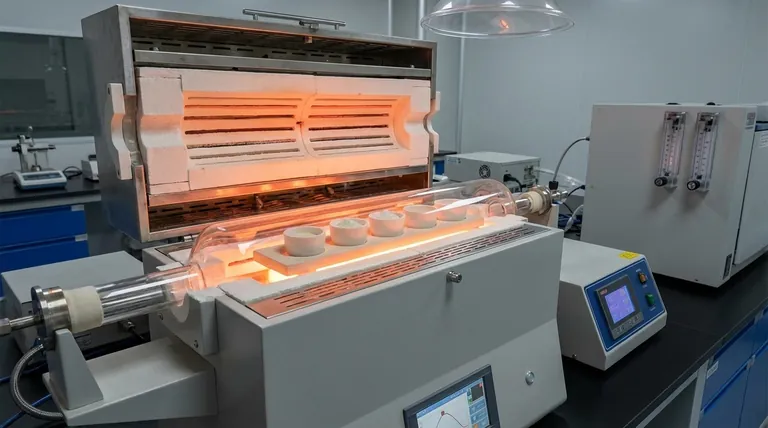
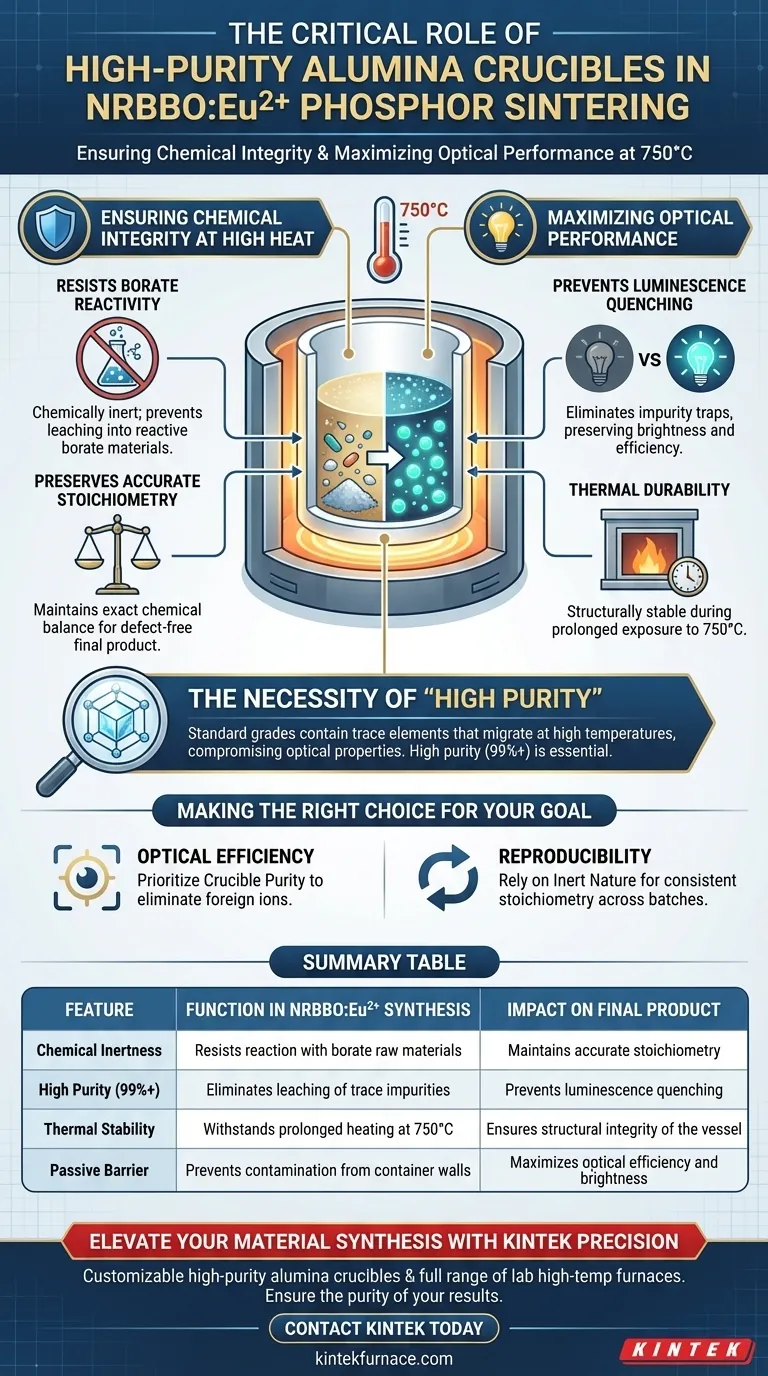
High-purity alumina crucibles serve as chemically inert containment vessels that define the quality of NRBBO:Eu2+ phosphors during synthesis. Their primary function is to withstand prolonged sintering at 750°C without interacting with the reactive borate raw materials.
