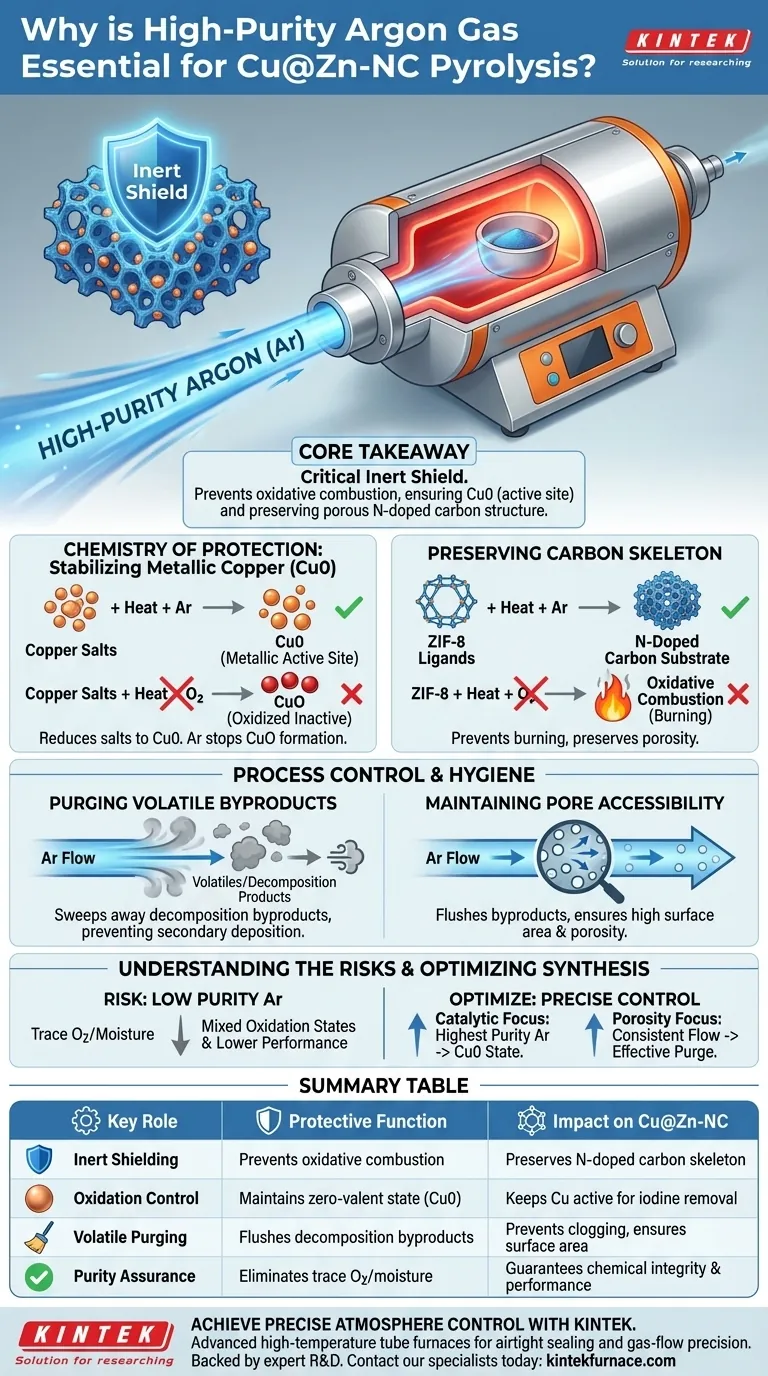
High-purity argon gas acts as a critical inert shield during the pyrolysis of Cu@Zn-NC. Its primary function is to prevent the oxidative combustion of the carbon substrate and to stop copper nanoparticles from oxidizing into copper oxide. Without this protective atmosphere, the material’s chemical integrity would be compromised, rendering it useless for its intended application.
Core Takeaway By strictly excluding oxygen, high-purity argon ensures that copper remains in its zero-valent metallic state (Cu0)—the essential active component for iodine removal—while simultaneously preserving the porous nitrogen-doped carbon structure that hosts these nanoparticles.

