Flexible packaging, like the plastic film used for bags and pouches, is lightweight and cost-effective. However, on a microscopic level, these polymer materials are porous.
The Permeability of Polymers
Standard plastic films contain microscopic gaps between their polymer chains. While invisible to the naked eye, these gaps are large enough for gas molecules, like oxygen and water vapor, to pass through over time.
The Enemies of Freshness: Oxygen and Water
For many food products, exposure to oxygen and moisture is detrimental. Oxygen leads to oxidation, causing fats to go rancid and flavors to degrade. Moisture can make crisp products like chips soggy and can cause clumping in powdered goods.
How PECVD Creates the High-Performance Barrier
PECVD addresses the permeability problem by adding a virtually impermeable layer to the polymer film in a highly controlled, low-temperature process.
Understanding the PECVD Process
PECVD uses an energized plasma field inside a vacuum chamber to decompose precursor gases. These decomposed molecules then condense and deposit onto the surface of the packaging film, forming an exceptionally thin, dense, and uniform coating.
The Silicon Oxide (SiOx) Barrier Layer
A common material used in this application is silicon oxide (SiOx). In essence, PECVD deposits a microscopic layer of flexible glass onto the plastic. This inorganic layer has a much tighter molecular structure than the underlying polymer, creating a formidable barrier against gas and water vapor transmission.
The Result: An Impermeable, Flexible Shield
The final product is a composite material that combines the best of both worlds. The polymer provides the bulk structure, flexibility, and sealability, while the ultra-thin PECVD coating provides the critical barrier function needed for long-term food preservation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While highly effective, PECVD is a sophisticated process with specific considerations compared to other barrier technologies.
Complexity and Cost
PECVD is a vacuum deposition technology, which requires significant capital investment in equipment and has higher operational costs than simpler methods like co-extruding multiple polymer layers. It is typically reserved for products where high-performance barrier properties are essential.
The Alternative: Metallization
Another common barrier technique is metallization, where a thin layer of aluminum is deposited on the film (giving chip bags their classic shiny interior). While an effective barrier, metallization creates an opaque package, prevents the product from being microwaved, and can complicate recycling.
Film Adhesion and Durability
The performance of a PECVD-coated film depends critically on the adhesion between the thin SiOx layer and the polymer substrate. The process must be precisely controlled to ensure this bond is strong and durable enough to withstand flexing, transport, and handling without cracking or delaminating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
The decision to use PECVD is driven by the specific protection requirements of the food product and the desired features of the final package.
- If your primary focus is maximum barrier performance and transparency: PECVD is a leading solution, allowing customers to see the product while ensuring its protection from oxygen and moisture.
- If your primary focus is microwaveability and a metal-free package: PECVD provides a clear advantage over traditional metallized films, creating consumer-friendly and more easily recyclable packaging.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible cost for less sensitive goods: Traditional multi-layer polymer films or metallization may offer a more cost-effective solution where transparency is not a requirement.
Ultimately, PECVD enables the creation of advanced packaging that protects its contents without compromising on the modern demands for product visibility, convenience, and performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Use | Applies ultra-thin, transparent barrier layers (e.g., silicon oxide) on polymer films |
| Key Benefits | Extends shelf life, maintains food quality, preserves flexibility and transparency |
| Common Applications | Potato chips, coffee, dried snacks |
| Process | Low-temperature plasma deposition in vacuum chambers |
| Advantages Over Alternatives | Transparent, microwave-safe, recyclable vs. opaque metallization |
| Considerations | Higher cost, requires precise control for adhesion and durability |
Ready to enhance your food packaging with advanced PECVD solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like our CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for developing superior barrier films. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve longer shelf life and better product protection!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods



