By acting as a non-reactive barrier, high-purity alumina prevents the container walls from contaminating the mixture. This is critical for maintaining accurate stoichiometry and avoiding impurity-induced "quenching" which destroys the phosphor's ability to emit light.

Ensuring Chemical Integrity at High Heat
Resisting Borate Reactivity
The synthesis of NRBBO:Eu2+ phosphors involves borate raw materials, which are known to be chemically reactive, particularly at elevated temperatures.
Standard containment materials often degrade or react when in contact with borates during the heating phase.
High-purity alumina offers superior chemical stability, ensuring the crucible remains passive and does not leach material into the phosphor mixture.
Preserving Accurate Stoichiometry
For a phosphor to function correctly, the ratio of its chemical components (stoichiometry) must be exact.
If the crucible reacts with the raw materials, it alters the chemical balance of the mixture, leading to a defective final product.
Alumina crucibles ensure that the chemical composition you calculate at the start is exactly what you produce at the end.
Maximizing Optical Performance
Preventing Luminescence Quenching
The performance of a phosphor is measured by its luminescence—its ability to absorb energy and emit light.
Impurities introduced during sintering act as "traps" for this energy, causing a phenomenon known as luminescence quenching.
By eliminating cross-contamination from the container, high-purity alumina preserves the phosphor's brightness and efficiency.
Thermal Durability
The sintering process requires prolonged exposure to temperatures around 750°C.
High-purity alumina is engineered to remain structurally stable and physically robust under these specific thermal conditions.
Understanding the Constraints
The Necessity of "High Purity"
It is insufficient to use standard industrial-grade alumina for this process.
The reference specifically mandates high-purity alumina because lower grades contain trace elements that can migrate into the phosphor at 750°C.
Using a crucible with even minor impurities negates the benefits of the material and risks compromising the optical properties of the NRBBO:Eu2+.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your NRBBO:Eu2+ phosphor synthesis, apply these principles:
- If your primary focus is Optical Efficiency: Prioritize crucible purity to eliminate foreign ions that cause luminescence quenching.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: Rely on the inert nature of alumina to ensure the stoichiometry of your borate mixture remains consistent across multiple batches.
High-purity alumina is not just a container; it is a critical process control variable that safeguards the chemical and optical integrity of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in NRBBO:Eu2+ Synthesis | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists reaction with borate raw materials | Maintains accurate stoichiometry |
| High Purity (99%+) | Eliminates leaching of trace impurities | Prevents luminescence quenching |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands prolonged heating at 750°C | Ensures structural integrity of the vessel |
| Passive Barrier | Prevents contamination from container walls | Maximizes optical efficiency and brightness |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precision in phosphor development begins with the right containment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-purity alumina crucibles alongside a full range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are sintering NRBBO:Eu2+ or developing next-generation optical materials, our lab high-temp furnaces and vessels are fully customizable to meet your unique thermal and chemical requirements.
Ensure the purity of your results—contact KINTEK today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Runtian Kang, Yuhua Wang. Chemical Pressure‐Induced FWHM Narrowing in Narrowband Green Phosphors for Laser Displays with Ultra‐High Saturation Thresholds. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202505385
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
People Also Ask
- What function does a high-purity quartz ampoule serve during the manganese atom diffusion process? Essential Role Explained
- Why are metal wire mesh trays preferred for thin-layer drying? Boost Efficiency and Accuracy in Your Lab
- What are the technical advantages of using a quartz tube as a reaction chamber? Optimize g-C3N4 Thin Film CVD Processes
- Why is vacuum quartz tube sealing technology required in the synthesis of ZnPS3 crystals? Ensuring Chemical Purity
- What are the technical advantages of using a high-purity alumina crucible for the synthesis of MnBi2Te4?
- What role does a quartz substrate holder play in MoS2 growth? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precision Hardware
- Why are high-purity alumina boats utilized as precursor containers in MoS2 synthesis? Ensure High-Quality 2D Materials
- What role does a ceramic crucible play in oxidation weight gain experiments for Ti-V-Cr alloys? Ensure Data Accuracy



