The Chemistry of Protection
Stabilization of Metallic Copper (Cu0)
The central goal of this pyrolysis process is to reduce copper salts into metallic copper nanoparticles.
If oxygen is present at high temperatures, the copper will inevitably oxidize into copper oxide (CuO).
Argon maintains the environment necessary to keep copper in the zero-valent state (Cu0), which is the core active site required for efficient iodine capture.
Preservation of the Carbon Skeleton
The thermal treatment converts organic ligands (specifically within ZIF-8) into a stable nitrogen-doped carbon substrate.
Without an inert argon barrier, the high operating temperatures (often around 600°C) would cause the carbon to react with atmospheric oxygen.
This would lead to oxidative combustion, effectively burning away the structural framework and destroying the material's porosity.
Process Control and Hygiene
Purging Volatile Byproducts
Pyrolysis generates volatile byproducts as the polymer and organic components decompose.
A continuous flow of argon serves as a purging medium, sweeping these volatiles out of the furnace chamber.
This prevents the secondary deposition of decomposition products (such as those from CF3 groups), ensuring the final material retains its intended chemical composition.
Maintaining Pore Accessibility
The removal of volatiles is not just about purity; it is about physical structure.
By flushing away byproducts, argon prevents them from clogging the newly formed pores.
This ensures the final adsorbent maintains the high surface area and porosity required for effective chemical interaction.
Understanding the Risks
The Impact of Gas Impurity
Using argon that is not "high-purity" introduces trace amounts of oxygen or moisture into the system.
Even minimal contamination can disrupt the reduction process, preventing the full conversion of copper salts to metallic copper.
This results in a material with mixed oxidation states, significantly lowering its performance in iodine removal applications.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Protocol
To ensure the successful synthesis of Cu@Zn-NC, align your atmosphere control with your specific material goals.
- If your primary focus is catalytic activity: Prioritize the highest available purity of argon to guarantee the copper remains in the metallic Cu0 state.
- If your primary focus is porosity and surface area: Ensure a consistent, strictly controlled flow rate to effectively purge volatile byproducts without disturbing the temperature uniformity.
Precise atmosphere control is the single most critical factor in transforming raw precursors into a high-performance functional material.
Summary Table:
| Key Role of Argon | Protective Function | Impact on Cu@Zn-NC |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Shielding | Prevents oxidative combustion | Preserves the nitrogen-doped carbon skeleton |
| Oxidation Control | Maintains zero-valent state (Cu0) | Keeps copper nanoparticles active for iodine removal |
| Volatile Purging | Flushes decomposition byproducts | Prevents pore clogging and ensures high surface area |
| Purity Assurance | Eliminates trace O2/moisture | Guarantees chemical integrity and catalytic performance |
Achieve Precise Atmosphere Control with KINTEK
Don’t let trace oxidation compromise your materials. KINTEK’s high-temperature tube furnaces provide the airtight sealing and gas-flow precision necessary for high-purity argon environments.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet the rigorous demands of Cu@Zn-NC synthesis and nitrogen-doped carbon production. Ensure your copper nanoparticles remain in the metallic Cu0 state with our advanced thermal solutions.
Contact our laboratory specialists today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Jiuyu Chen, Zhiwen Liu. Cu0-Functionalized, ZIF-8-Derived, Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Composites for Efficient Iodine Elimination in Solution. DOI: 10.3390/nano15020105
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in the hydrogenation process of Ti6Al4V alloys? Master Hydrogen Diffusion Control
- What are the safety and usability features of tube furnaces? Essential for Precise Material Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the performance of carbon nanowire networks? Enhance Electrode Performance
- How is a tubular furnace utilized in the homogenization annealing of Ti-20Zr alloys? Precision Thermal Profiles
- How does a two-zone tube furnace achieve stepwise control of precursors? Master CVD Heterostructure Growth
- Why is a tube annealing furnace used for SiC hydrogenation? Unlock Pure Atomic Surfaces for Superior Crystal Bonding
- What conditions does a tube furnace provide for the carbonization of aerogels? Master Precision Thermal Control
- What role does a high-temperature Tube Furnace play in ScSZ thin film post-treatment? Master Structural Refinement



















