The essential function of high-purity alumina crucibles in this synthesis is to provide a strictly inert environment that withstands extreme thermal stress. For the creation of Ni3In2Se2, these vessels allow the reaction to proceed at 1000°C without the crucible itself chemically interacting with the Nickel, Indium, or Selenium reactants.
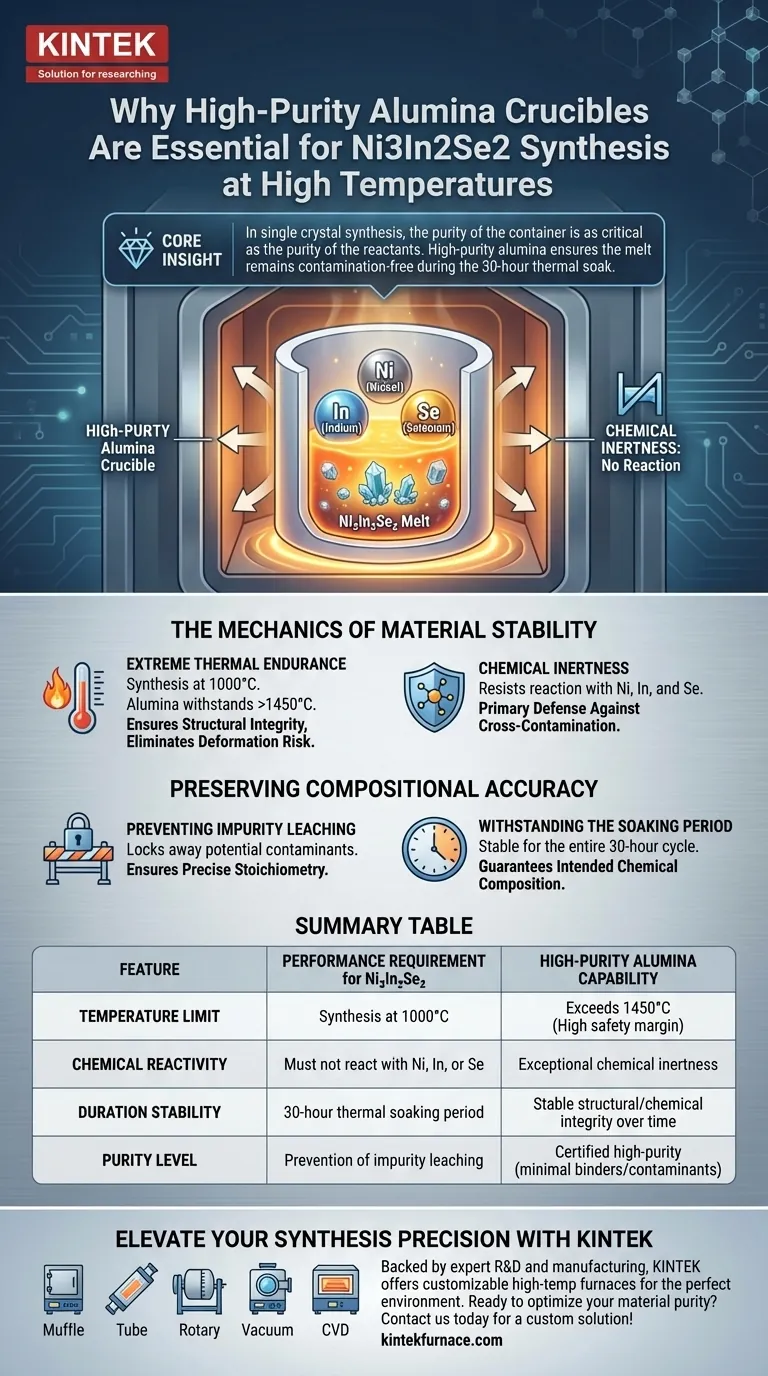
Core Insight In single crystal synthesis, the purity of the container is as critical as the purity of the reactants. High-purity alumina is the standard choice for Ni3In2Se2 because it ensures the melt remains free from contamination during the specific 30-hour thermal soaking period required for this material.

