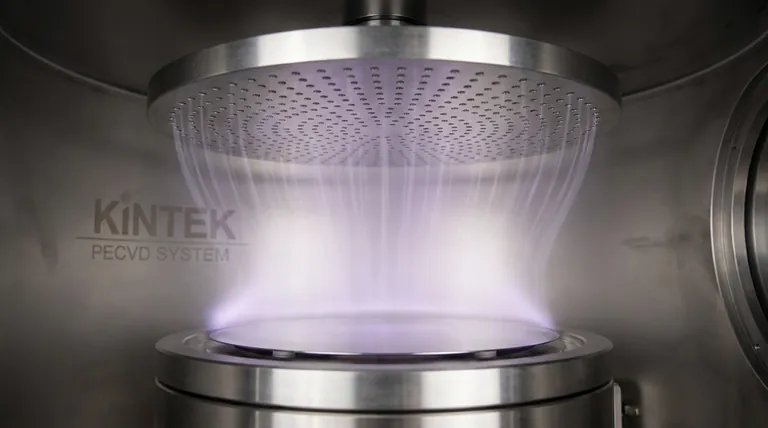
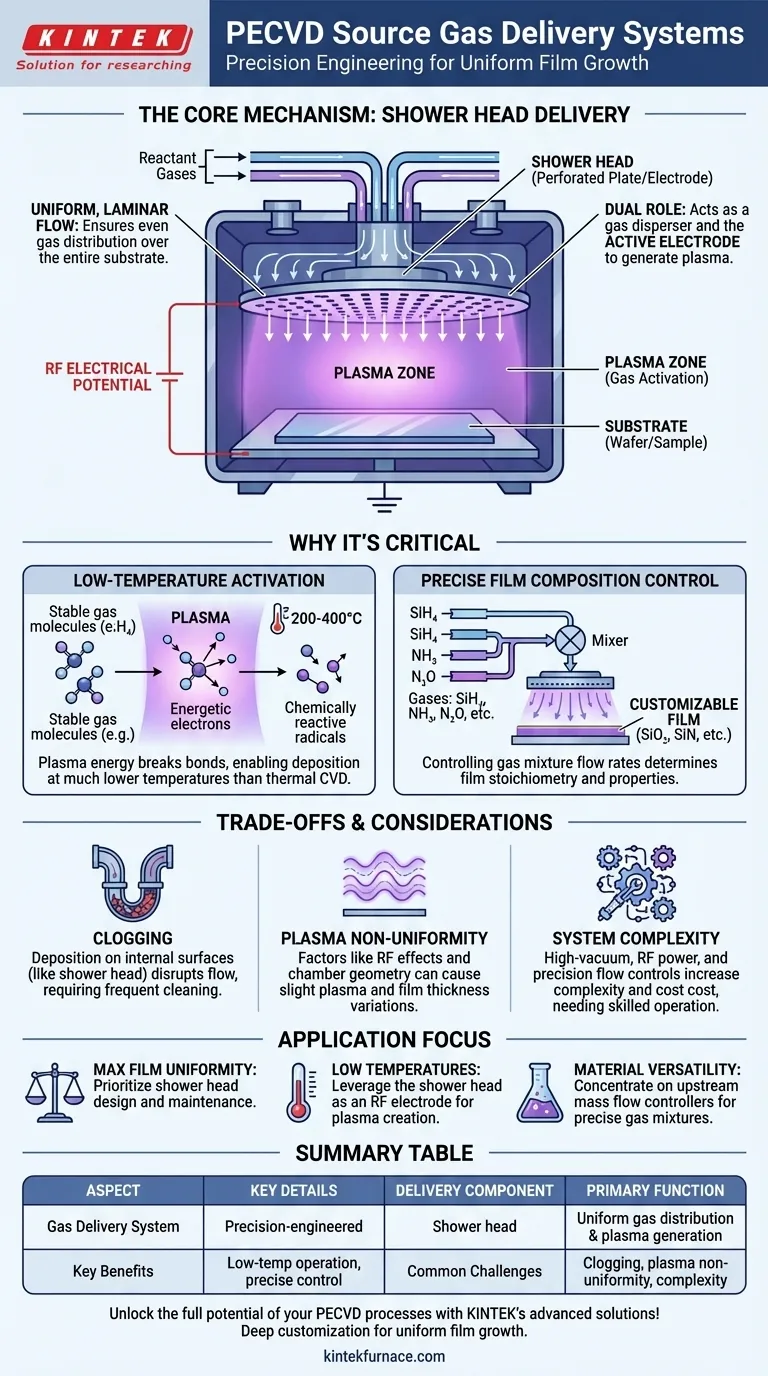
In a PECVD system, source gases are delivered into the process chamber through a specialized component, most commonly a shower head. This perforated plate is positioned directly above the substrate to ensure the reactant gases are distributed evenly across the wafer's surface, which is the critical first step for achieving uniform film growth.
