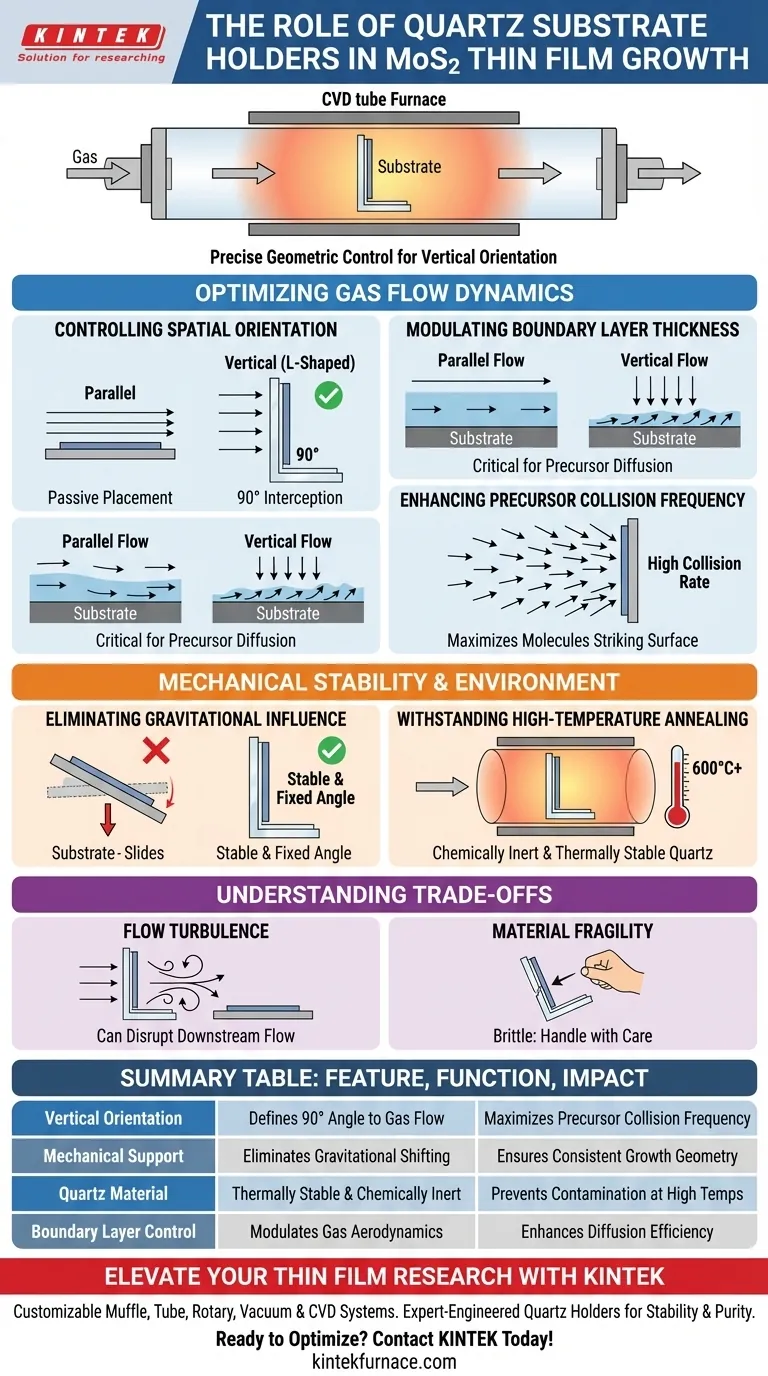
A quartz substrate holder or L-shaped mounting plate acts as a precise geometric control tool used to dictate the spatial orientation of a substrate during thin film growth. Its primary function is to mechanically stabilize the substrate—often positioning it vertically perpendicular to the gas flow—to eliminate gravitational shifting and ensure a fixed angle for reaction.
By rigidly maintaining a specific orientation, typically 90 degrees to the gas flow, these holders directly influence reaction kinetics by optimizing boundary layer thickness and increasing the frequency of precursor collisions.
Optimizing Gas Flow Dynamics
Controlling Spatial Orientation
The primary role of the holder is to define how the substrate faces the incoming chemical vapor.
While substrates can be placed parallel to the flow, the L-shaped design specifically facilitates vertical positioning. This allows the researcher to choose the exact angle of incidence between the gas and the growth surface.