The Mechanics of Material Stability
Extreme Thermal Endurance
The synthesis of Ni3In2Se2 requires subjecting materials to temperatures reaching 1000°C. High-purity alumina is capable of withstanding temperatures significantly higher than this, often exceeding 1450°C.
This thermal headroom ensures the crucible maintains its structural integrity throughout the process. It eliminates the risk of physical deformation or failure that could ruin the sample during the heating phase.
Chemical Inertness
At high temperatures, many standard laboratory ceramics become reactive. However, high-purity alumina possesses excellent chemical inertness.
It specifically resists reaction with the reactive elements in this synthesis: Nickel, Indium, and Selenium. This lack of interaction is the primary defense against cross-contamination.
Preserving Compositional Accuracy
Preventing Impurity Leaching
The primary goal during the melt is to prevent "precipitation of impurities" from the container walls. Lower-grade crucibles often release trace elements into the melt when heated.
High-purity alumina effectively locks these potential contaminants away. This ensures that the stoichiometry (the precise chemical ratio) of the Ni3In2Se2 crystal remains accurate.
Withstanding the Soaking Period
This specific synthesis involves a "thermal soaking" period lasting 30 hours. Prolonged exposure increases the probability of chemical interaction between the vessel and the melt.
Alumina’s stability ensures it remains inert not just for minutes, but for the entire duration of this extended cycle. This guarantees the final single crystals reflect the intended chemical composition, not a hybrid of reactants and crucible material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of "High Purity"
It is critical to distinguish between standard alumina and high-purity alumina. Using a lower grade vessel is a common pitfall that undermines the experiment.
Standard alumina may contain binders or impurities that can leach out at 1000°C. To achieve the results described—specifically the lack of contamination—certified high-purity crucibles are non-negotiable.
Thermal Shock Considerations
While alumina is heat resistant, it is generally sensitive to rapid temperature changes. Although the primary reference highlights its resistance during the soak, operators must typically manage heating and cooling rates carefully to prevent cracking the vessel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When planning your high-temperature synthesis, your equipment choice dictates your data quality.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Select high-purity alumina to ensure zero interaction with Nickel, Indium, or Selenium during the 30-hour soak.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Rely on alumina’s ability to exceed the 1000°C requirement, providing a safety margin against deformation.
By using high-purity alumina, you remove the variable of container interference, ensuring your results stem solely from your experimental design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Performance Requirement for Ni3In2Se2 | High-Purity Alumina Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Limit | Synthesis at 1000°C | Exceeds 1450°C (High safety margin) |
| Chemical Reactivity | Must not react with Ni, In, or Se | Exceptional chemical inertness |
| Duration Stability | 30-hour thermal soaking period | Stable structural/chemical integrity over time |
| Purity Level | Prevention of impurity leaching | Certified high-purity (minimal binders/contaminants) |
Elevate Your Synthesis Precision with KINTEK
Don't let crucible contamination compromise your research results. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of high-performance laboratory equipment, including specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique thermal processing needs, ensuring the perfect environment for Ni3In2Se2 synthesis and beyond.
Ready to optimize your material purity? Contact us today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Yi Zhou. The Preparation and Physical Properties Study of the Kagome Lattice Semimetal Ni3In2Se2. DOI: 10.47297/taposatwsp2633-456926.20250604
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an industrial vacuum drying oven in Si-RuO2 catalyst preparation? Achieve Uniformity.
- Why are Type K thermocouples preferred in industrial furnaces? Unlock Reliable Precision for High-Heat Control
- What is the technical objective of using vacuum-sealed quartz capsules for Co-Ti-V alloy homogenization? Safeguard Chemical Integrity
- What role does an alumina crucible play during the gas nitriding process for stainless steel? Ensure Surface Purity
- What is the function of ceramic balls within a box furnace? Improve Coke Graphitization & System Safety
- What are the technical functions of condensation units and gas collection bags? Optimize Your Reduction Experiments
- What is the function of high-purity alumina crucibles in NRBBO:Eu2+ sintering? Ensure Pure Phosphor Synthesis
- Why use a covered crucible for g-C3N4 calcination? Enhance Surface Area via Self-Exfoliation


