The gas delivery mechanism in PECVD is more than just plumbing; it is a precision-engineered system designed for uniformity. The "shower head" not only disperses the gas but is often the very electrode used to ignite the plasma, directly linking gas distribution to the chemical reaction process.

The Core Mechanism: From Gas Inlet to Plasma
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) relies on precise control to create high-quality films. The gas delivery system is the foundation of that control.
Introducing the Shower Head
The most common method for gas delivery is the shower head. Imagine a large, flat metal disc, typically made of aluminum, with hundreds or thousands of tiny, precisely drilled holes.
This component is mounted inside the vacuum chamber, parallel to and a short distance from the substrate (the wafer or sample being coated).
The Goal of Uniform Distribution
The primary function of the shower head is to introduce the reactant gases in a uniform, laminar flow across the entire surface of the substrate.
Without this, gases would concentrate in one area, leading to a film that is thicker on one side of the wafer than the other—a critical failure in semiconductor manufacturing.
The Dual Role of the Shower Head
Crucially, the shower head is not just a passive gas nozzle. An RF (Radio Frequency) electrical potential is applied directly to it, making it an active electrode.
This RF energy excites the evenly distributed gas flowing through the holes, ionizing it and creating the plasma directly above the substrate. This integration of gas delivery and plasma generation is a hallmark of modern PECVD reactor design.
Why This Method is Critical for PECVD
The shower head's dual function is what enables the key advantages of the PECVD process over purely thermal methods like conventional CVD.
Activating Gases at Low Temperatures
The energetic electrons within the plasma, generated at the shower head, have enough energy to break down the stable source gas molecules (like silane, SiH₄) into chemically reactive radicals.
These radicals are highly reactive and readily form a solid film on the cooler substrate surface. This plasma-driven activation is why PECVD can operate at much lower temperatures (e.g., 200-400°C) than thermal CVD, which requires high heat (600-800°C) to break the same chemical bonds.
Controlling Film Composition
The final properties of the deposited film are determined by the mixture of gases fed into the shower head.
By precisely controlling the flow rates of different source gases (e.g., silane and ammonia for silicon nitride, or silane and nitrous oxide for silicon dioxide), operators can precisely control the film's stoichiometry and physical characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While effective, the shower head-based delivery system presents its own set of operational challenges that must be managed.
The Challenge of Clogging
Because deposition occurs everywhere the reactive radicals exist, a thin film will also deposit on the internal surfaces of the chamber, including the shower head itself.
Over time, this buildup can clog the small gas holes, disrupting the uniform gas flow and compromising film uniformity. This necessitates periodic, and sometimes frequent, chamber cleaning cycles.
Plasma Uniformity Issues
While the shower head ensures uniform gas flow, it does not guarantee perfectly uniform plasma density.
Factors like chamber geometry, gas pressure, and the standing wave effect of RF energy can create non-uniformities in the plasma itself. This can still result in slight variations in film thickness or properties across the wafer, a problem that reactor designers work continuously to minimize.
System Complexity
The combination of precision gas flow control, high-vacuum systems, and RF power generation makes PECVD systems significantly more complex and expensive than some simpler deposition methods. This complexity requires skilled technicians for operation and maintenance.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which aspect of the gas delivery system you need to focus on most.
- If your primary focus is maximum film uniformity: Your priority must be the design and maintenance of the shower head, ensuring it remains clean and undamaged.
- If your primary focus is depositing at low temperatures: The key is understanding that the shower head's function as an RF electrode is what enables the low-temperature process by creating the necessary plasma.
- If your primary focus is material versatility: Concentrate on the upstream mass flow controllers that feed the shower head, as precise control of the gas mixture is what allows you to deposit a range of materials like silicon dioxide and nitride.
Ultimately, recognizing the gas delivery system as an active and critical component is fundamental to mastering the PECVD process and achieving consistent, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Delivery Component | Shower head (perforated plate) |
| Primary Function | Uniform gas distribution and plasma generation |
| Key Benefits | Low-temperature operation, precise film control |
| Common Challenges | Clogging, plasma non-uniformity, system complexity |
| Applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, thin-film deposition |
Unlock the full potential of your PECVD processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform film growth and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition



