Modulating Boundary Layer Thickness
The orientation of the substrate dictates the aerodynamics of the reaction.
When a substrate is held vertically by an L-shaped plate, it alters the boundary layer—the thin layer of gas immediately adjacent to the surface. Controlling this layer is critical because precursor molecules must diffuse through it to reach the surface and react.
Enhancing Precursor Collision Frequency
A vertically mounted substrate effectively intercepts the flow of gas.
This perpendicular alignment maximizes the number of precursor molecules striking the surface per unit of time. By increasing this collision frequency, the holder helps facilitate a more efficient reaction compared to a passive, parallel placement.
Mechanical Stability and Environment
Eliminating Gravitational Influence
Without a specialized holder, positioning a substrate vertically is mechanically unstable.
The L-shaped plate provides the structural support necessary to counteract gravity. This ensures that the substrate does not shift, slide, or change angles during the process, maintaining the precise 90-degree geometry required for consistent results.
Withstanding High-Temperature Annealing
The choice of quartz as the material for the holder is not accidental; it matches the environment of the reaction chamber.
As MoS2 growth and annealing occur at temperatures often exceeding 550°C to 600°C, the holder must remain chemically inert and thermally stable. A quartz holder withstands these conditions without introducing contaminants or degrading, ensuring the high-purity environment required for improving grain quality and electrical properties is maintained.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Flow Turbulence and Shadowing
While vertical placement increases collision frequency, it acts as a physical barrier in the tube.
This can create turbulence or "shadowing" effects downstream from the holder. If you are processing multiple substrates in a series, the holder for the first substrate may disrupt the laminar flow required for subsequent substrates, potentially leading to non-uniform growth on downstream samples.
Material Fragility
Quartz is chemically robust but mechanically brittle.
L-shaped mounting plates are prone to breakage during loading and unloading, particularly when applying the force necessary to secure the substrate. This requires careful handling to maintain the precise geometry without snapping the mounting arm.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your CVD or annealing setup, consider your specific growth objectives when employing these holders.
- If your primary focus is increasing reaction efficiency: Utilize the L-shaped holder to mount the substrate vertically (90 degrees), as this maximizes precursor collision frequency and reduces the diffusion path through the boundary layer.
- If your primary focus is purity and phase stability: Ensure the holder is made of high-purity quartz to match the thermal expansion and inertness of the tube furnace during 600°C annealing cycles.
Proper use of the substrate holder transforms the substrate from a passive participant into an active, optimized interception point for film growth.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in MoS2 Growth | Impact on Thin Film Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Orientation | Defines 90° angle to gas flow | Maximizes precursor collision frequency |
| Mechanical Support | Eliminates gravitational shifting | Ensures consistent growth geometry and repeatability |
| Quartz Material | Thermally stable and chemically inert | Prevents contamination during high-temp (600°C) annealing |
| Boundary Layer Control | Modulates gas aerodynamics | Enhances diffusion efficiency of precursor molecules |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK
Precision in 2D material synthesis begins with controlled environments and reliable hardware. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements.
Whether you are growing MoS2 thin films or conducting high-purity annealing, our expert-engineered quartz holders and high-temperature furnaces provide the stability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your deposition process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace and substrate mounting needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Feng Liao, Zewen Zuo. Optimizing the Morphology and Optical Properties of MoS2 Using Different Substrate Placement: Numerical Simulation and Experimental Verification. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15010059
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is quartz wool utilized in the assembly of reaction tubes? Optimize Crystal Growth and Flux Separation
- What is the purpose of a laboratory vacuum system in photocatalytic hydrogen evolution? Ensure Accurate Data Results
- How do the quartz crucible and descending device function in Bridgman method? Precision Growth for CsPbBr3 Crystals
- What are the advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Cast Iron Phase Equilibrium Data
- What are the advantages of 0.7 mm quartz capillaries for SXRD? Optimize High-Energy In-Situ X-ray Experiments
- What processes can a circulating water vacuum pump provide negative pressure conditions for? Essential Lab Techniques Explained
- What role do refractory bricks and graphite paper play within a quartz tube? Optimize RuMoOx/NC Synthesis Efficiency
- What function does a PTFE liner serve in NiWO4 synthesis? Ensure Purity & Prevent Corrosion in Hydrothermal Reactors


